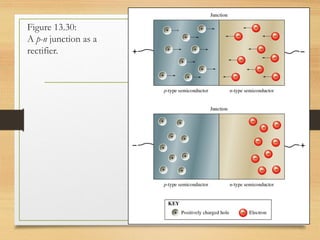
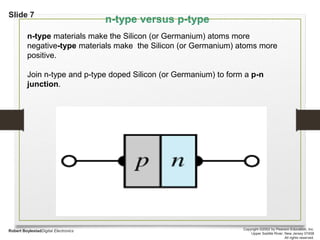
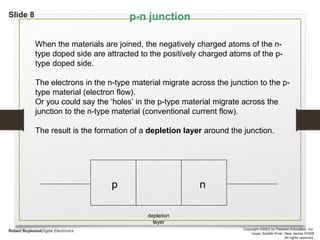
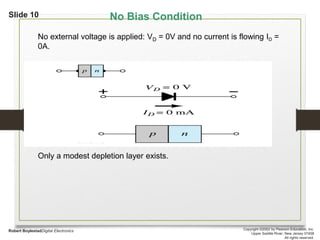
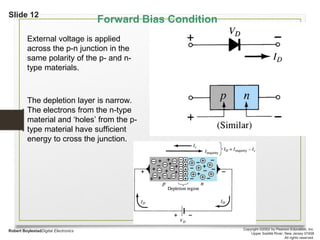
This document discusses different types of solids and semiconductors. It describes conductors as mostly metals, insulators as mostly nonmetals, and semiconductors as metalloids with an intermediate-sized band gap between the valence and conduction bands. Semiconducting elements like silicon and germanium are the basis for solid-state electronic devices, and their conductivity increases when doped with small amounts of other elements to become either n-type or p-type semiconductors. Joining an n-type and p-type semiconductor produces a p-n junction that can function as a rectifier, allowing current to flow in only one direction.