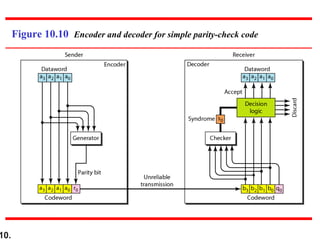
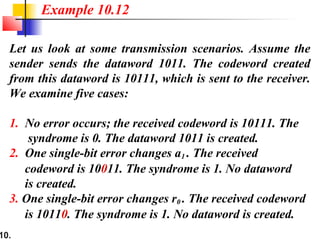
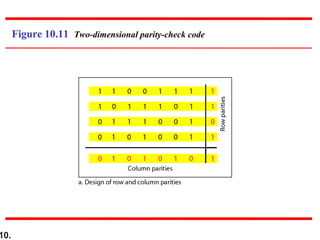
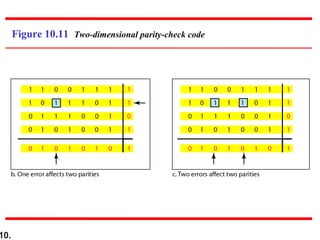
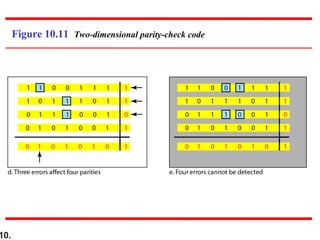
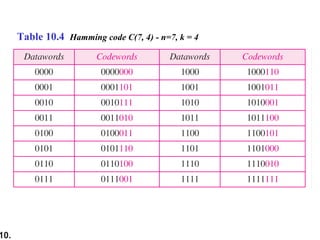
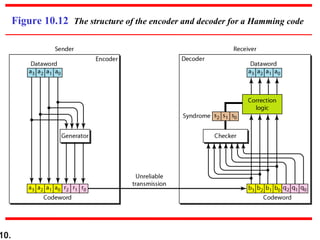
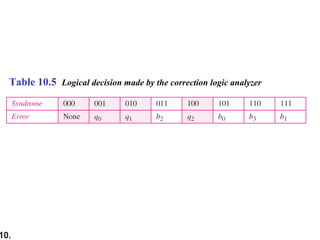
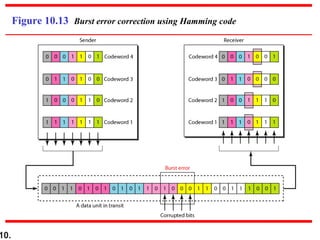
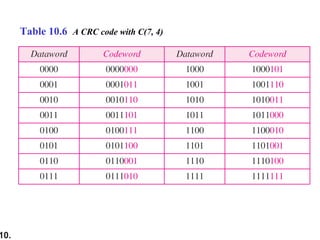
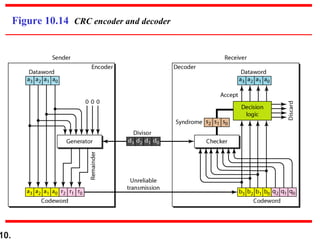
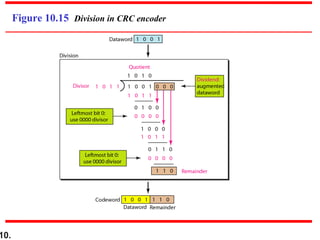
This document discusses error detection and correction techniques in digital communications. It covers Hamming distance, block codes, linear block codes, cyclic codes, cyclic redundancy checks (CRCs), and checksums. Key points include:
- The Hamming distance between words is the number of differing bits
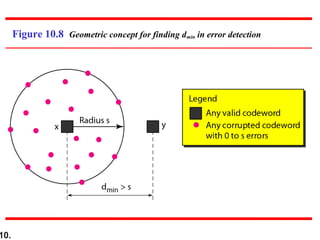
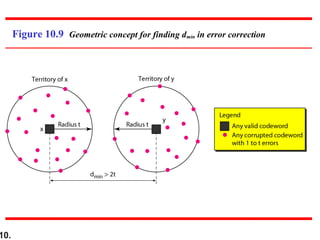
- Minimum Hamming distance determines a code's error detection/correction capability
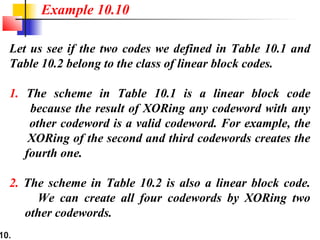
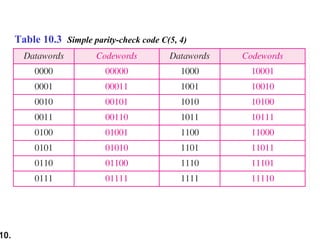
- Linear block codes allow valid codewords to be created by XORing other codewords
- Cyclic codes maintain codeword validity under cyclic shifts
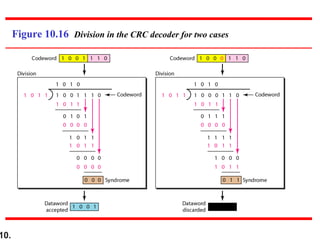
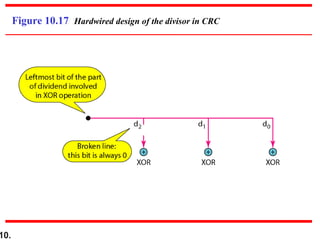
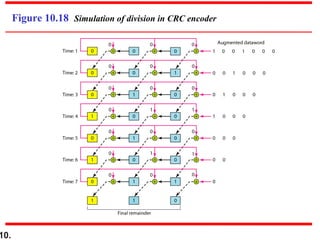
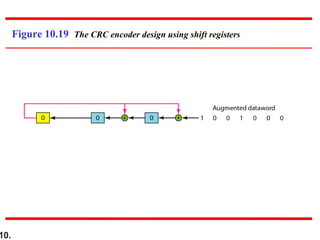
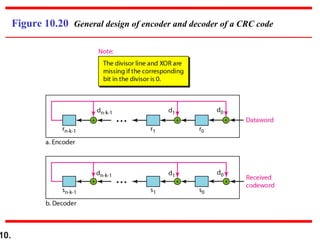
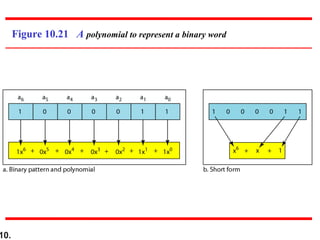
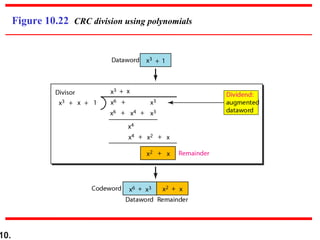
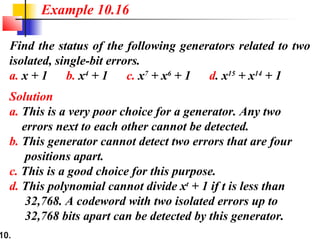
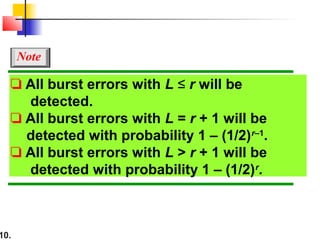
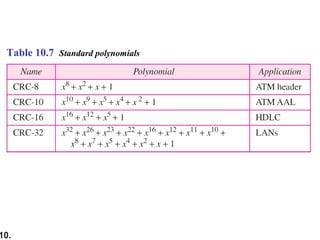
- CRCs use polynomial division to embed a checksum in transmitted data
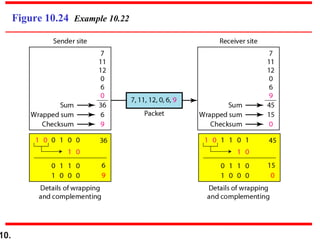
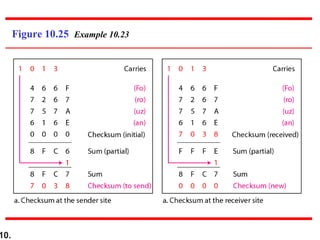
- Checksums provide error detection by transmitting a calculated value over transmitted data