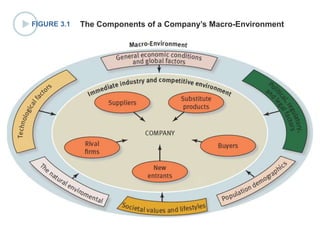
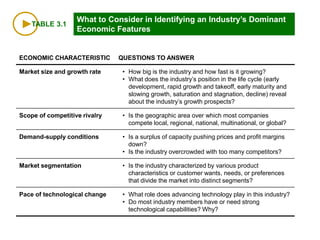
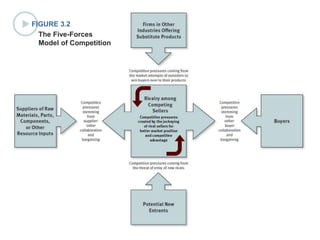
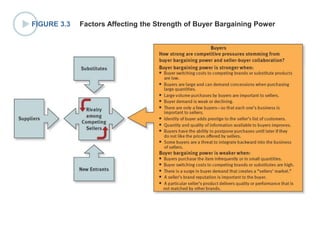
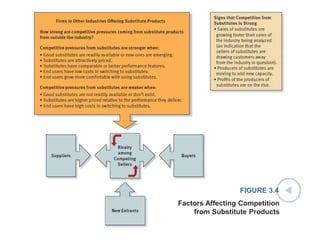
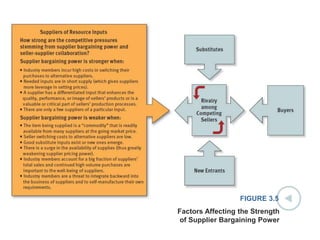
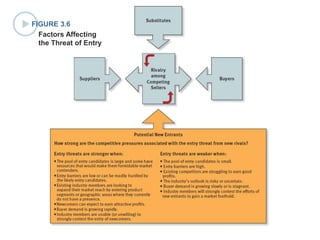
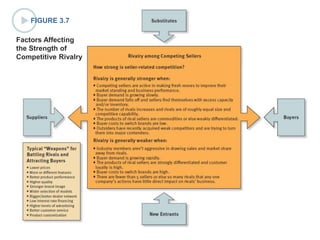
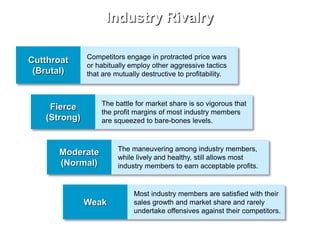
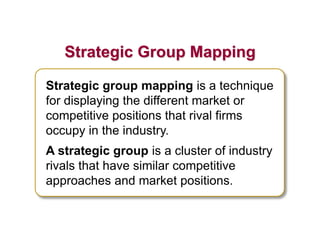
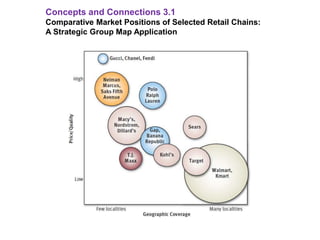
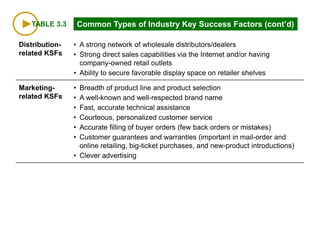
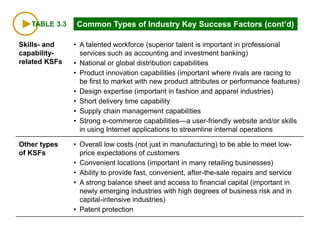
This document discusses evaluating a company's external environment by assessing its industry and competitive conditions. It outlines 7 steps for evaluating the industry: 1) analyzing dominant economic characteristics, 2) assessing competitive forces using Porter's 5 Forces model, 3) identifying drivers of industry change, 4) analyzing competitor positions, 5) anticipating competitor strategies, 6) determining success factors, and 7) evaluating industry profitability outlook. Porter's 5 Forces model examines the competitive threats from buyers, suppliers, substitutes, potential entrants and industry rivals. The document provides questions to consider for each step of the industry evaluation.