This document discusses computer arithmetic and the arithmetic logic unit (ALU). It covers several key topics:
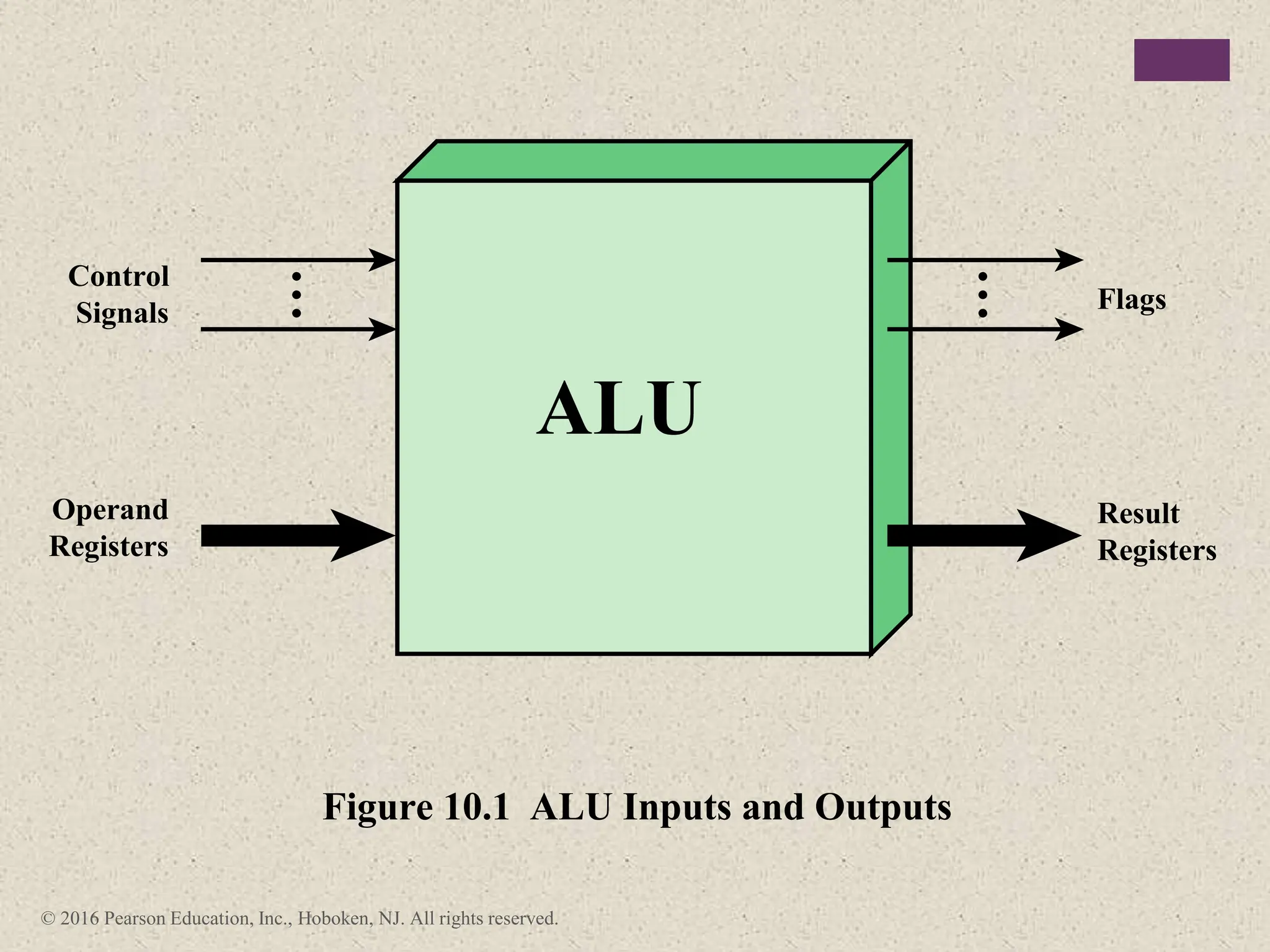
1) The ALU is the part of the computer that performs arithmetic and logical operations on data. It uses simple digital logic and can store binary digits and perform Boolean operations.
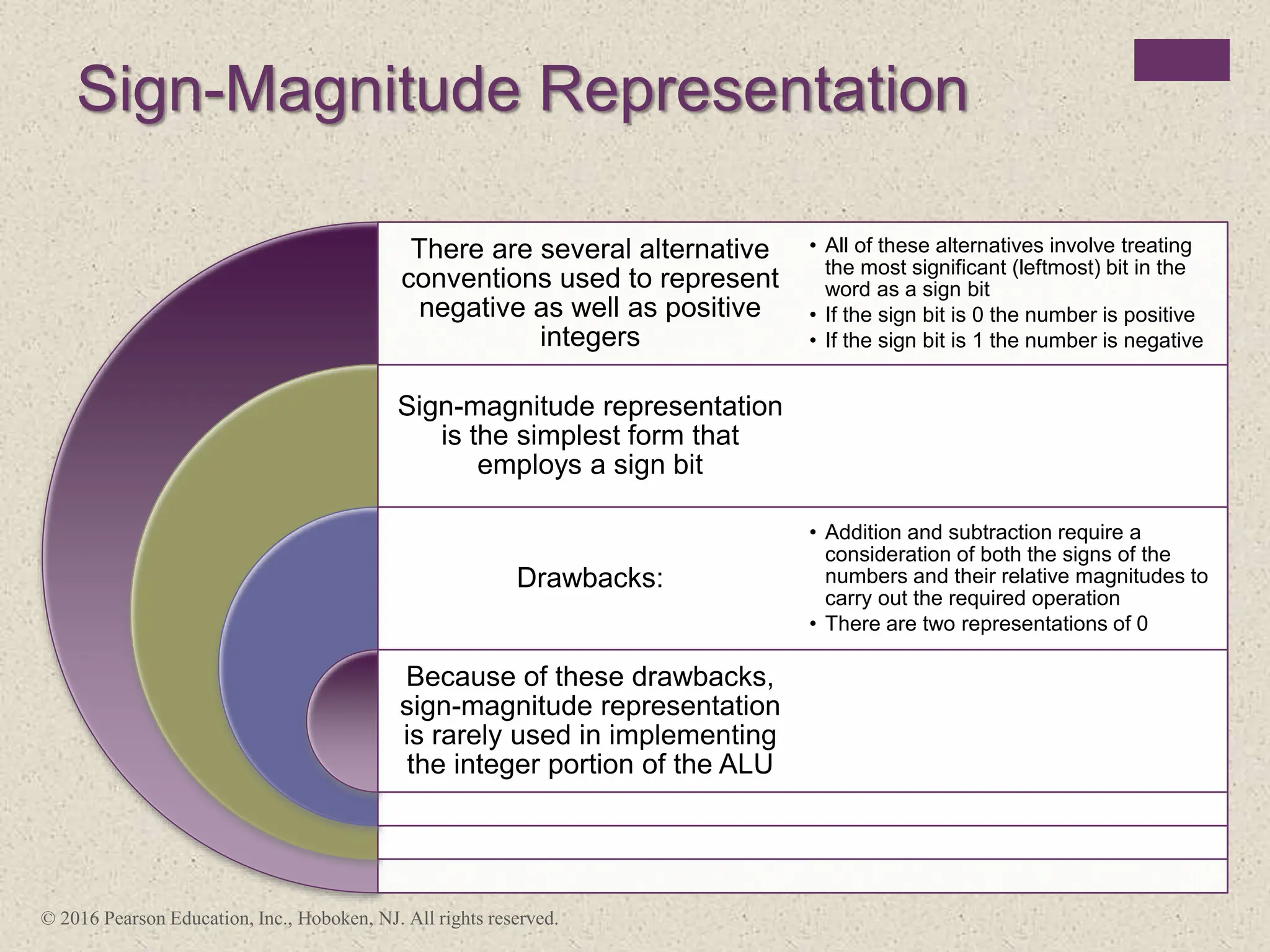
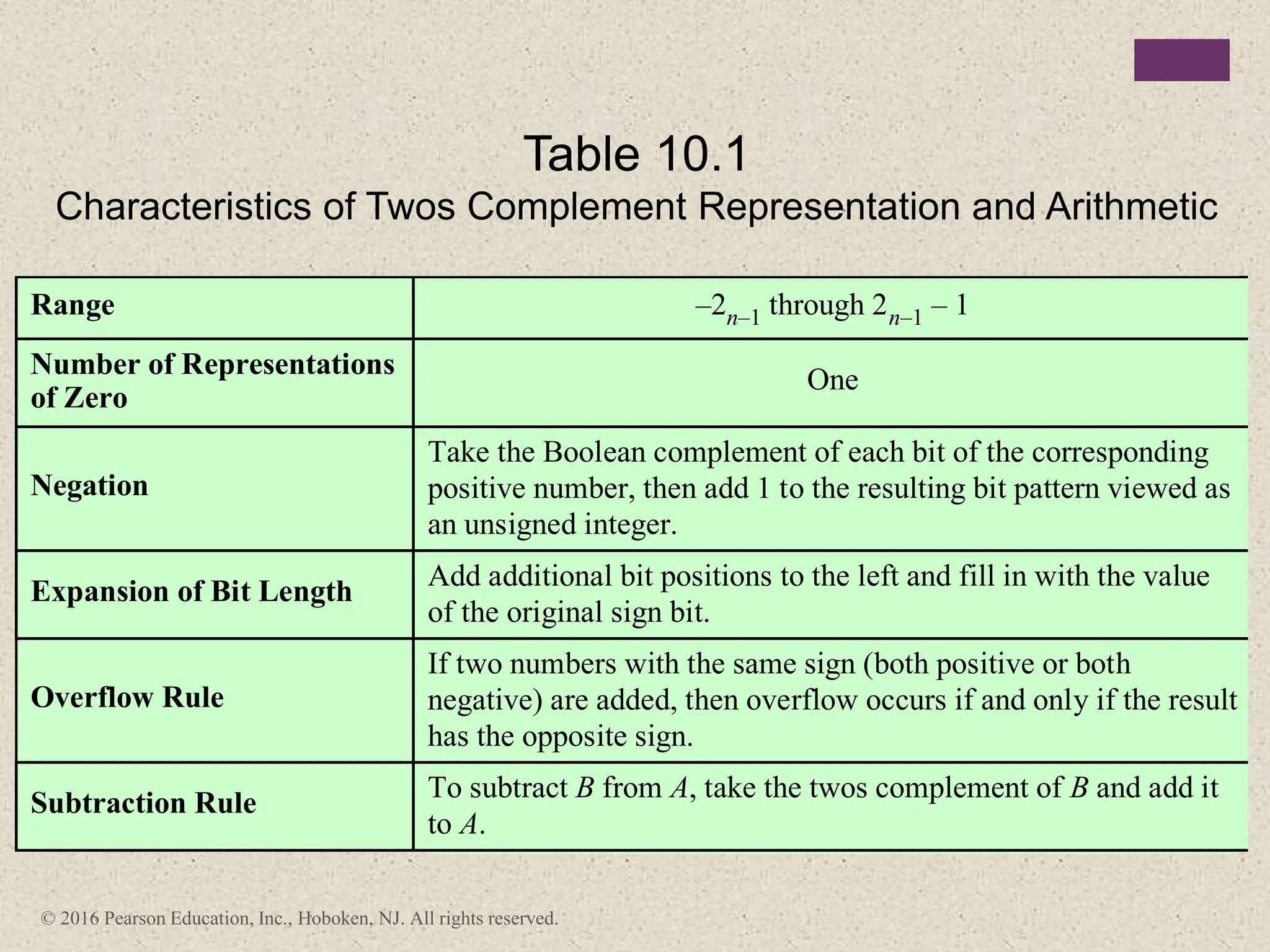
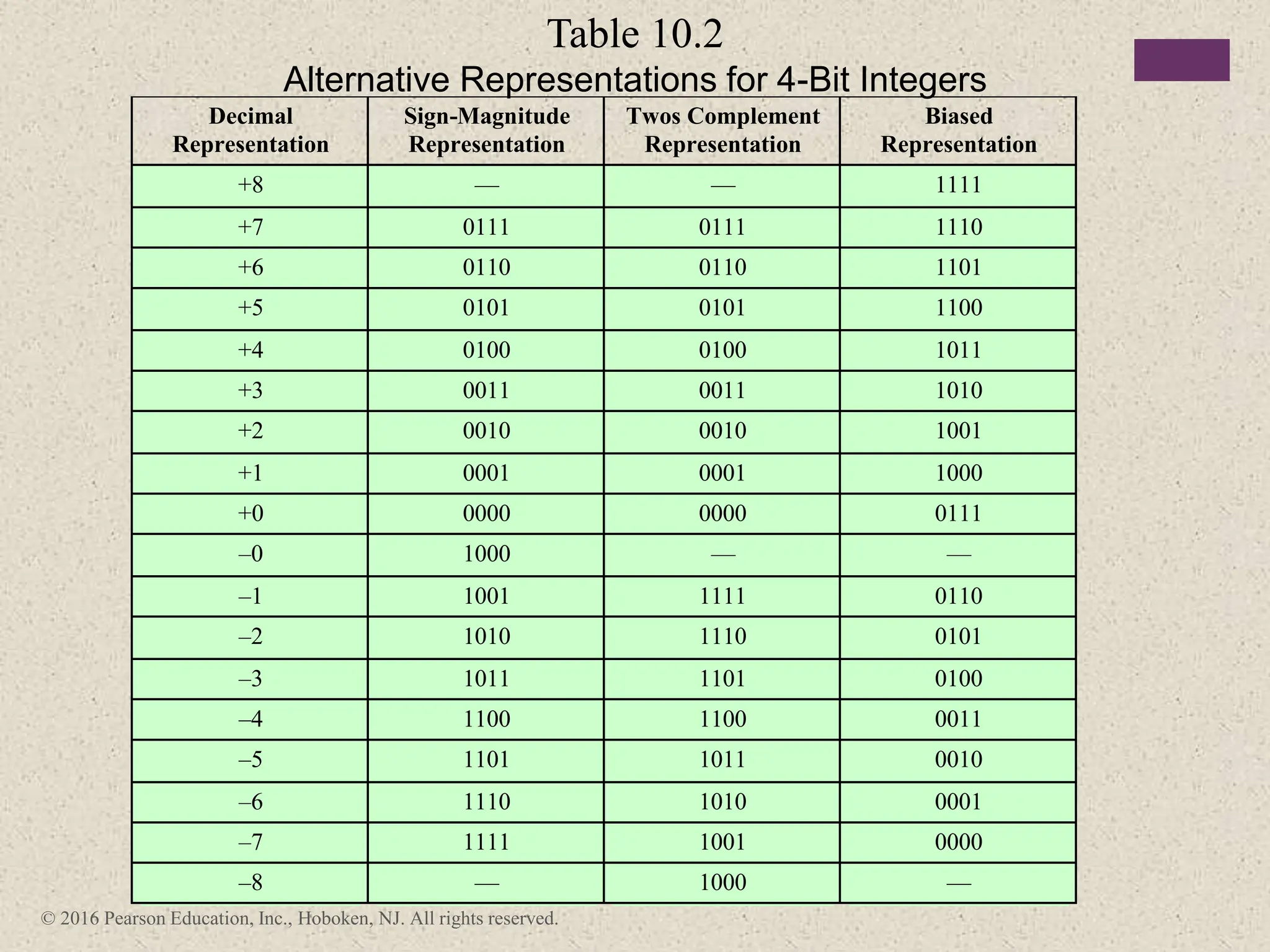
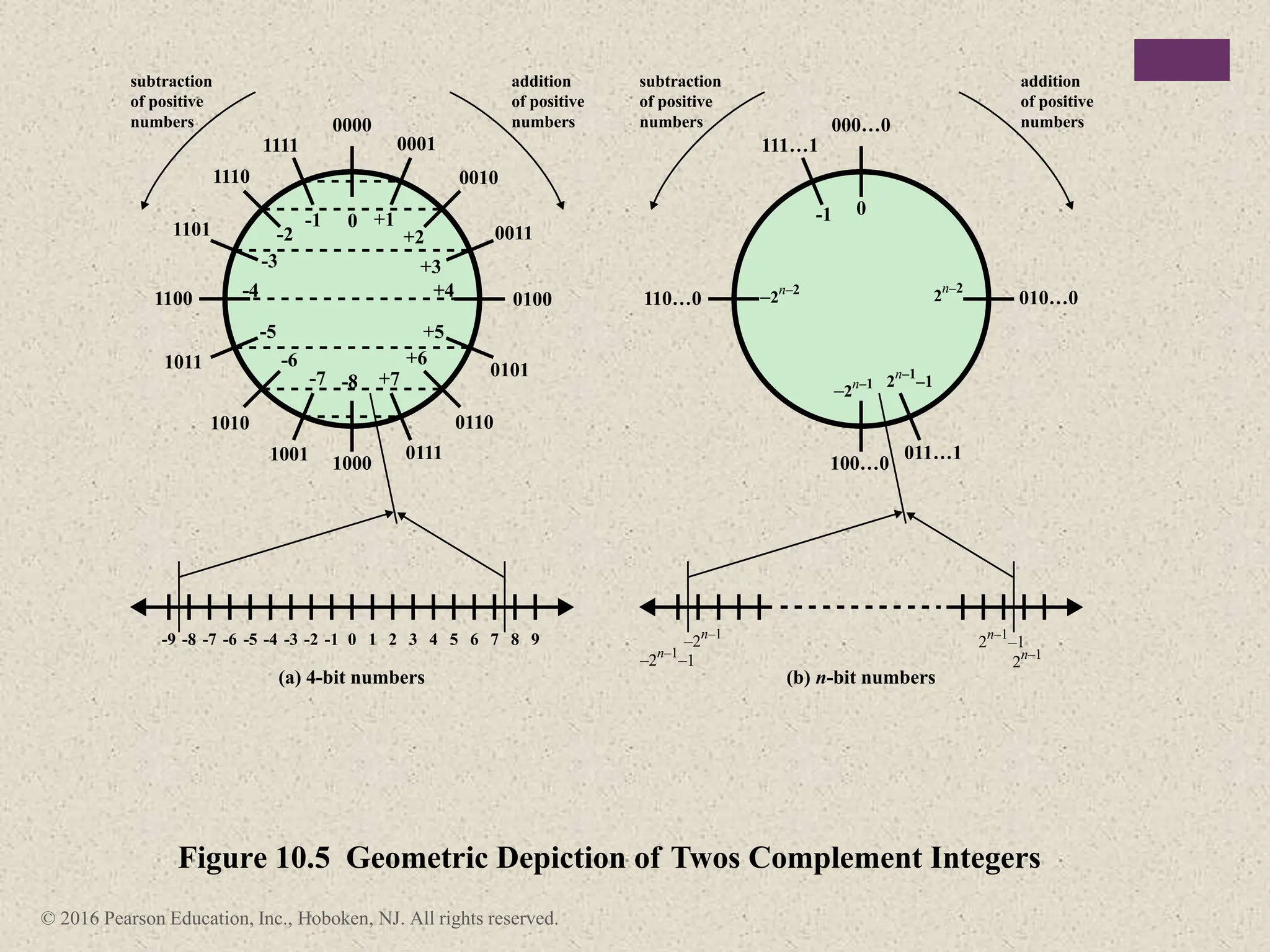
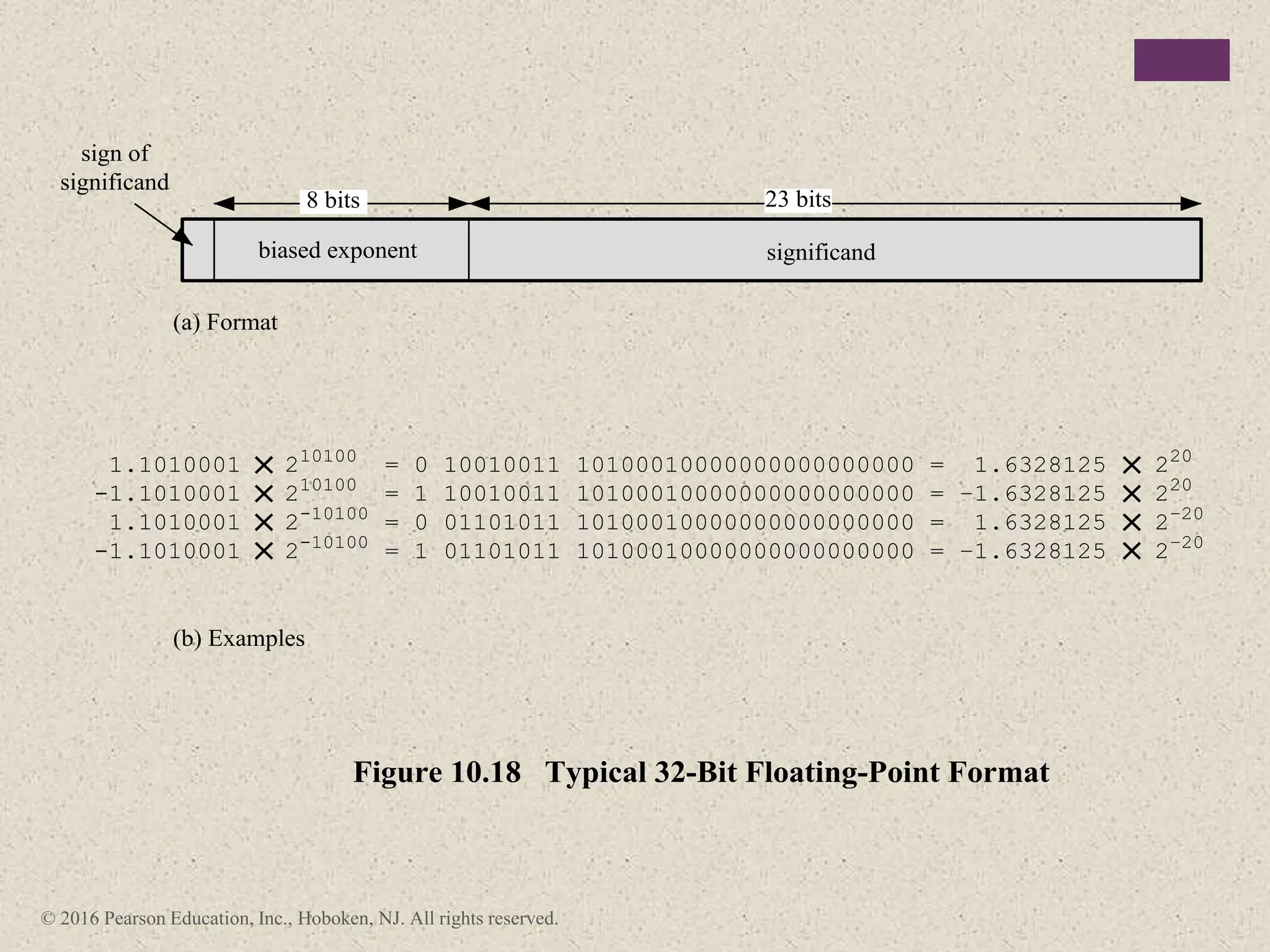
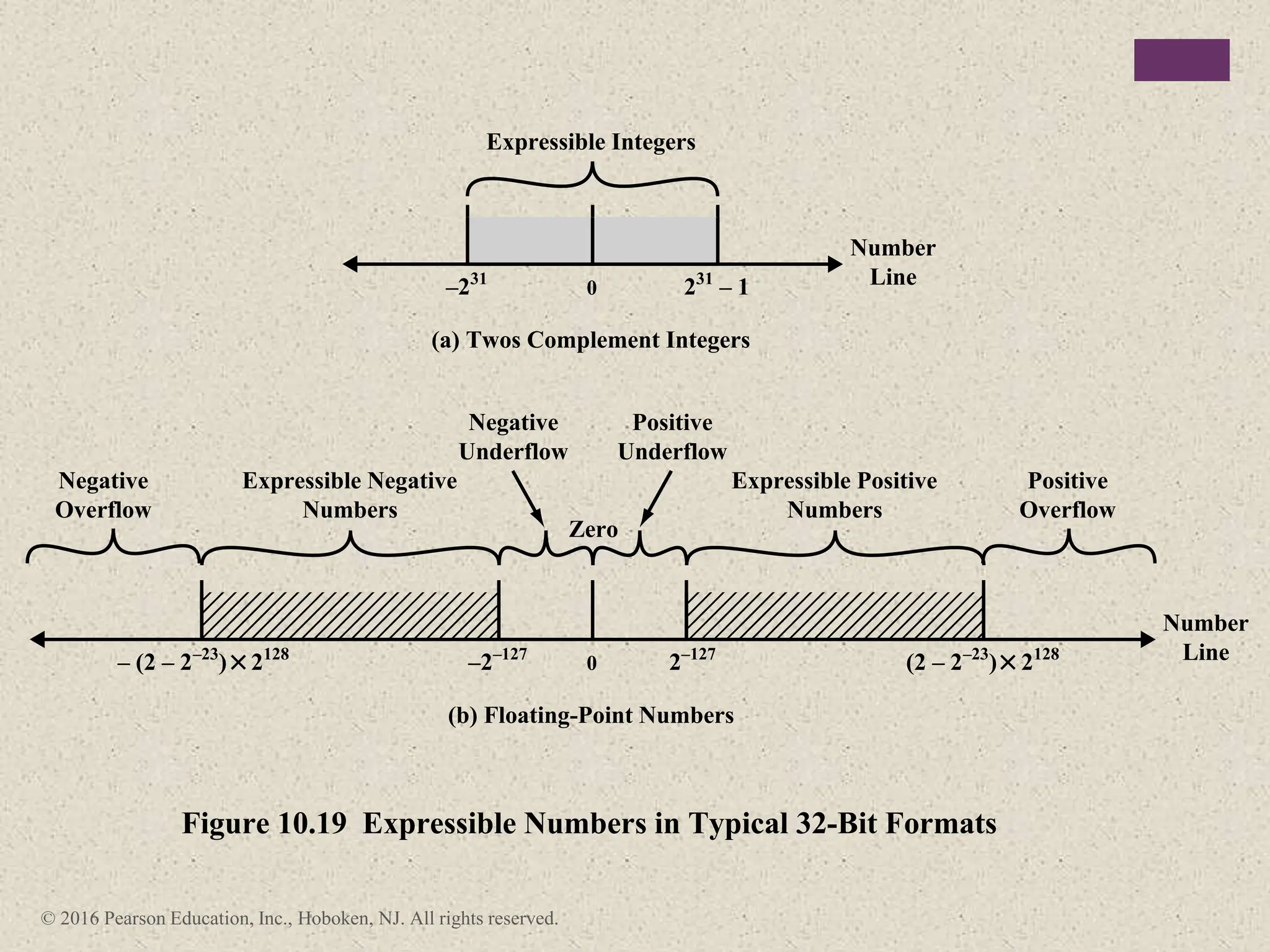
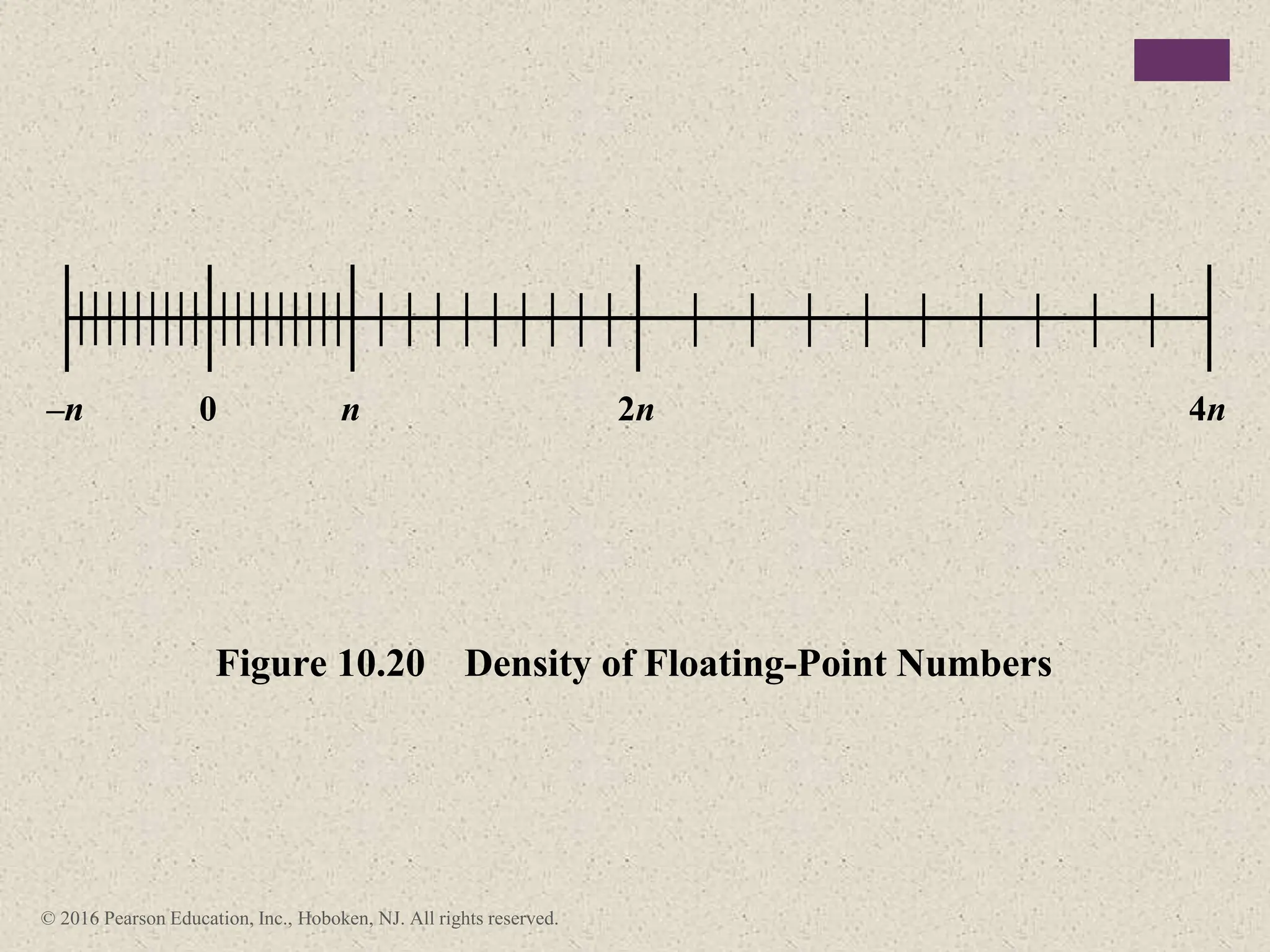
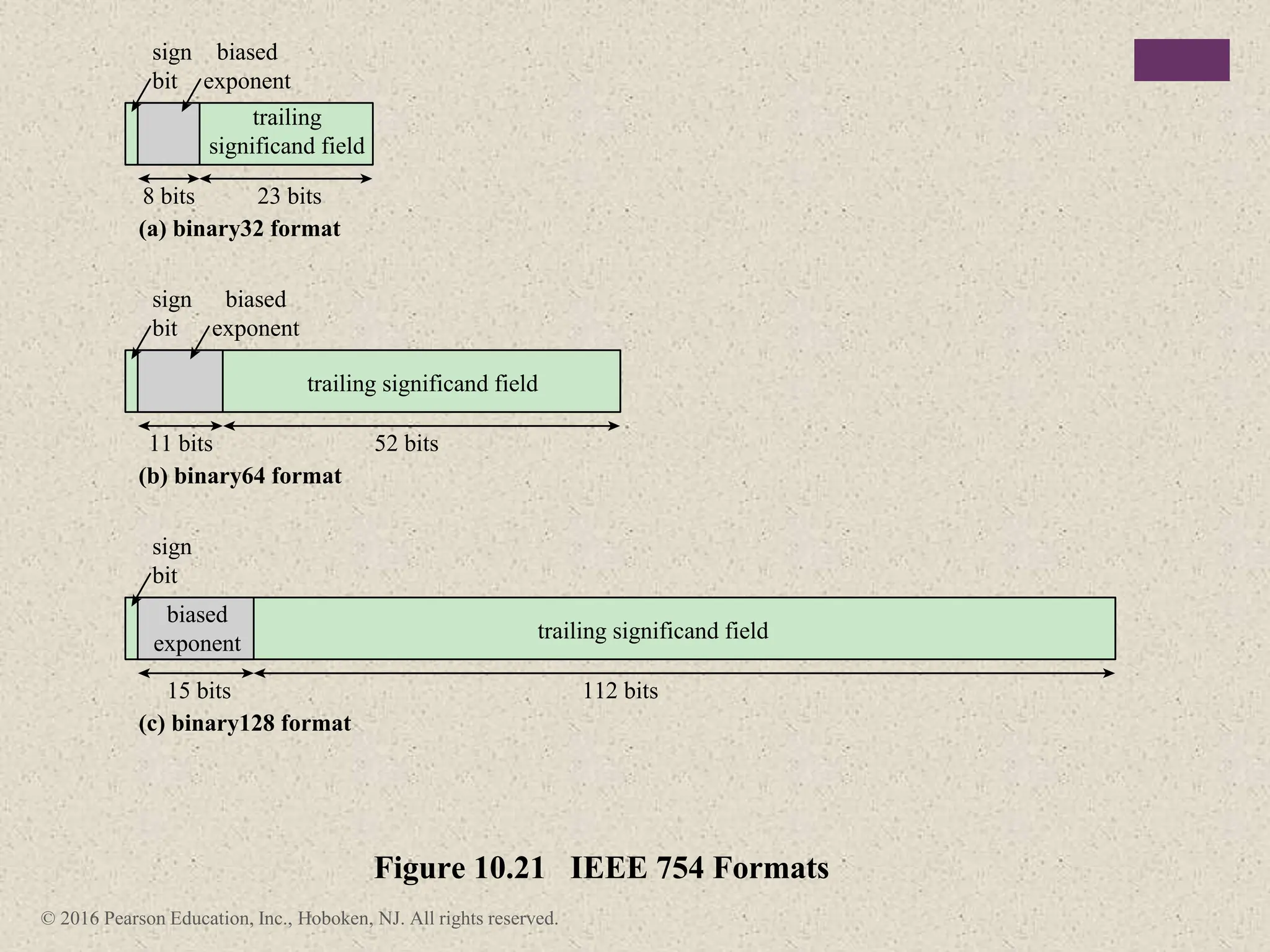
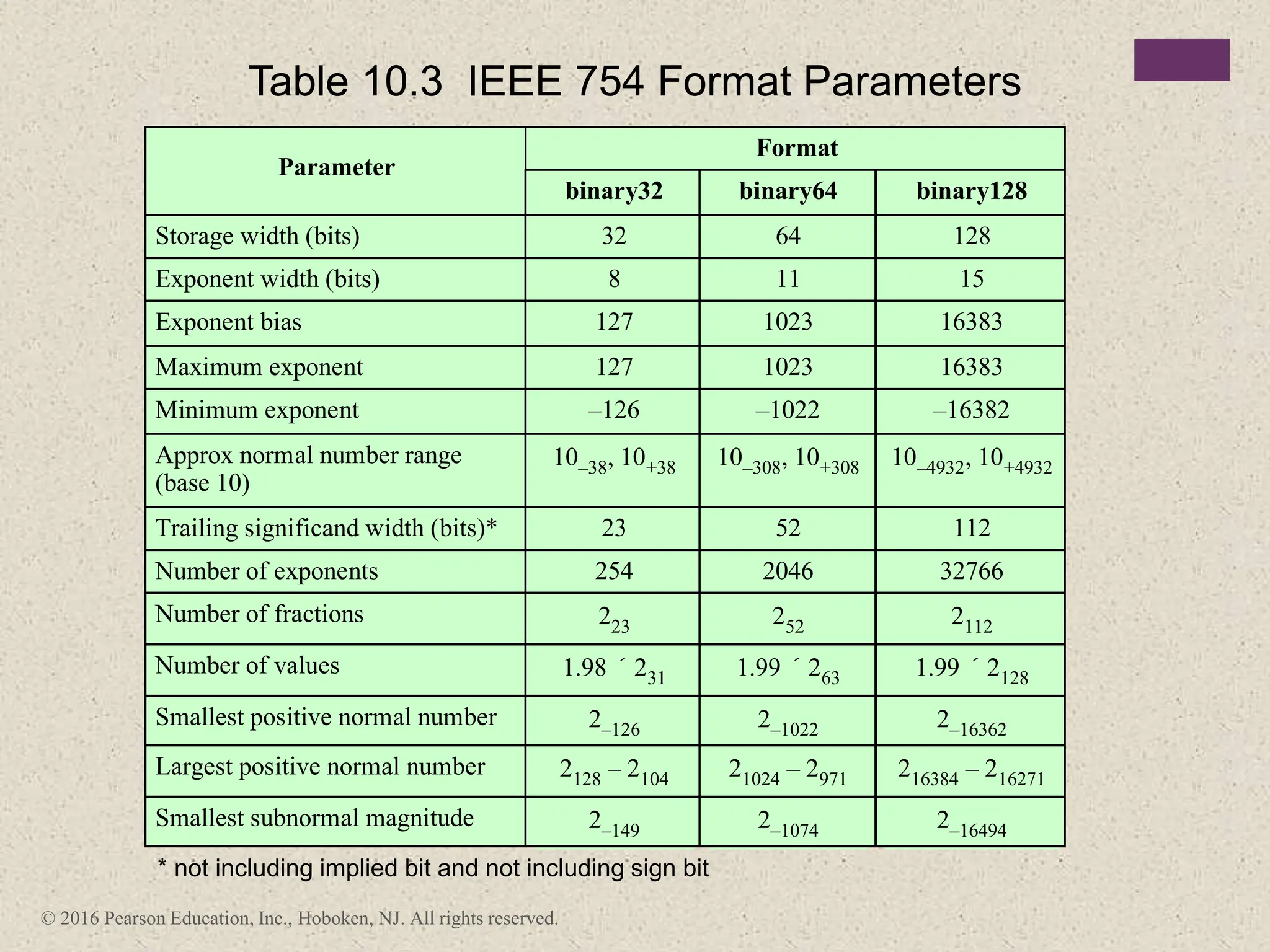
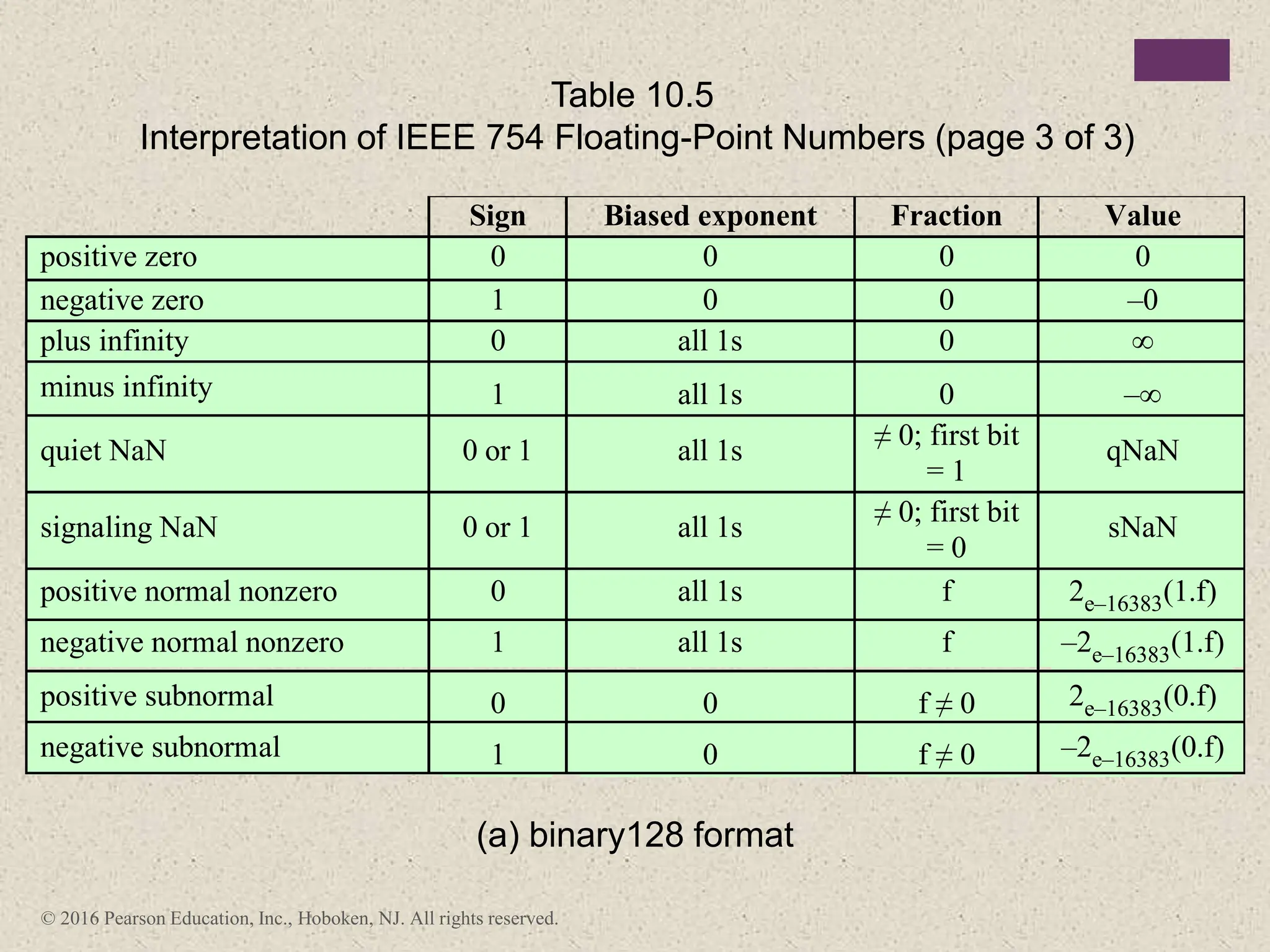
2) There are different ways to represent integers in binary, including sign-magnitude, twos-complement, and biased representations. Twos-complement is now most commonly used.
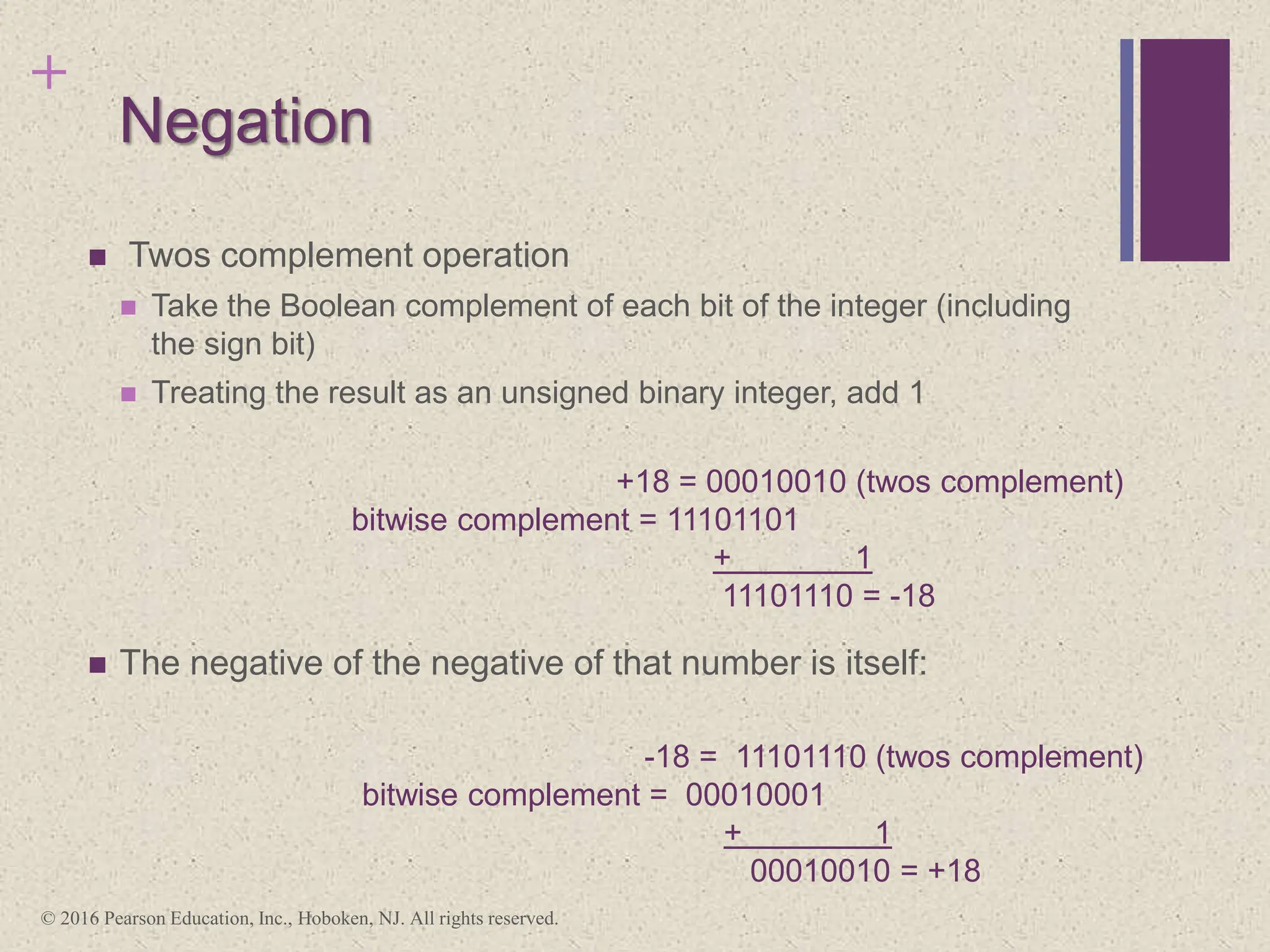
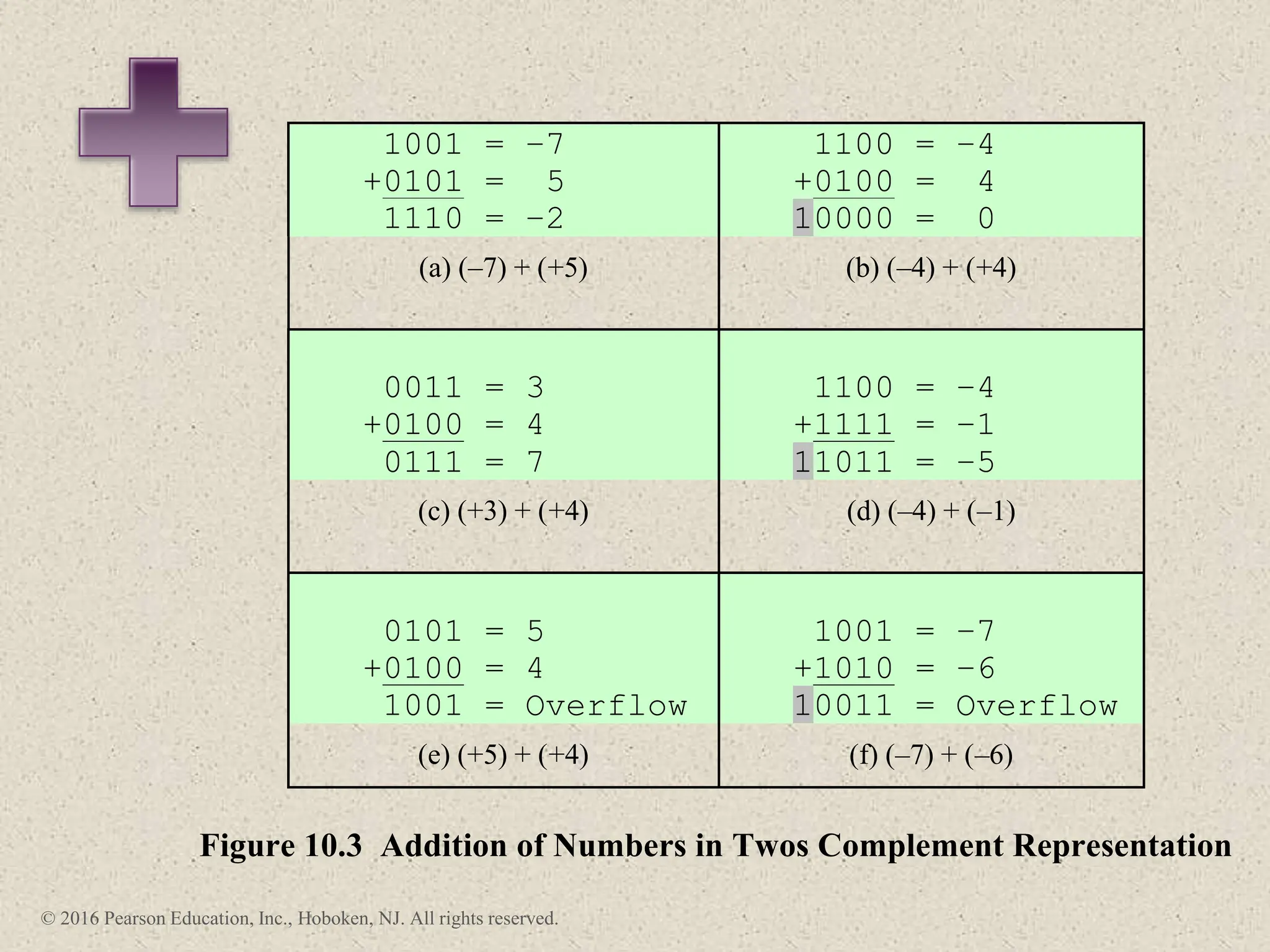
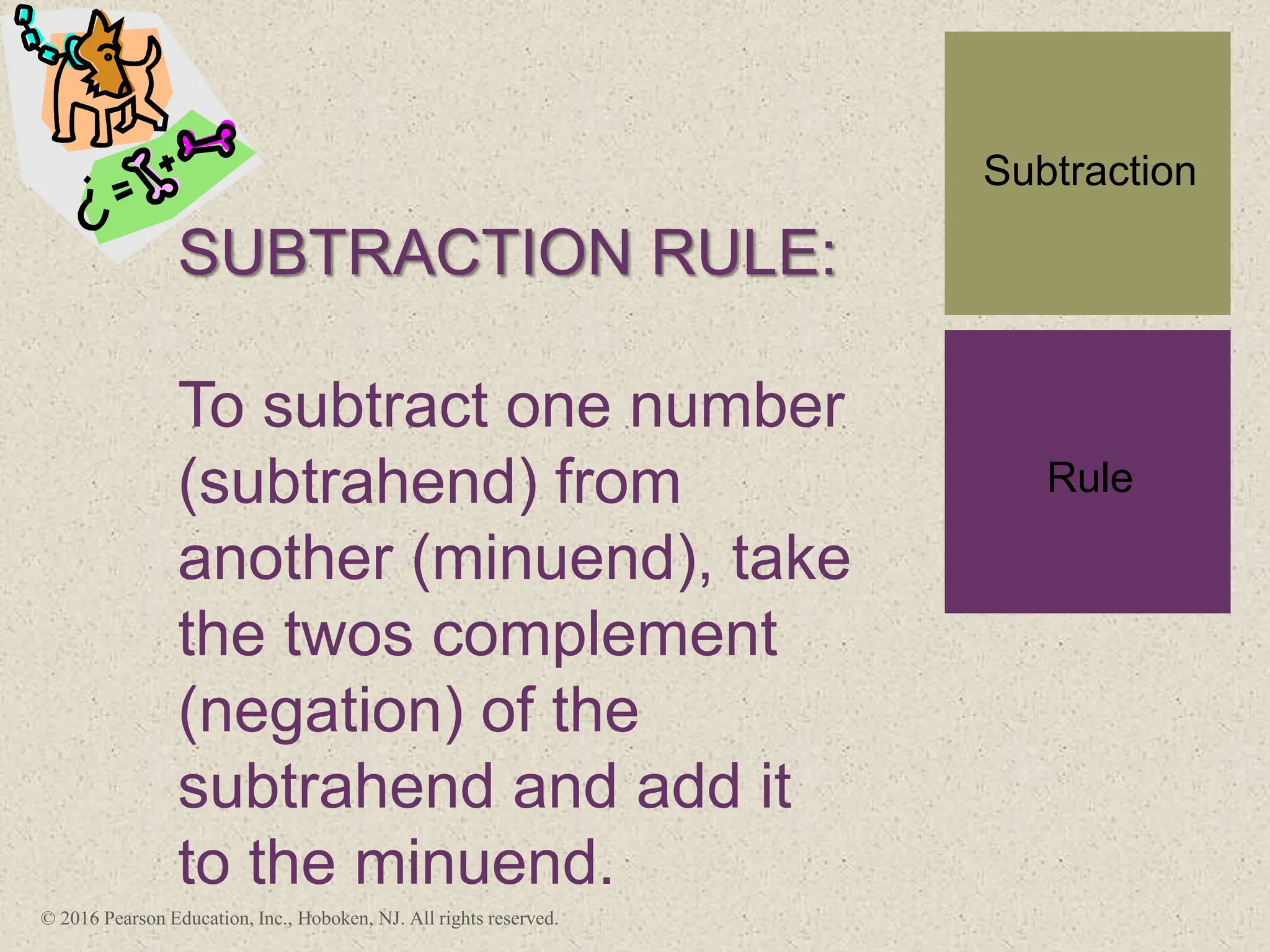
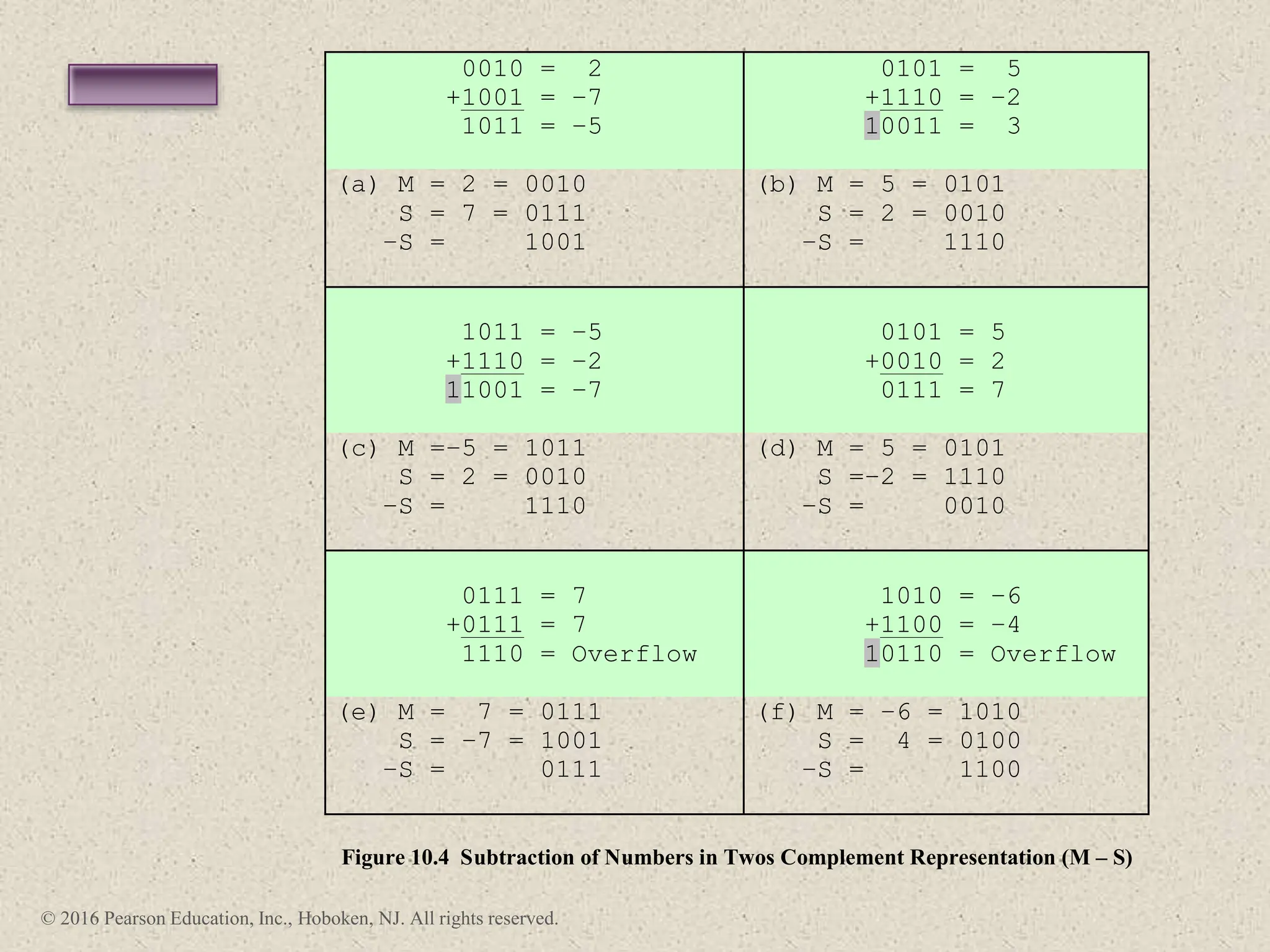
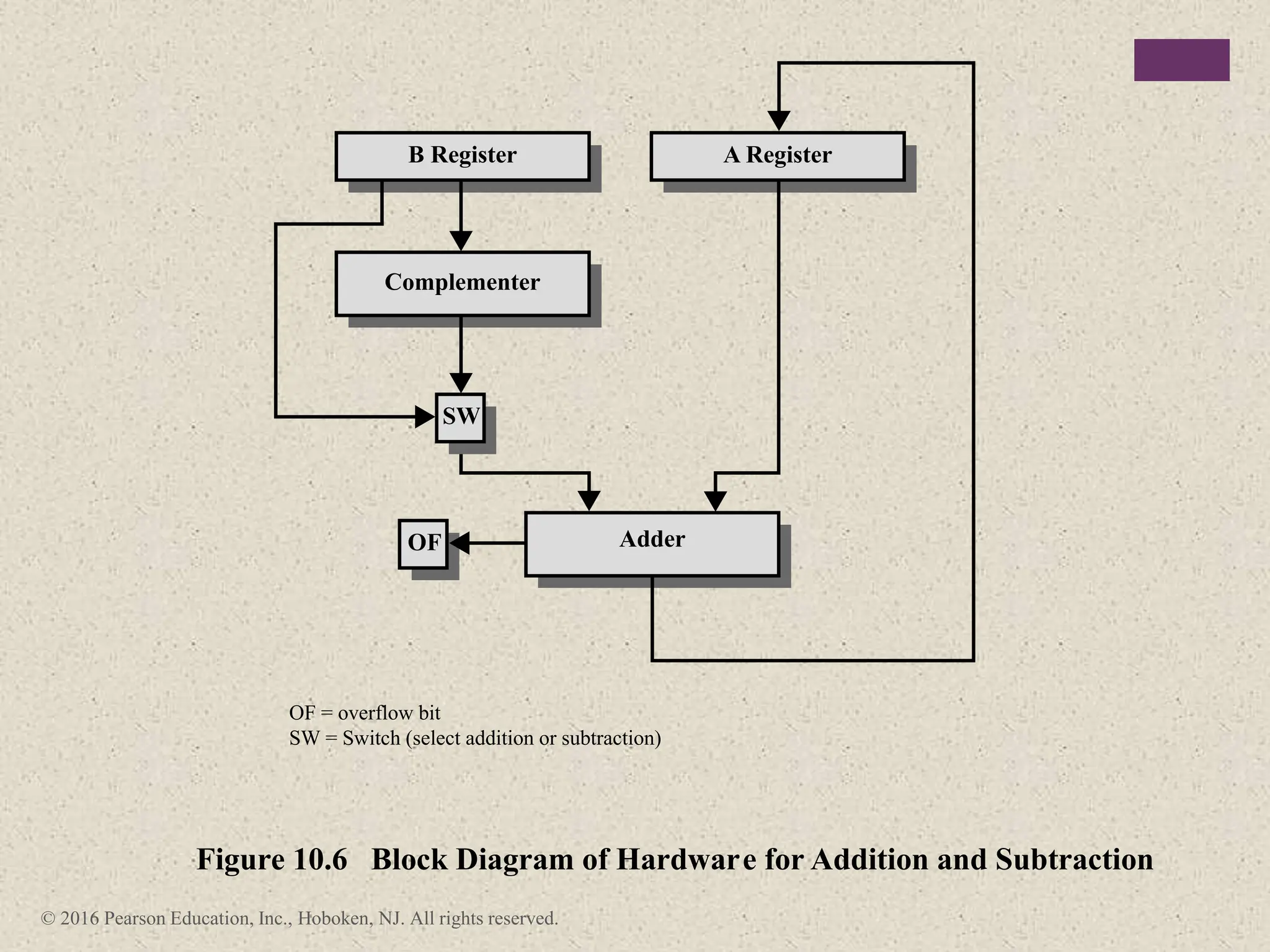
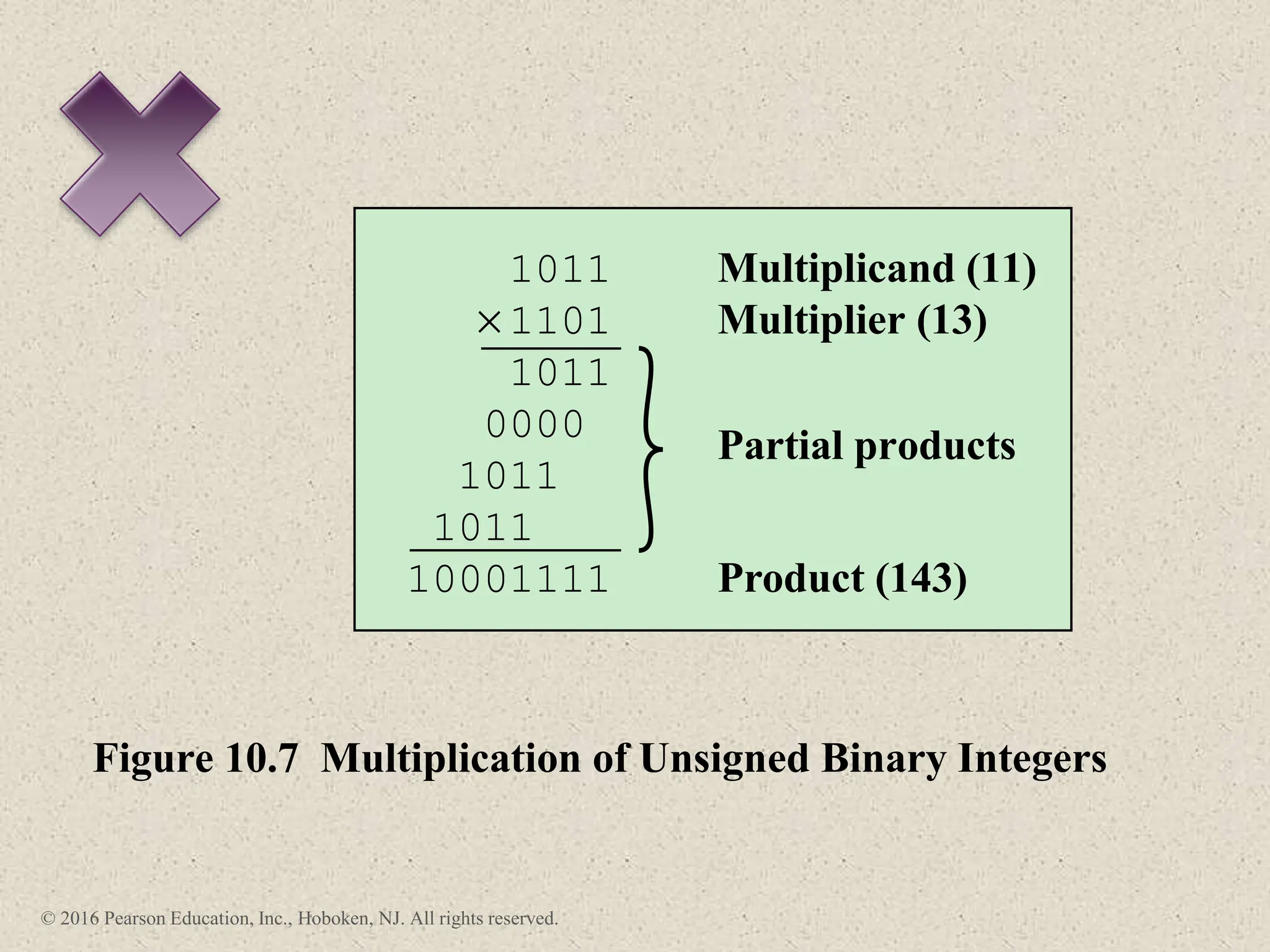
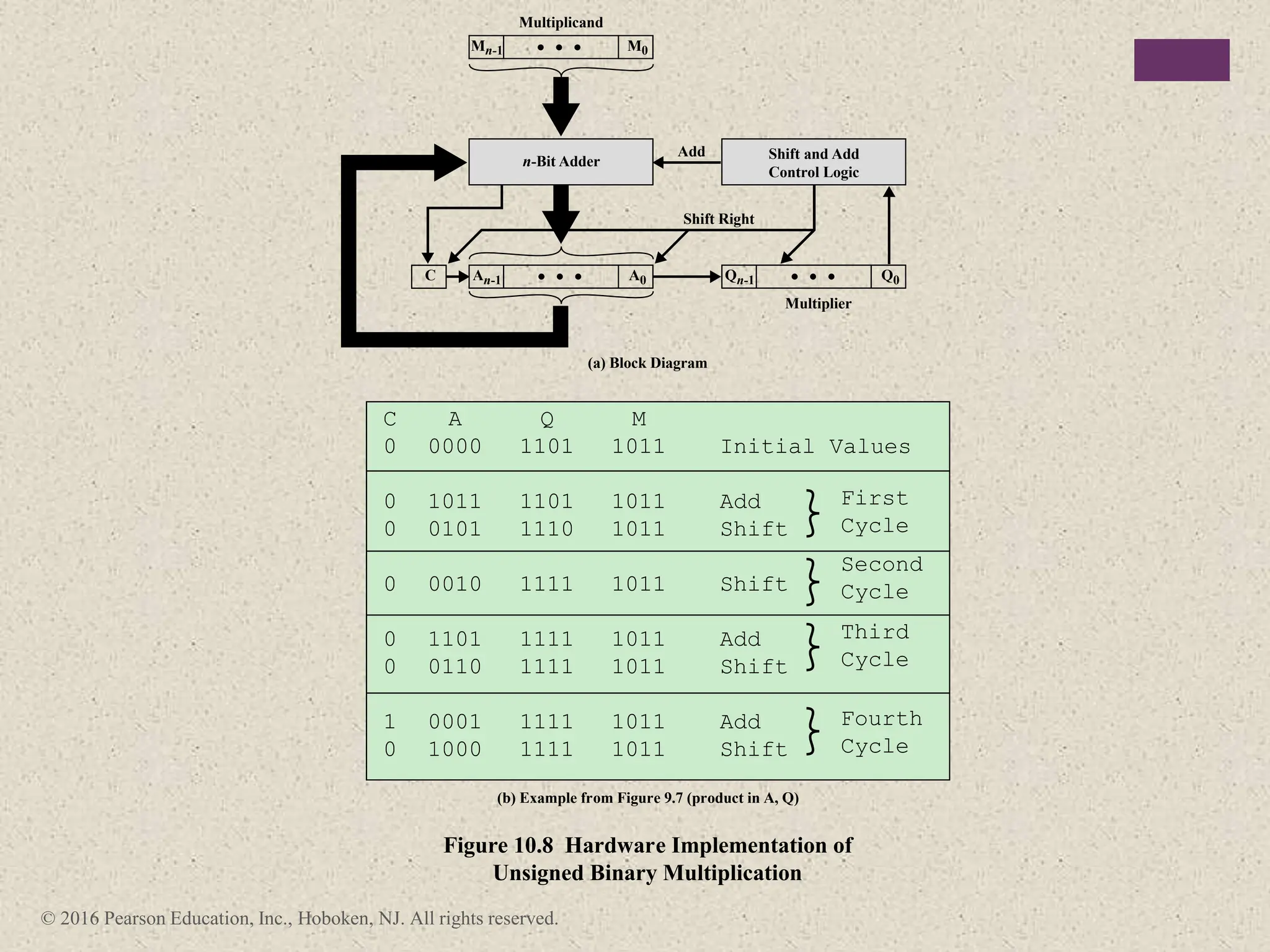
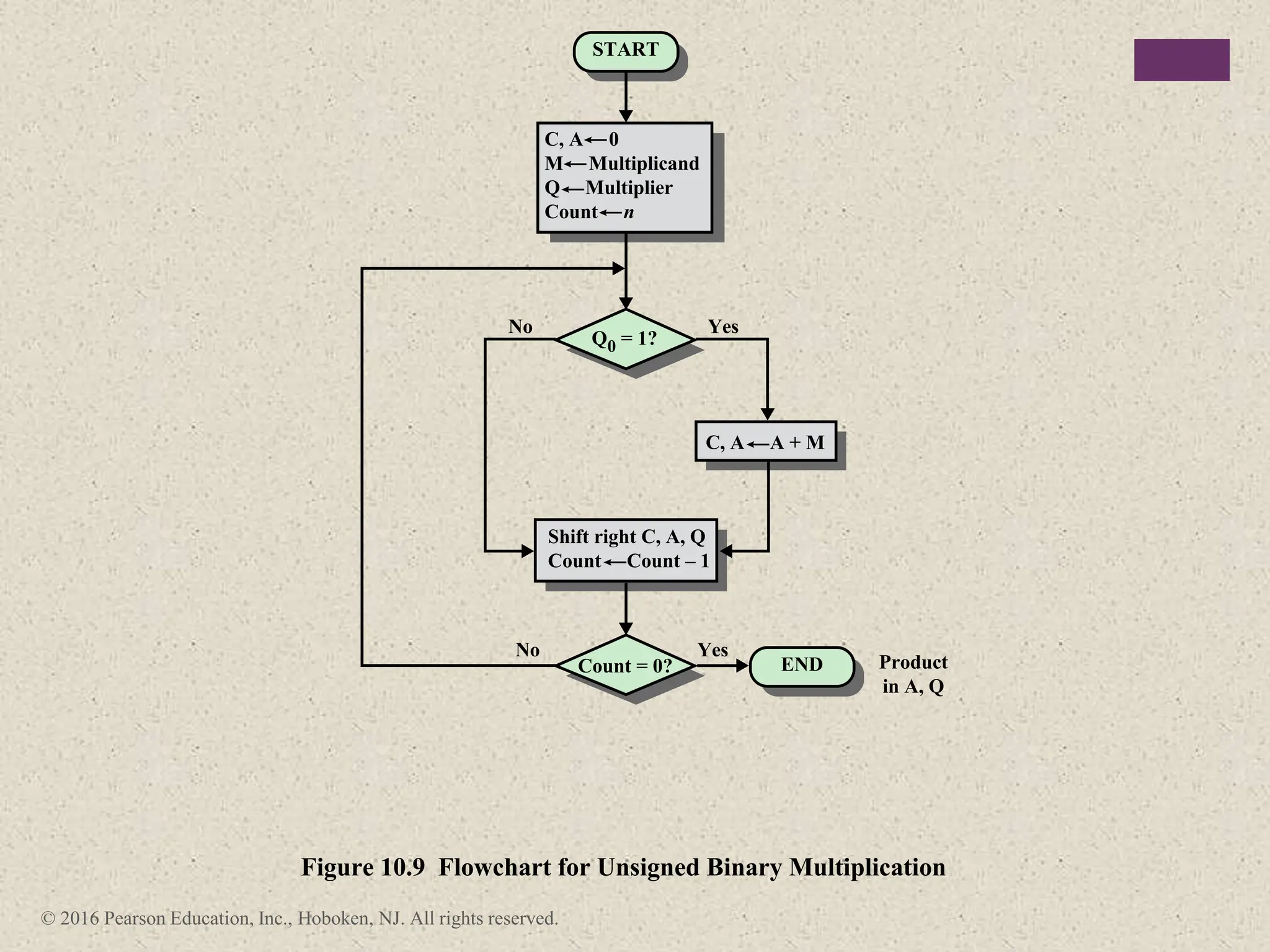
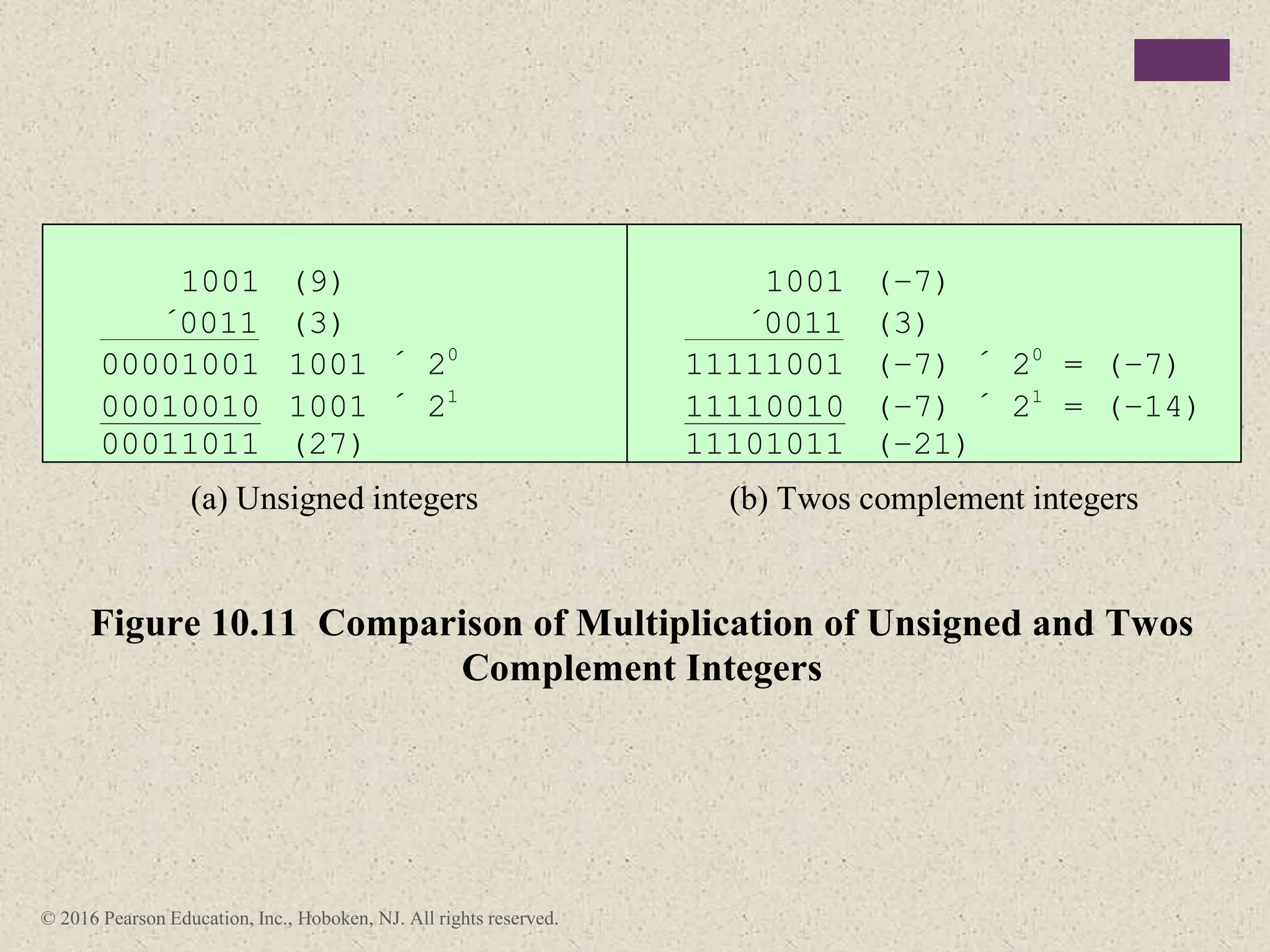
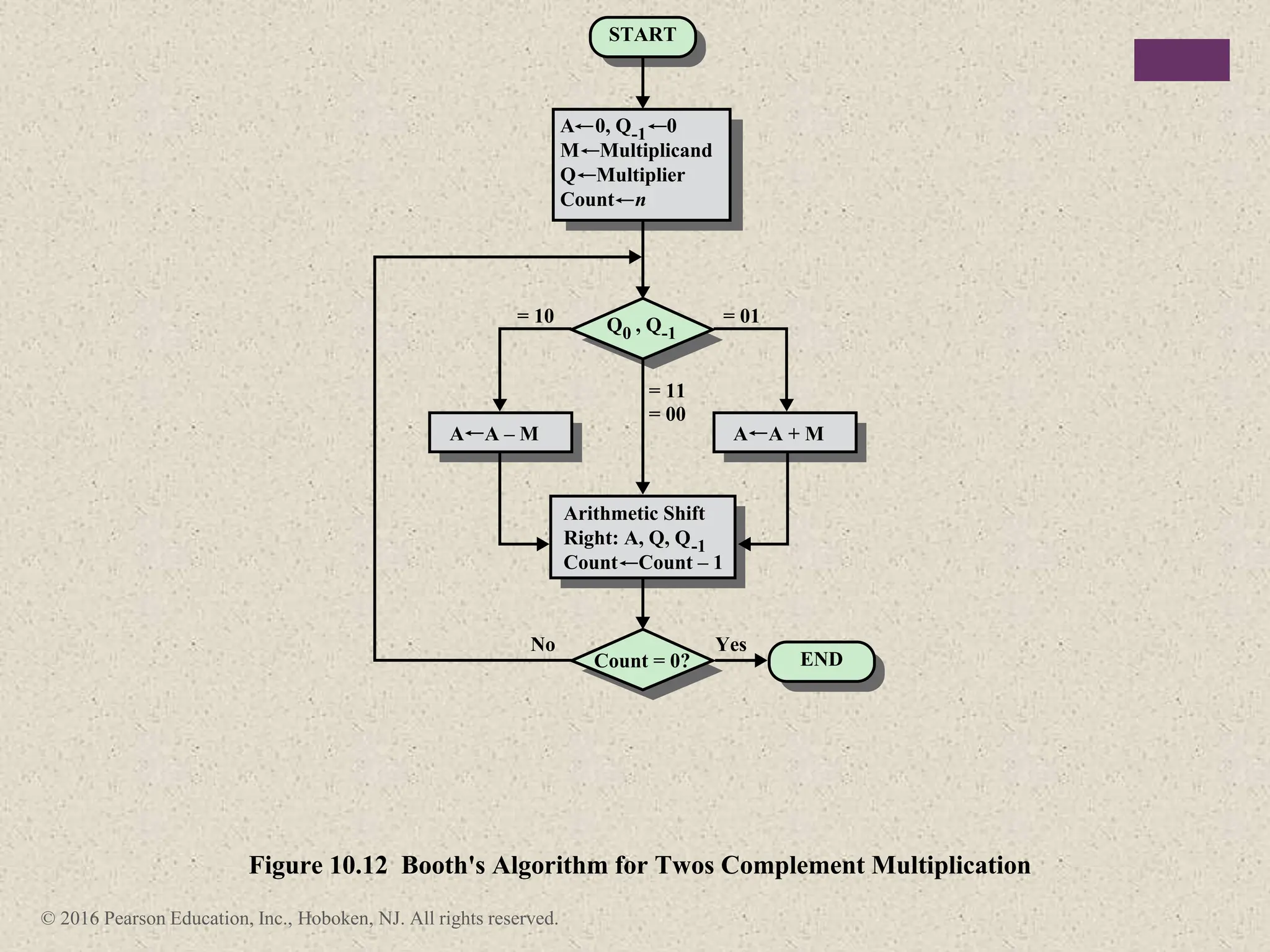
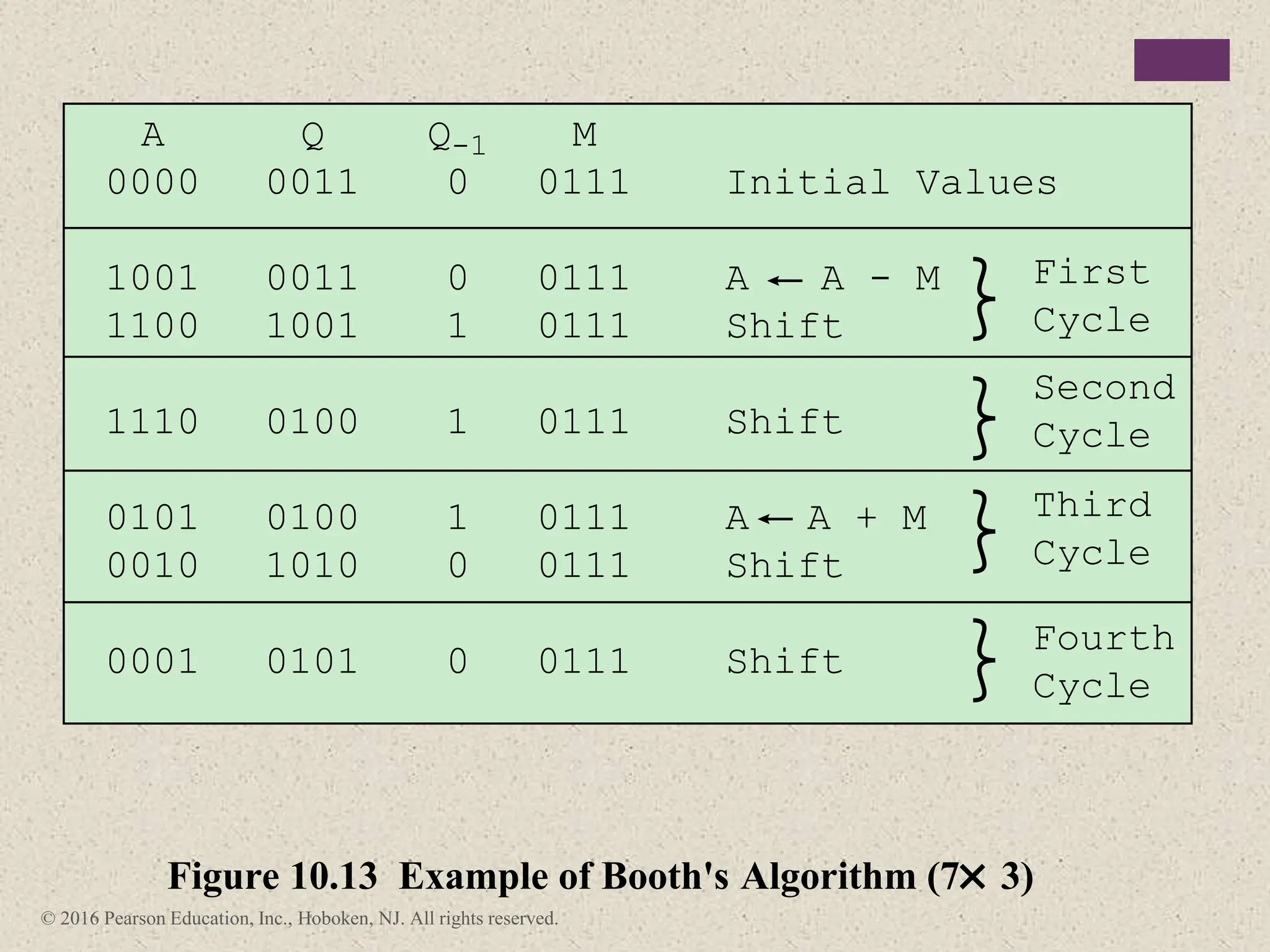
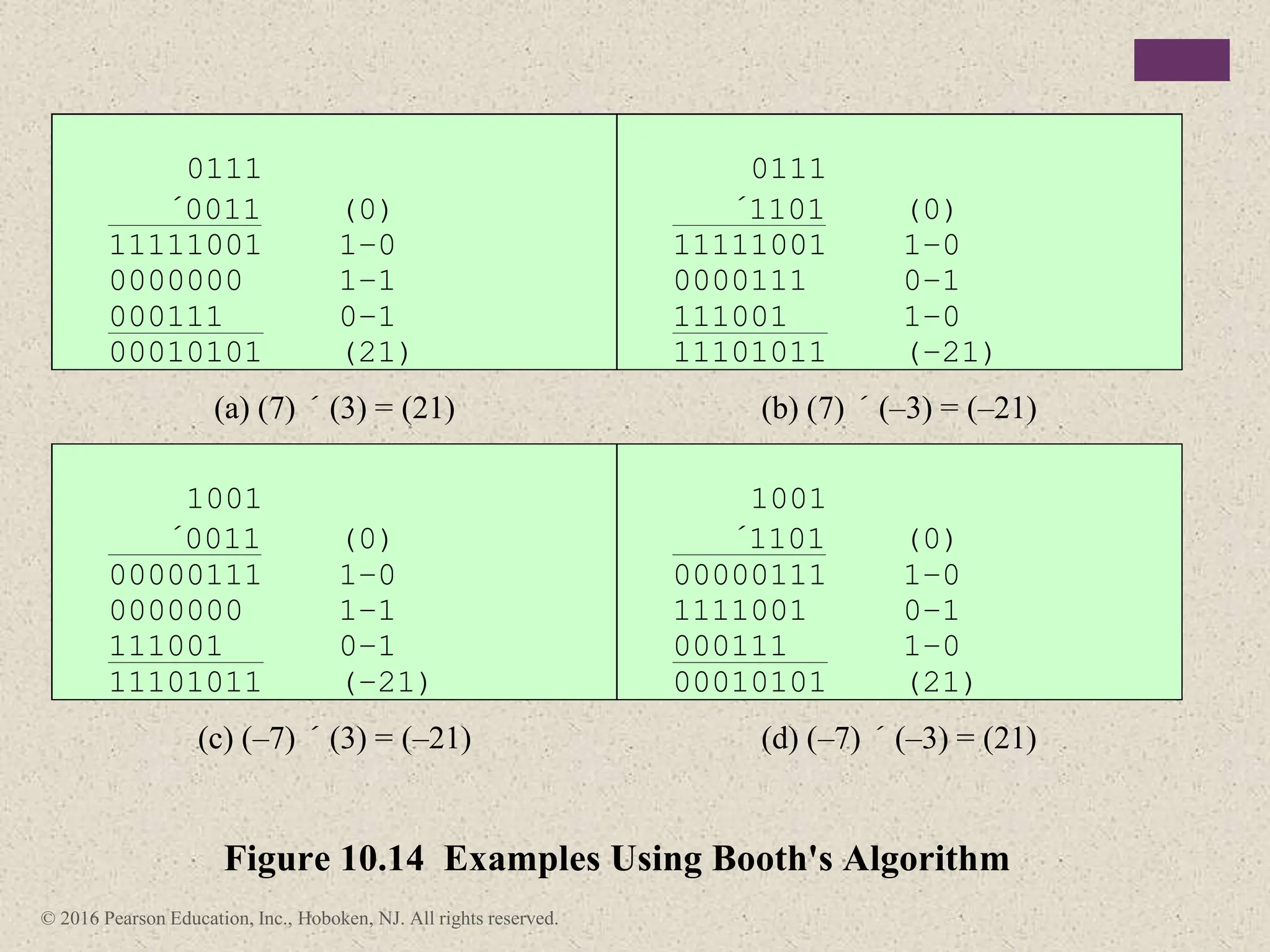
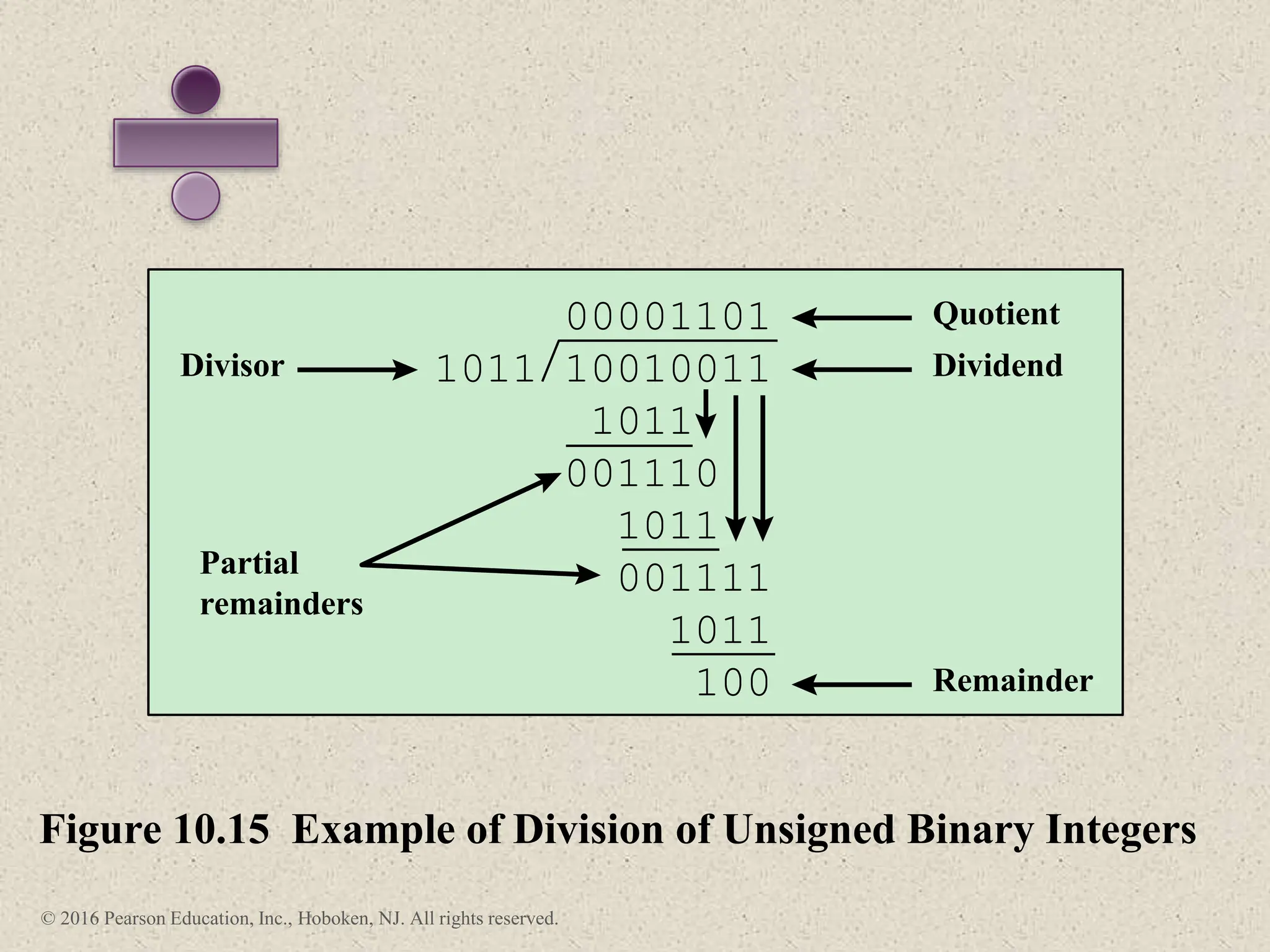
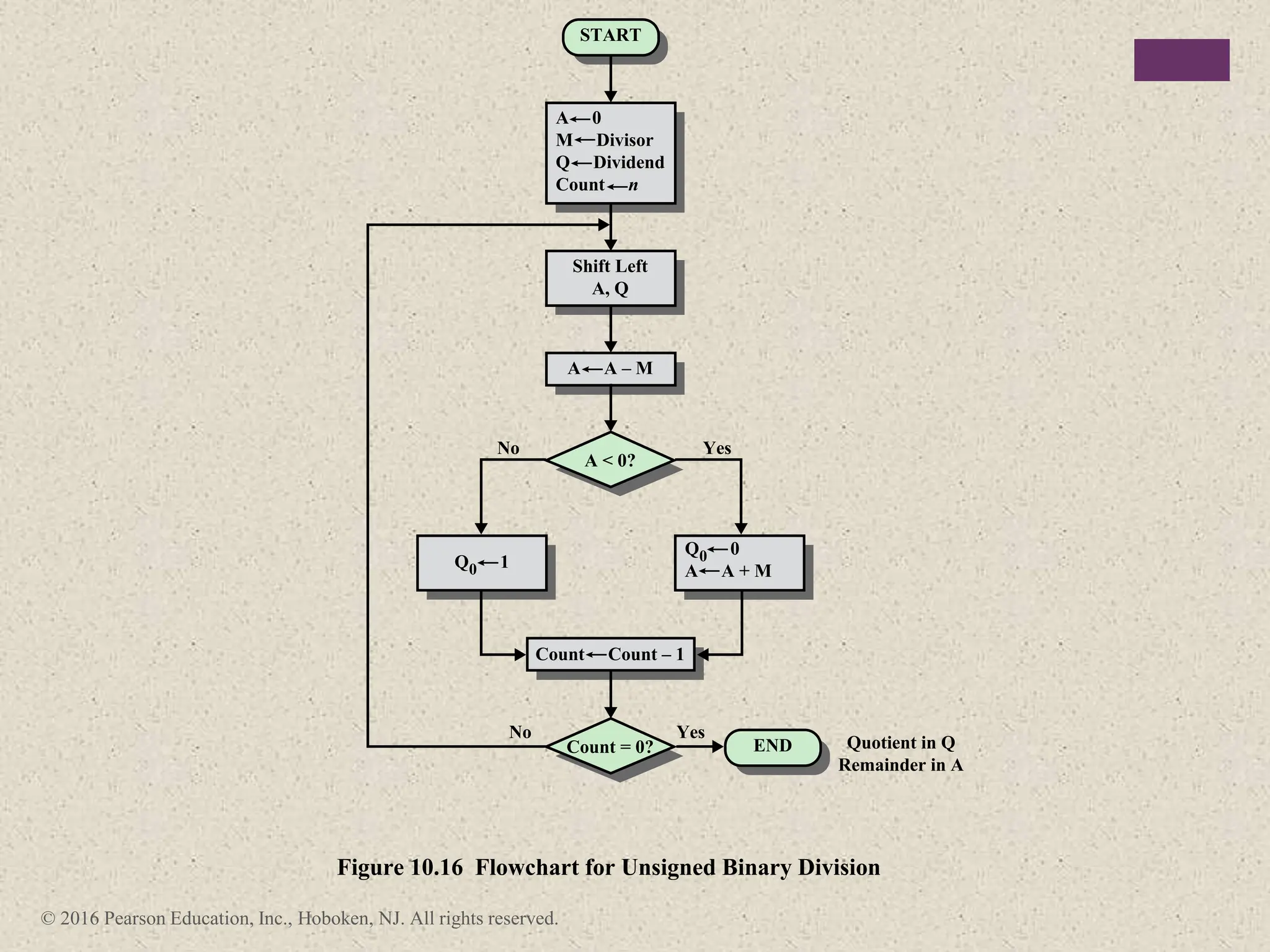
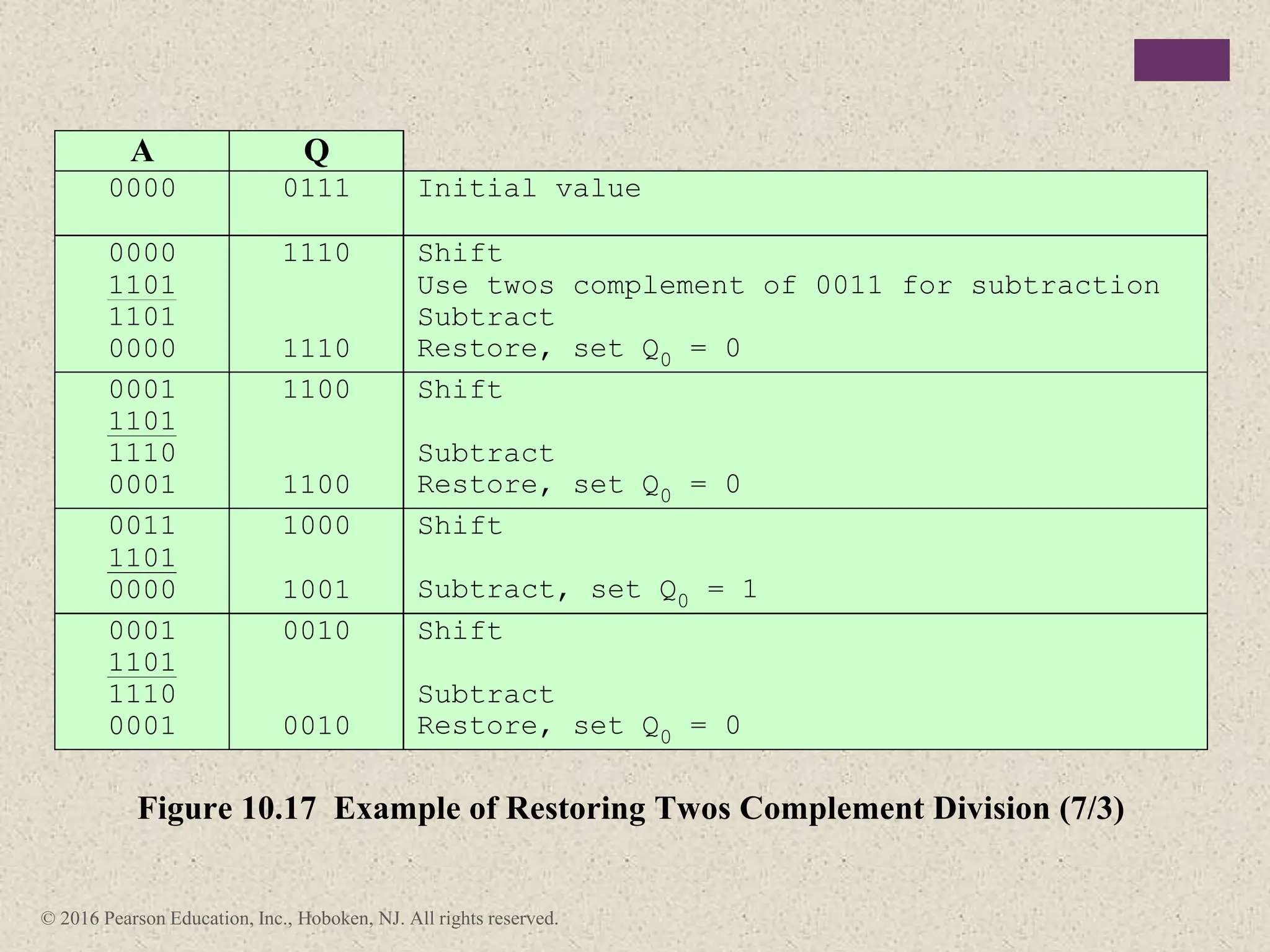
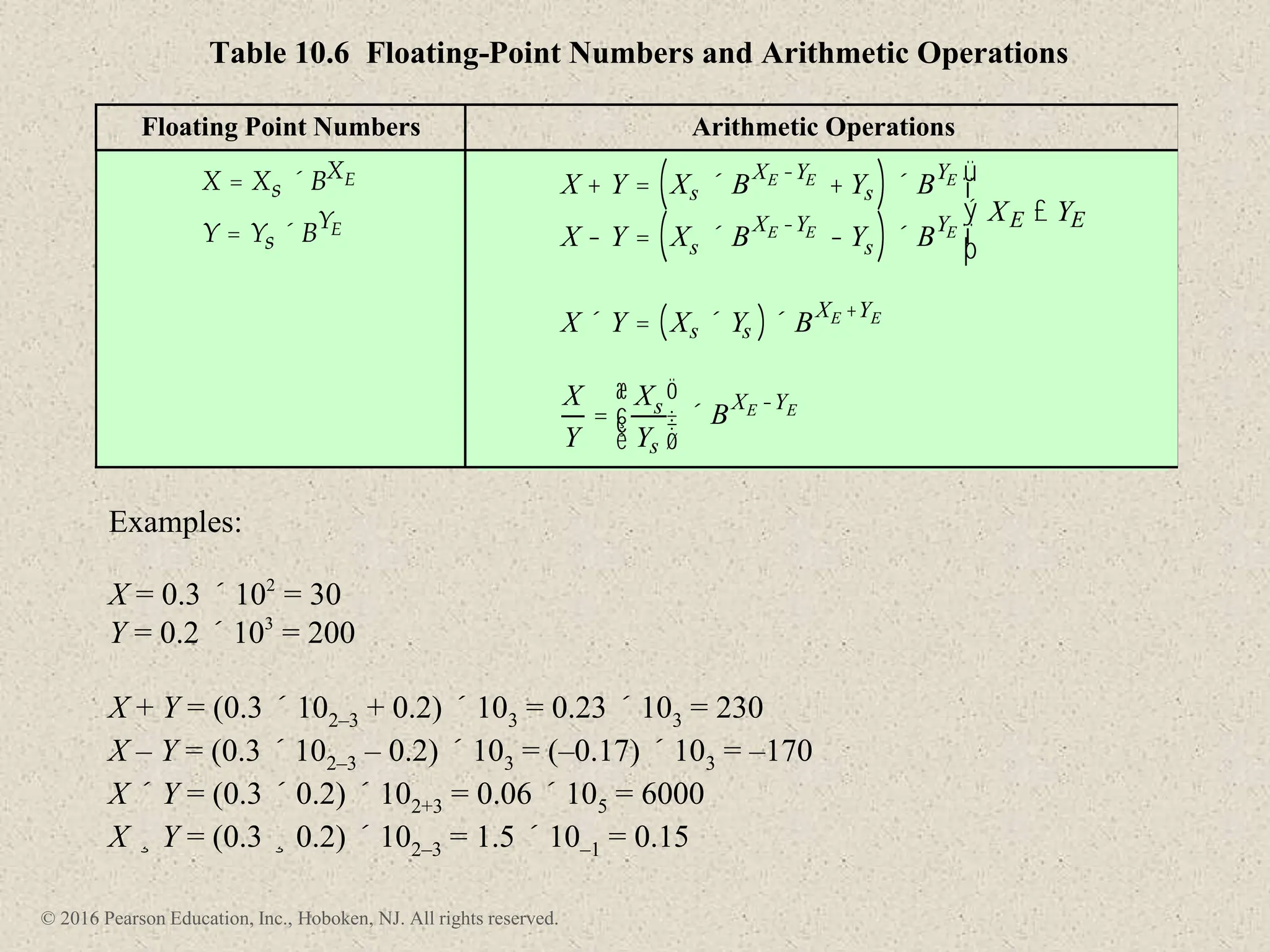
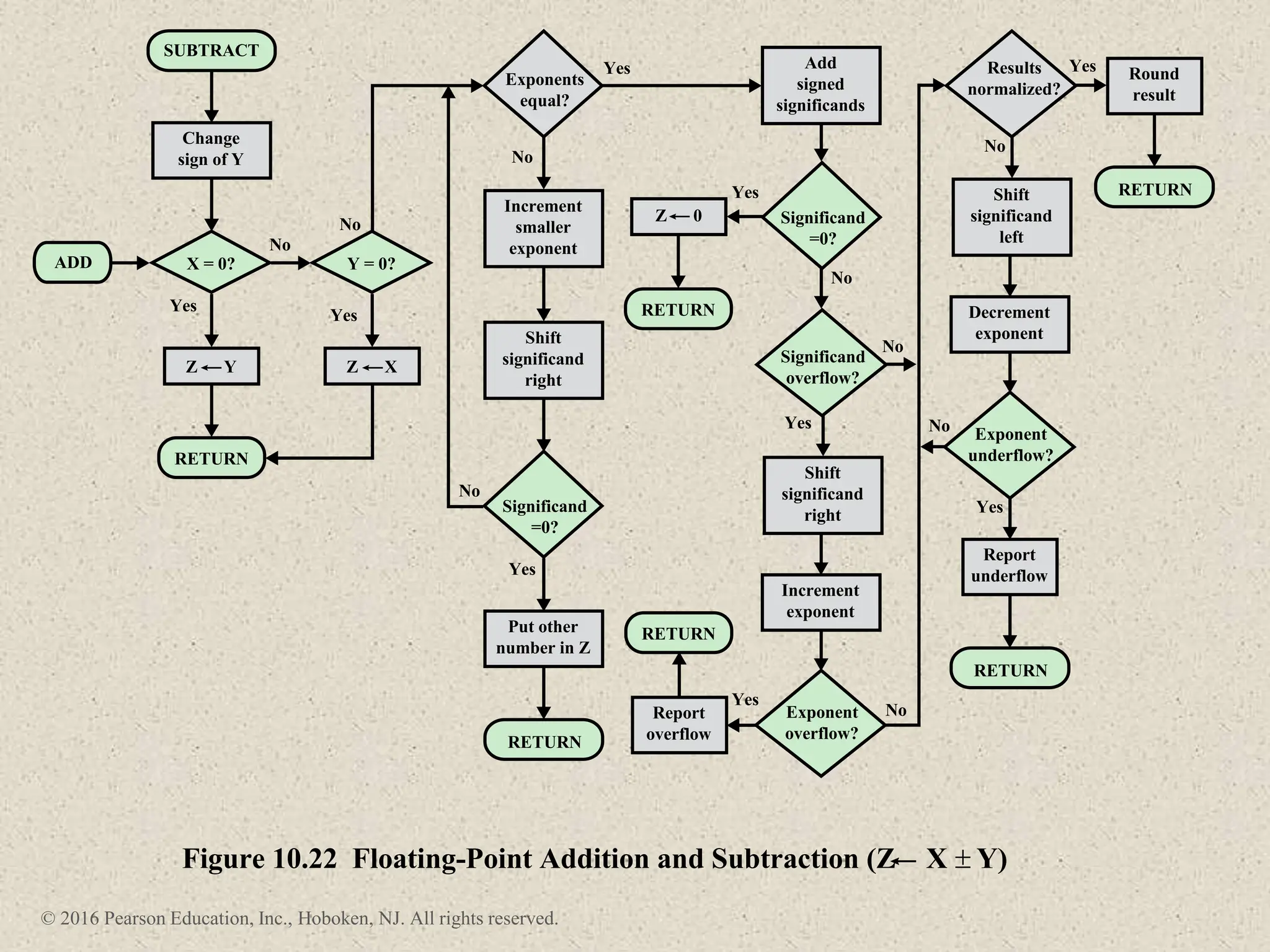
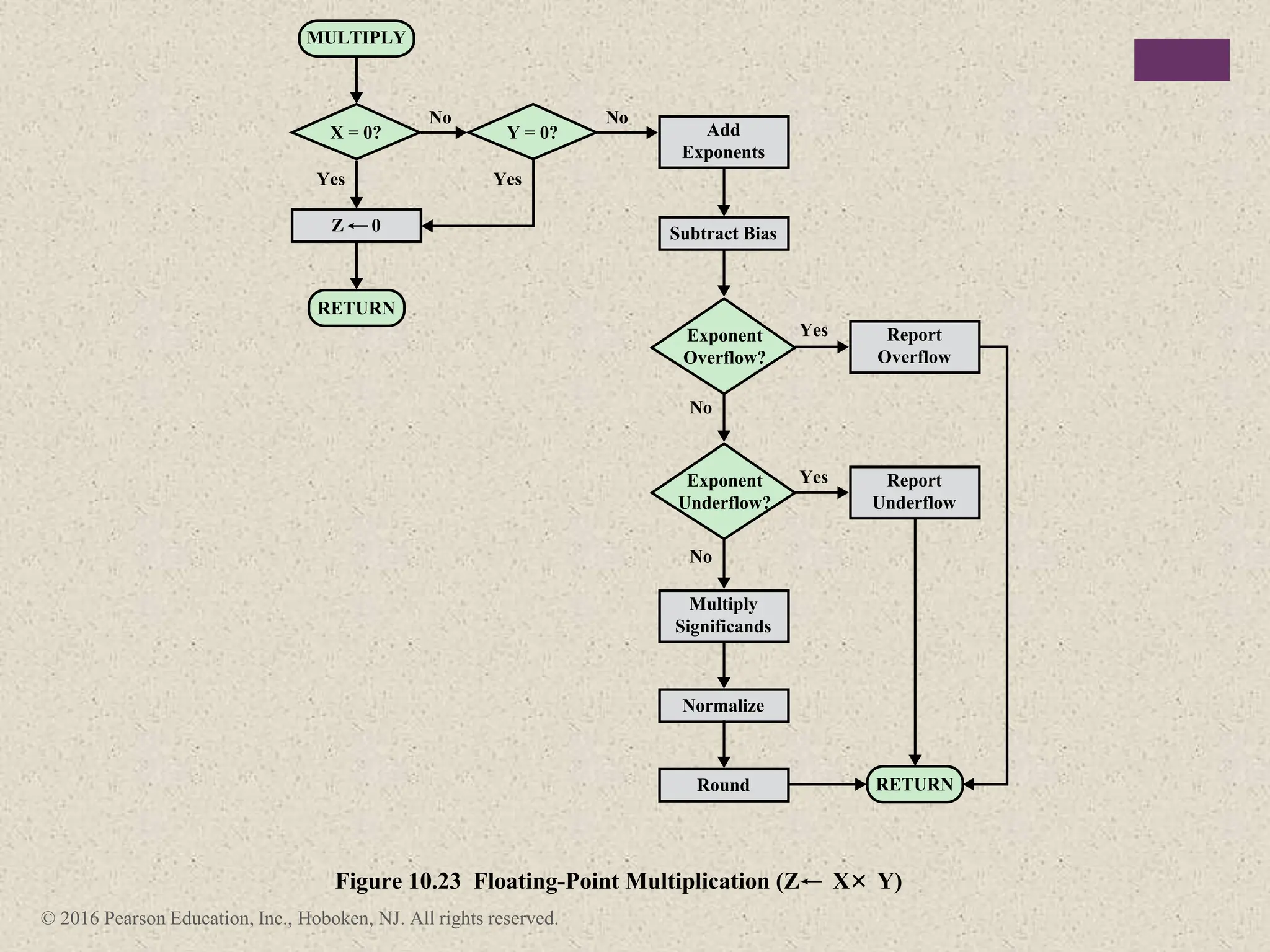
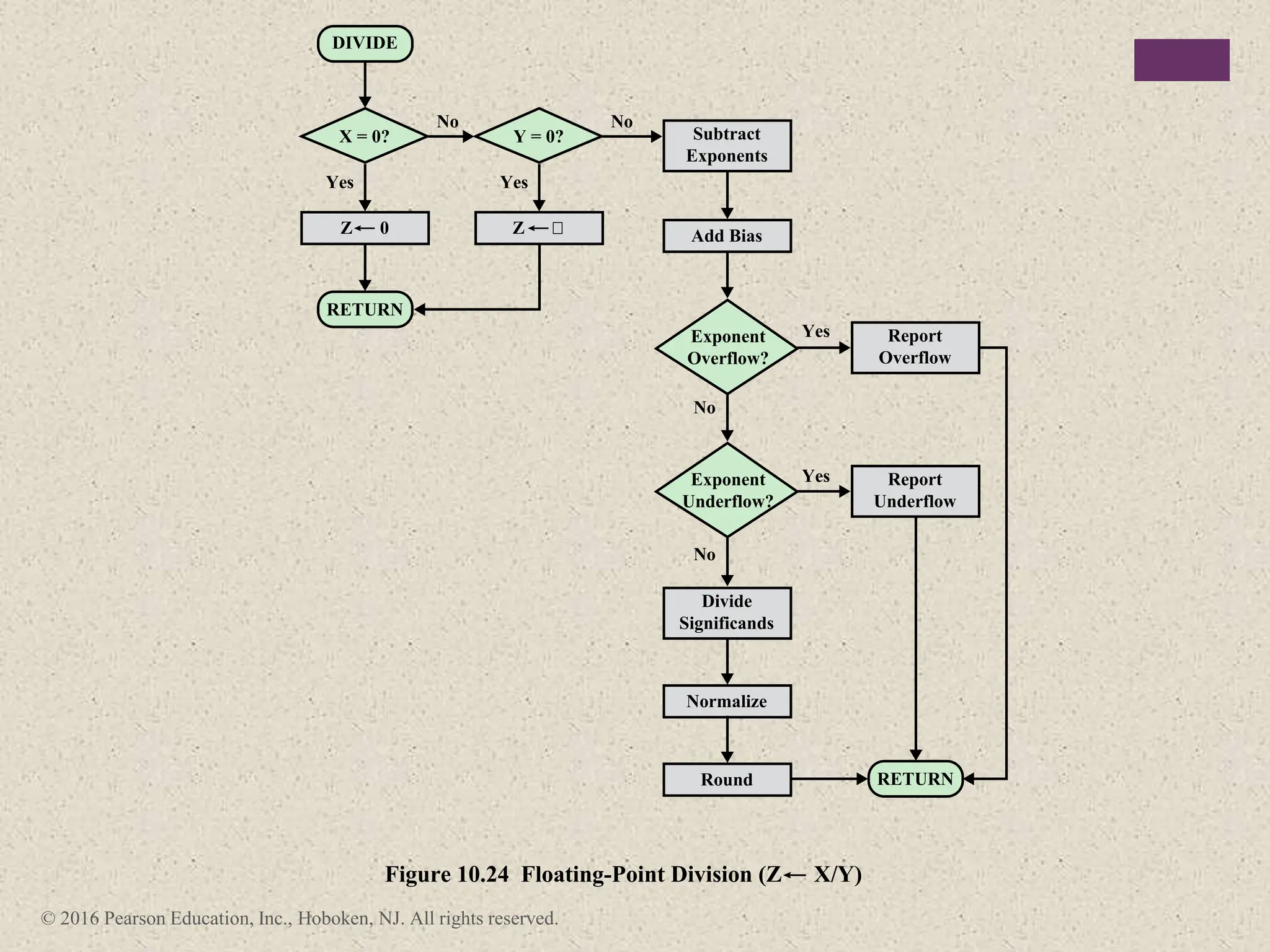
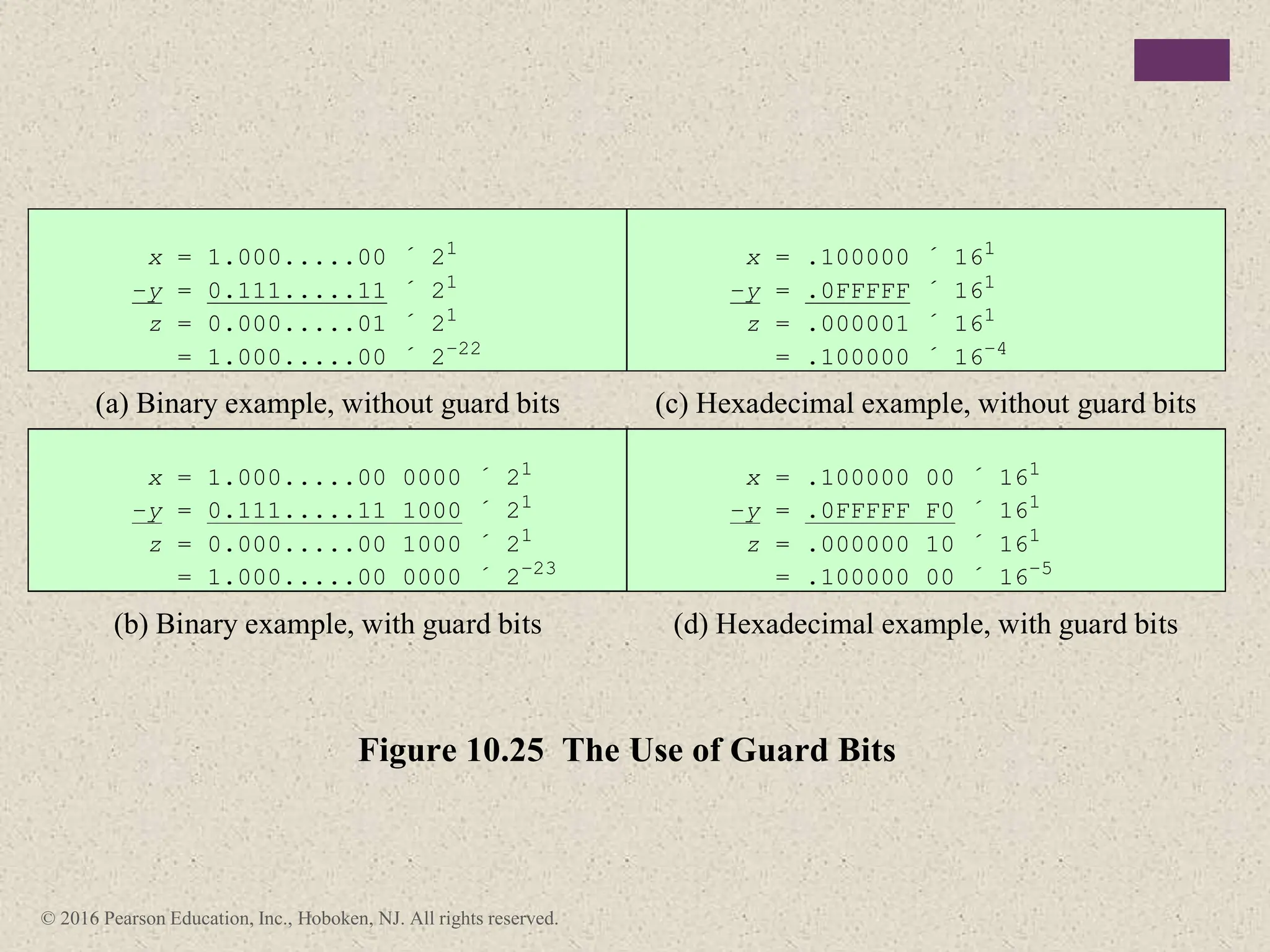
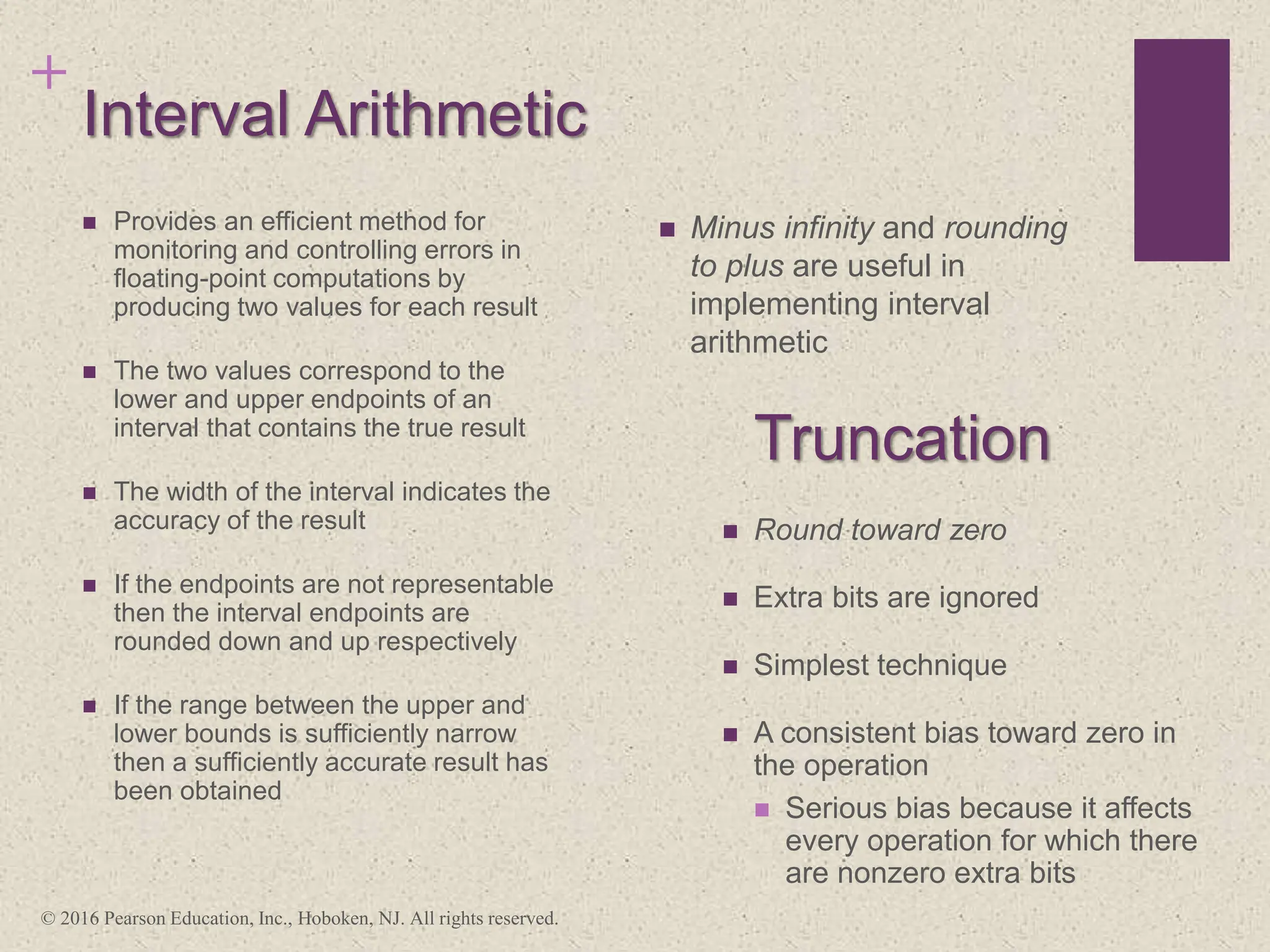
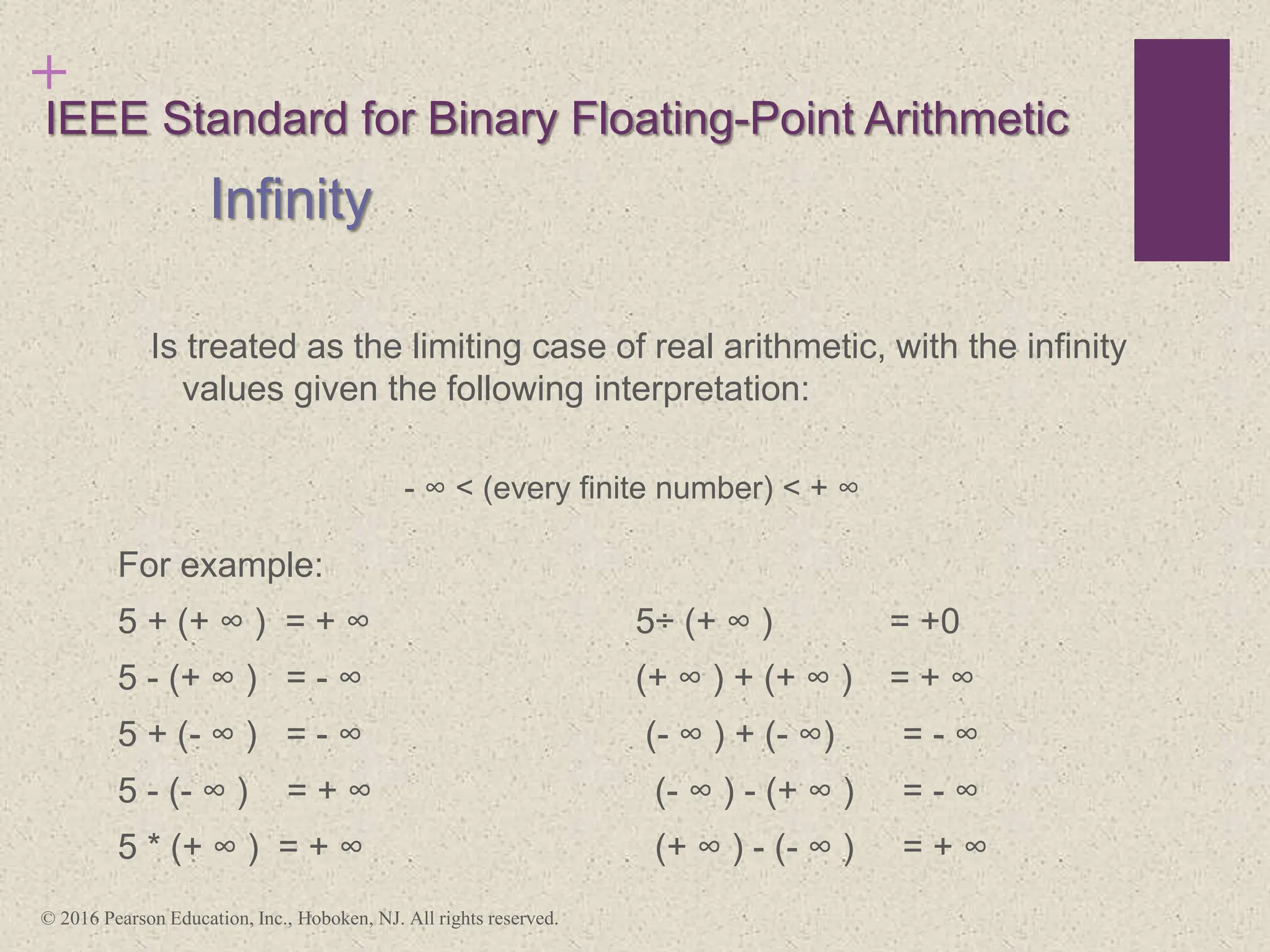
3) Arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, and negation are described for twos-complement integers. Special cases and rules for overflow are also covered.