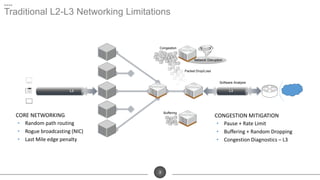
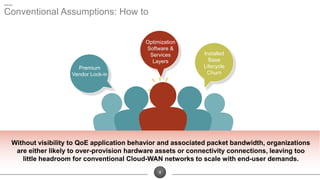
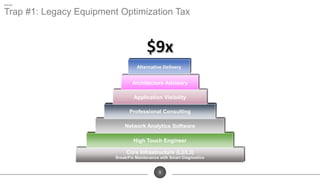
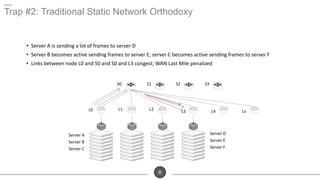
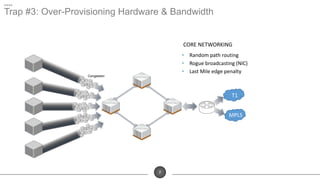
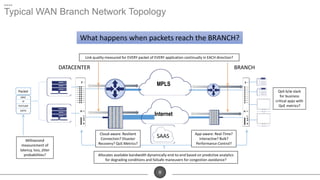
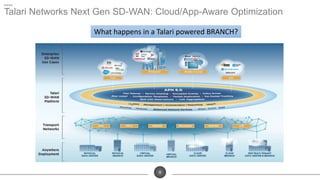
The document discusses the challenges of network optimization in a WAN-cloud environment, highlighting issues like over-provisioning bandwidth and traditional network limitations that hinder performance. It emphasizes the need for dynamic bandwidth allocation and application-aware networks to address congestion and improve overall quality of experience. The role of advanced analytics and SD-WAN solutions like Talari is underscored for enhancing network efficiency and adaptability.