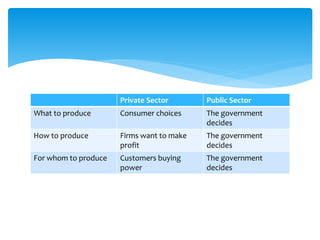
This document discusses how the importance of different business sectors has changed over time. It explains that countries have transitioned from developing to developed as industrialization increased the importance of the secondary sector. Now, many countries are undergoing de-industrialization as the tertiary sector becomes more important. Consumer and business behaviors have also evolved, with consumers demanding higher quality products and businesses needing to communicate more effectively. Most economies now have both private and public sectors, with the private sector focused on profit and consumer choice, and the public sector prioritizing government objectives.