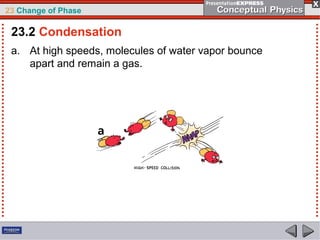
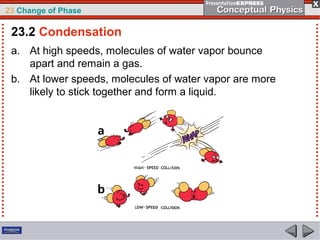
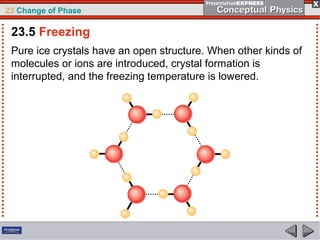
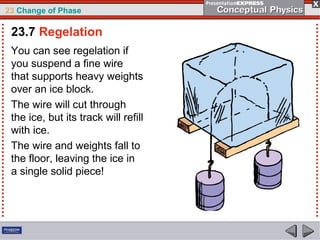
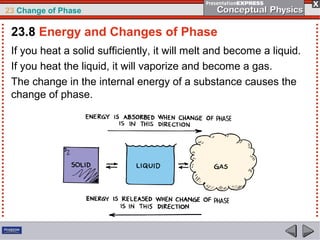
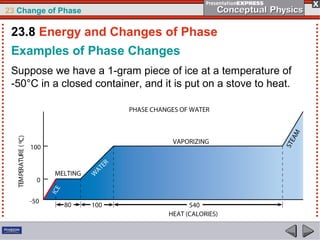
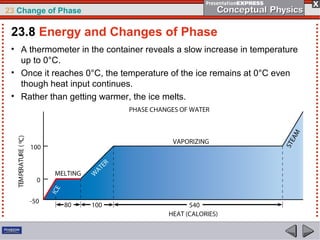
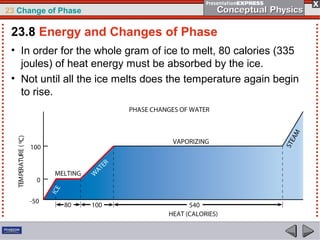
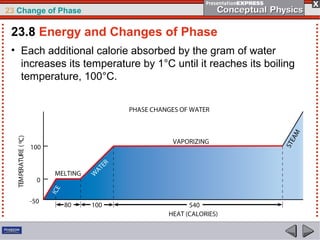
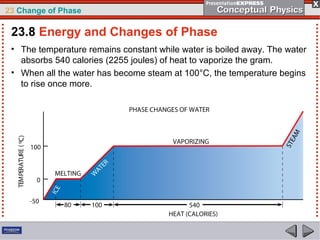
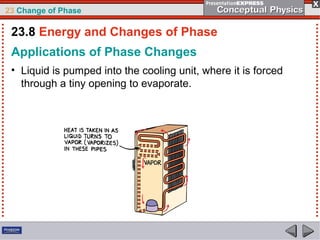
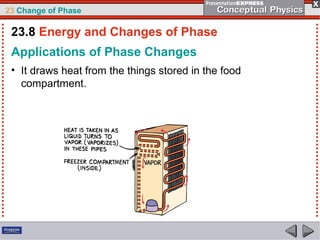
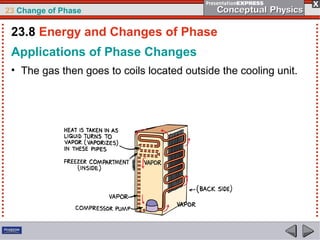
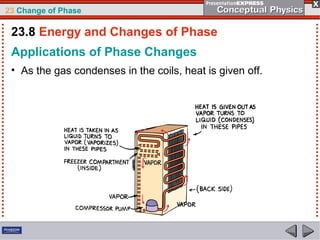
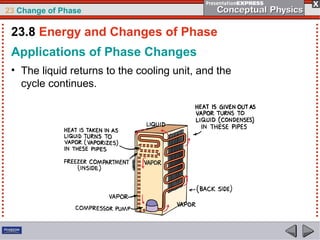
This document discusses phase changes in matter such as evaporation, condensation, and boiling. It explains that evaporation occurs when molecules at the surface of a liquid gain enough kinetic energy to break free of the liquid as a gas. Condensation is the opposite change where gas molecules lose kinetic energy and stick together as a liquid. The rates of evaporation and condensation can be equal, resulting in no temperature change. Boiling occurs below the surface of a liquid when vapor pressure allows bubbles to form and rise. Pressure affects the boiling point temperature, with higher pressure requiring higher temperatures for boiling.