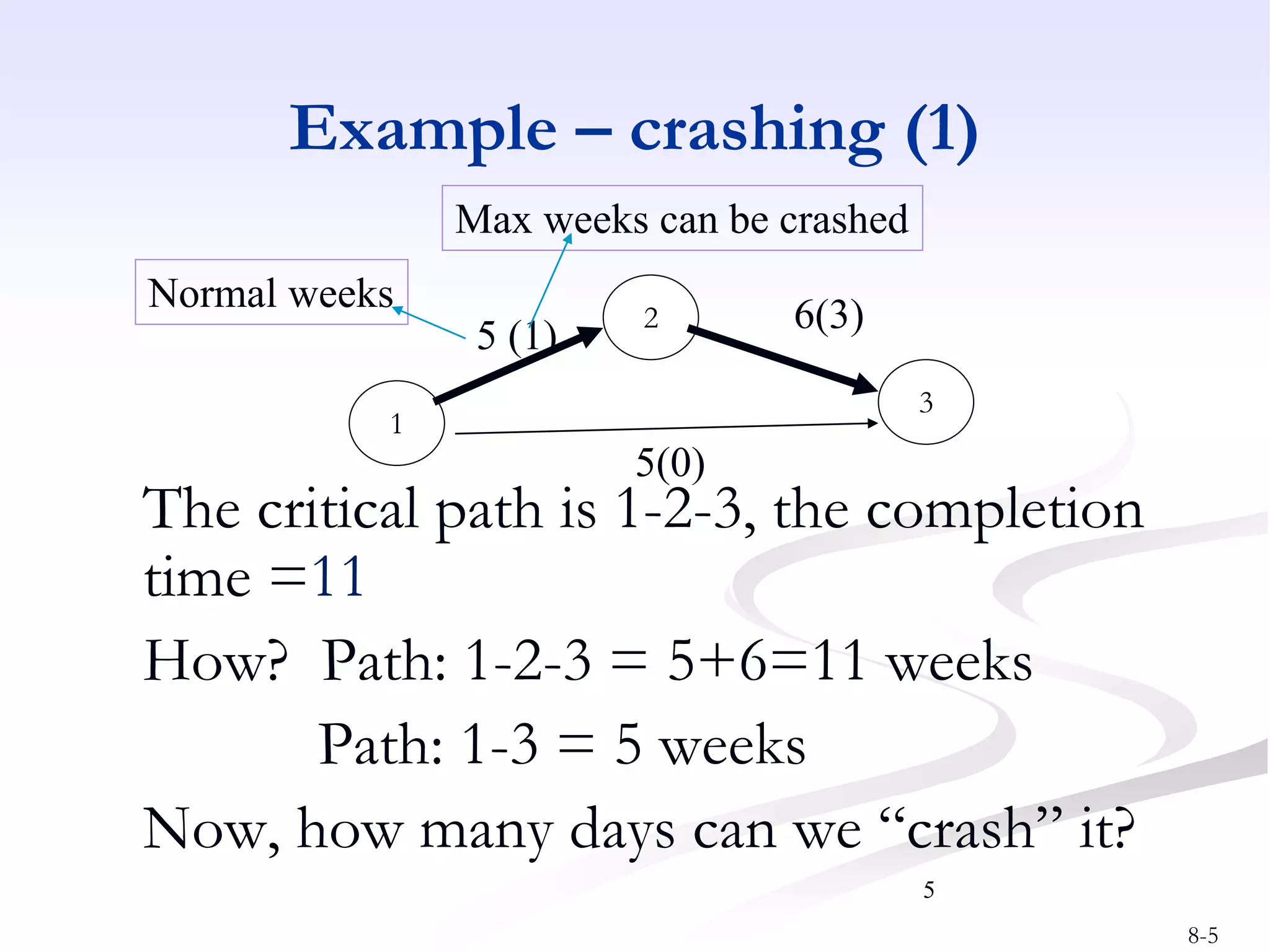
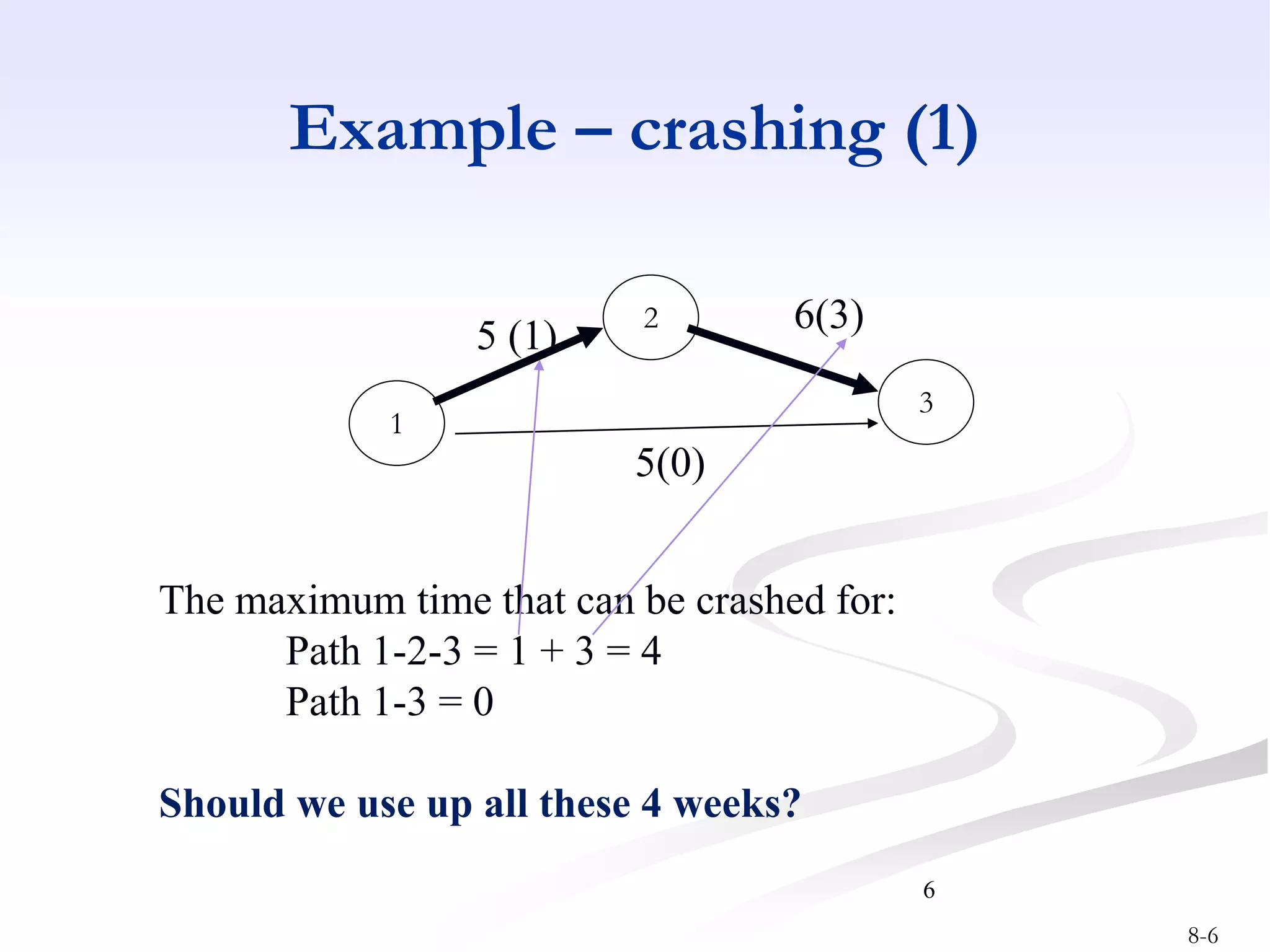
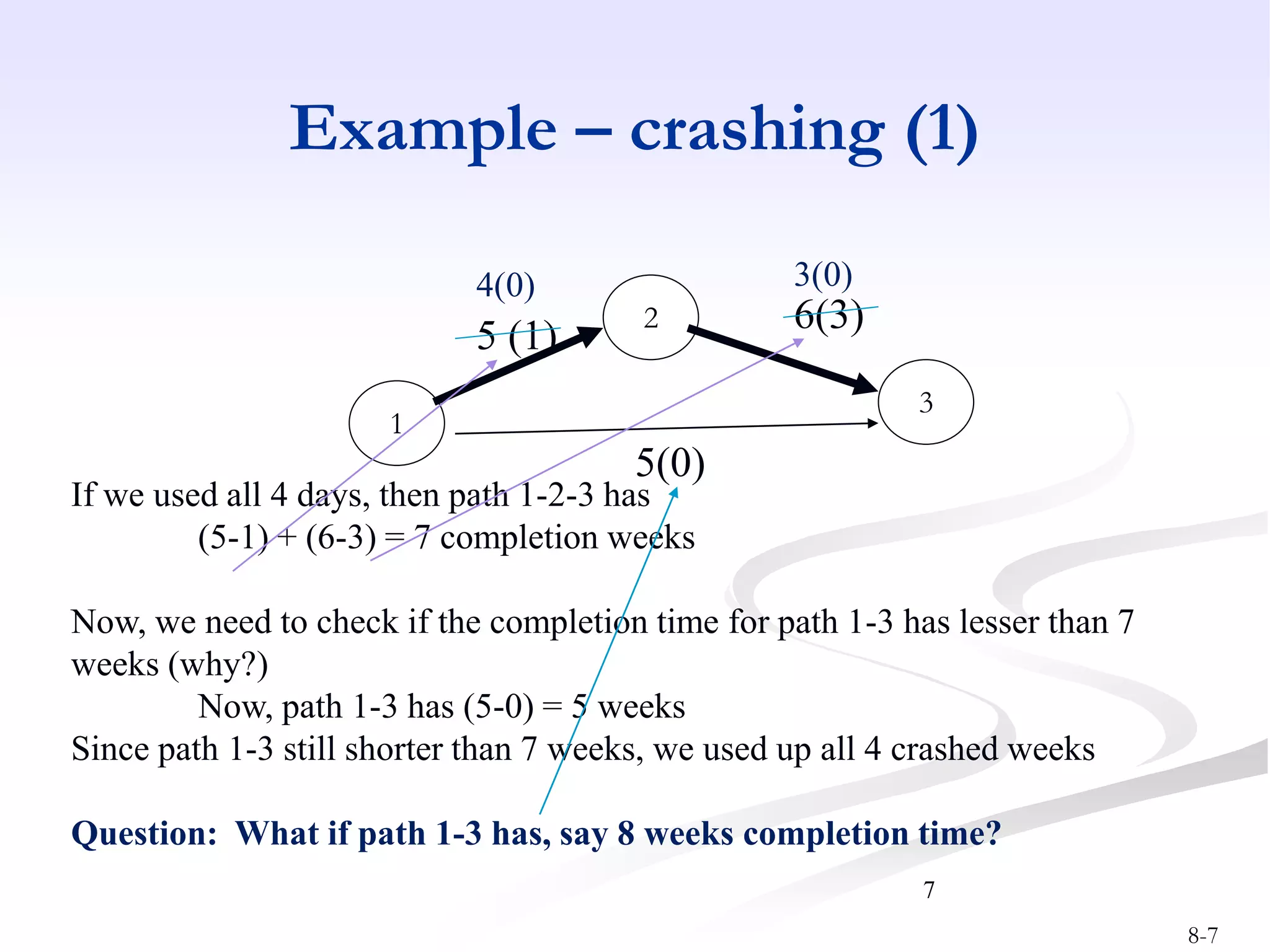
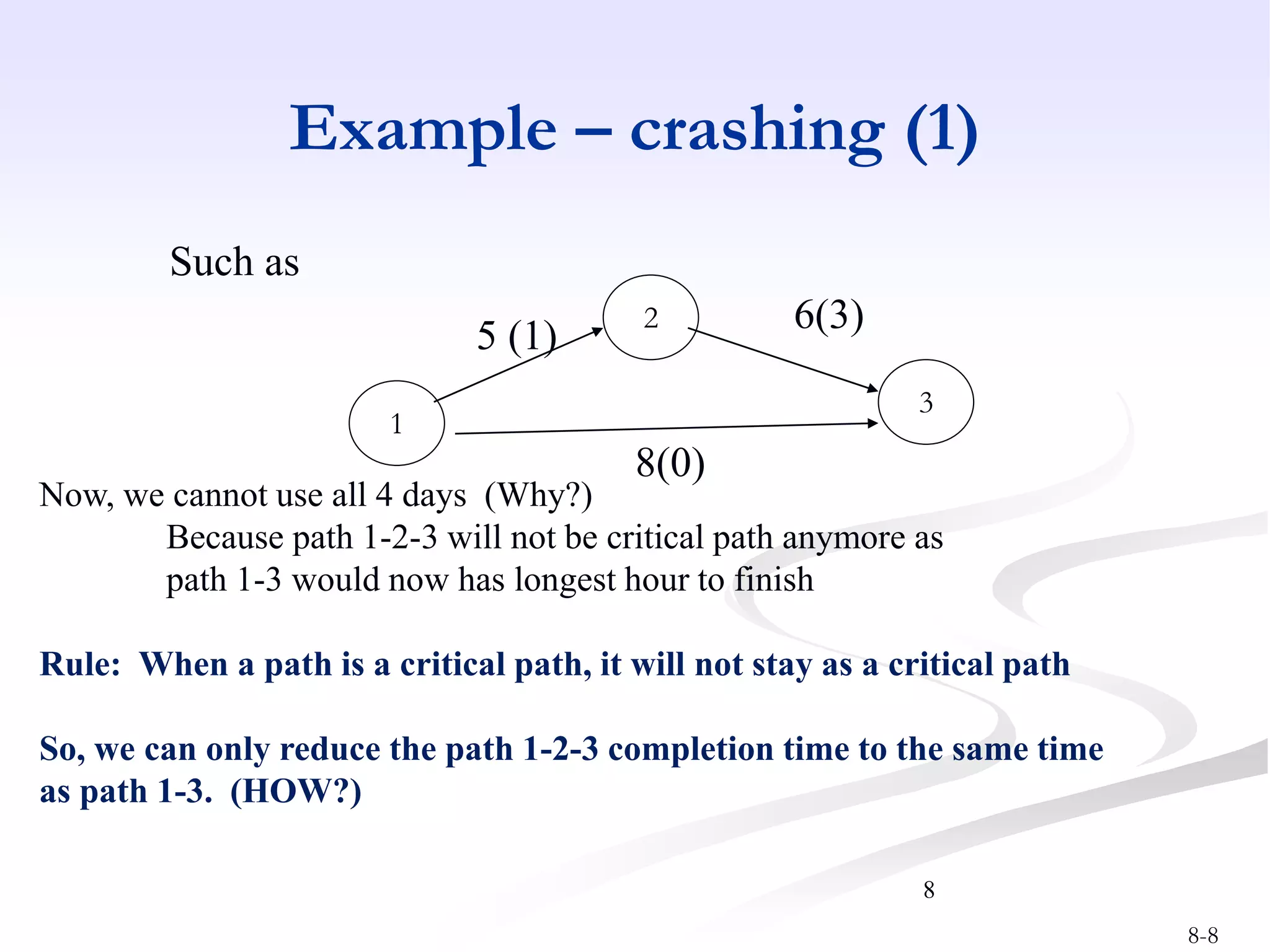
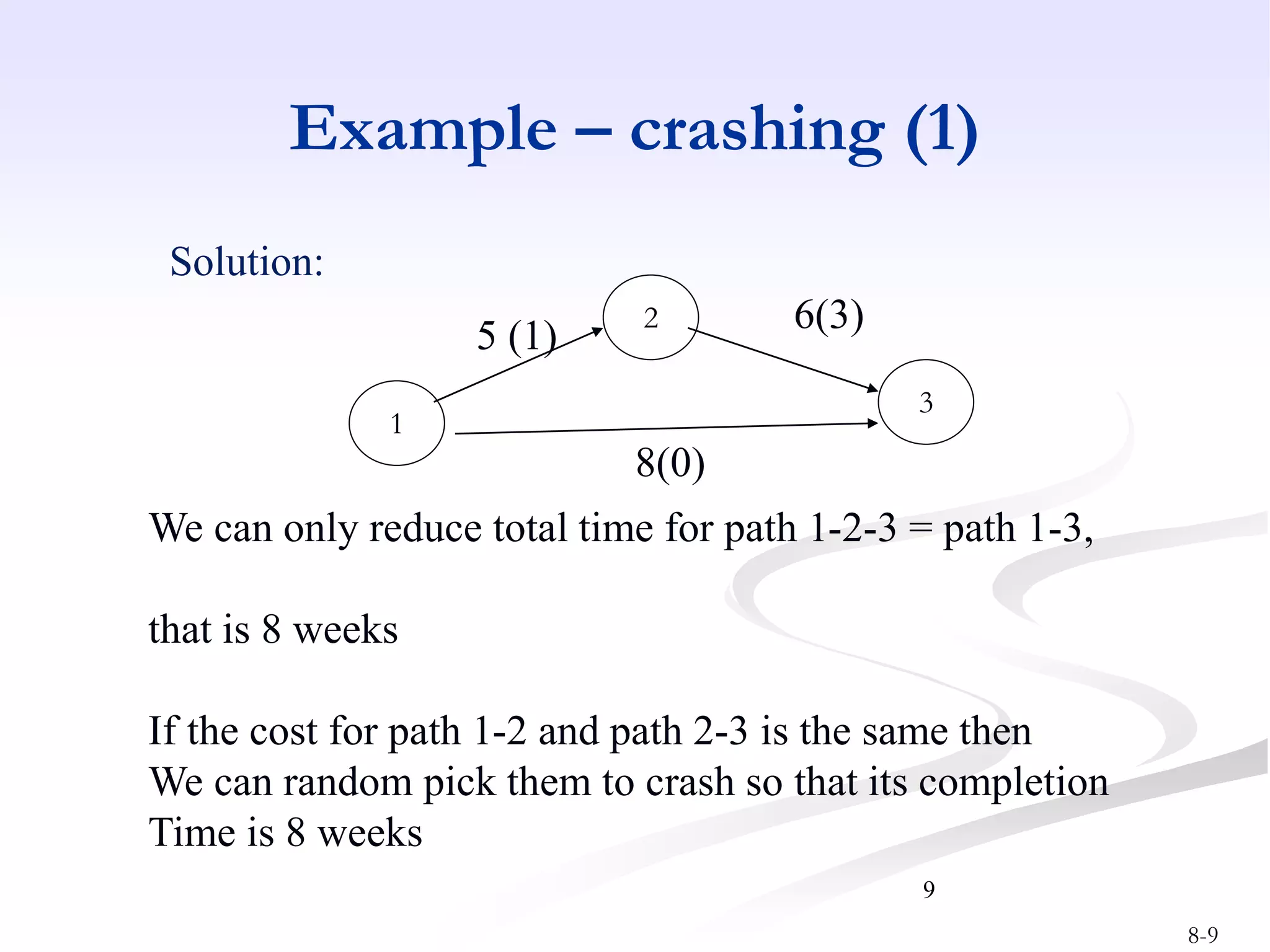
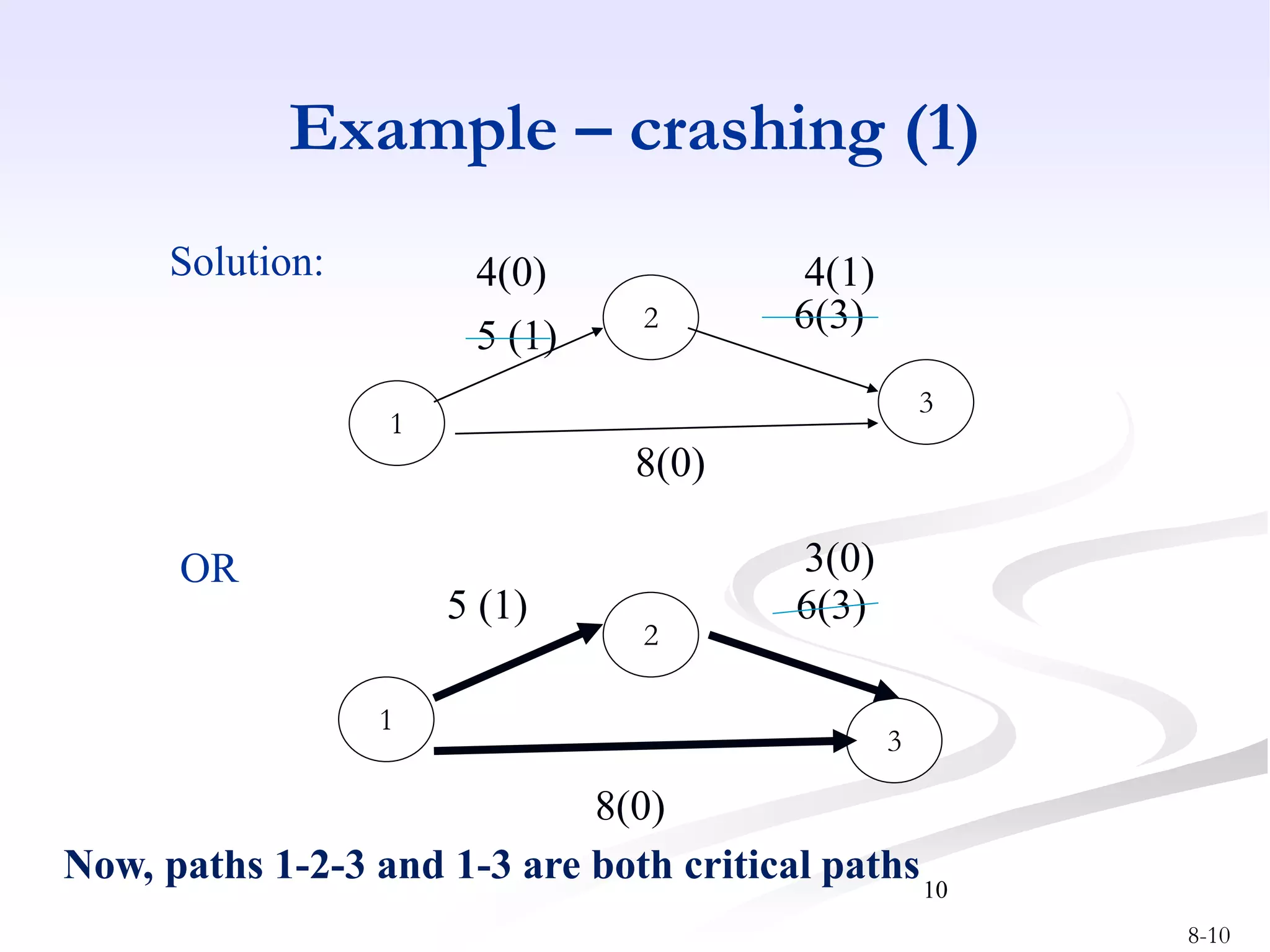
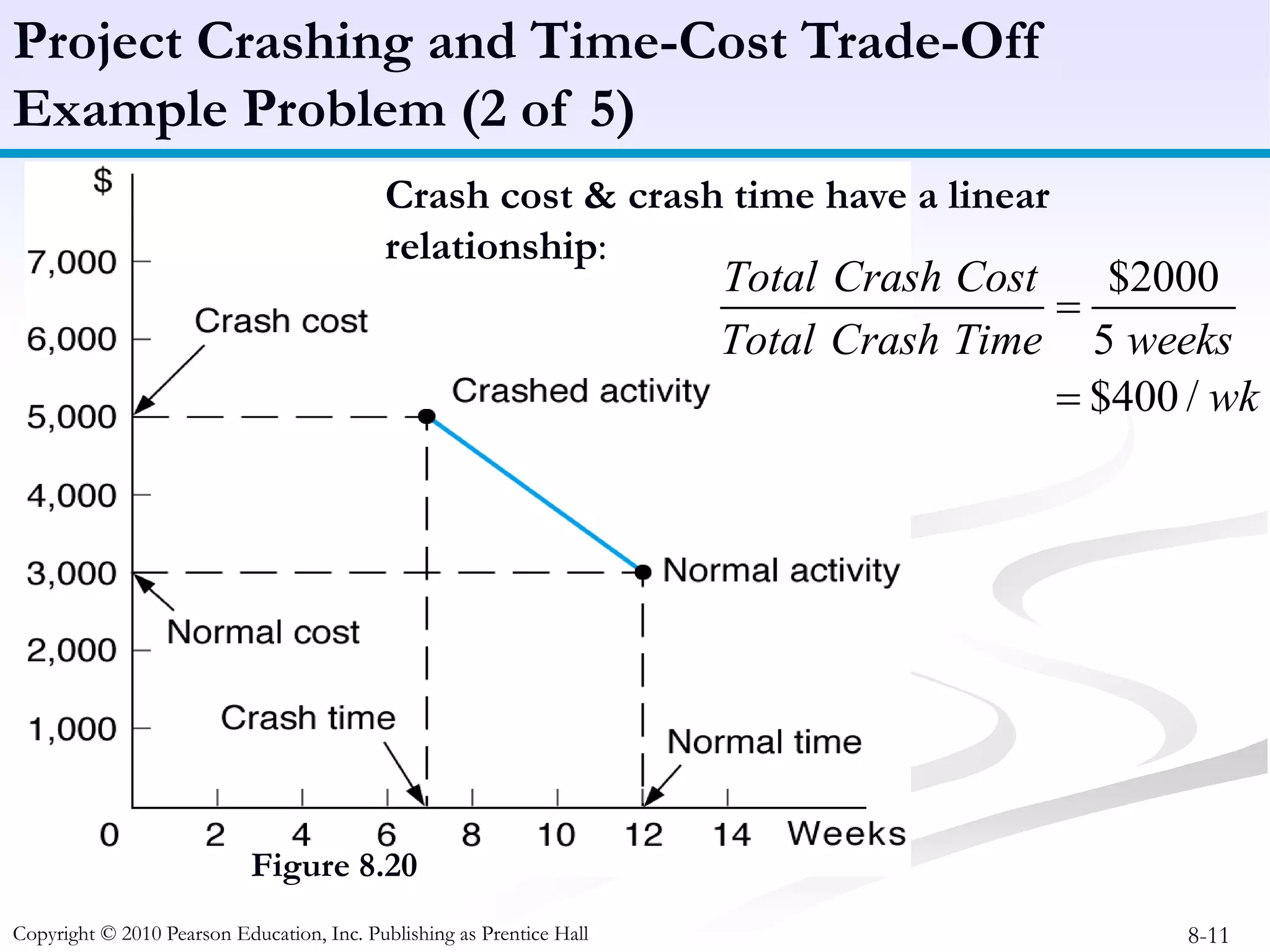
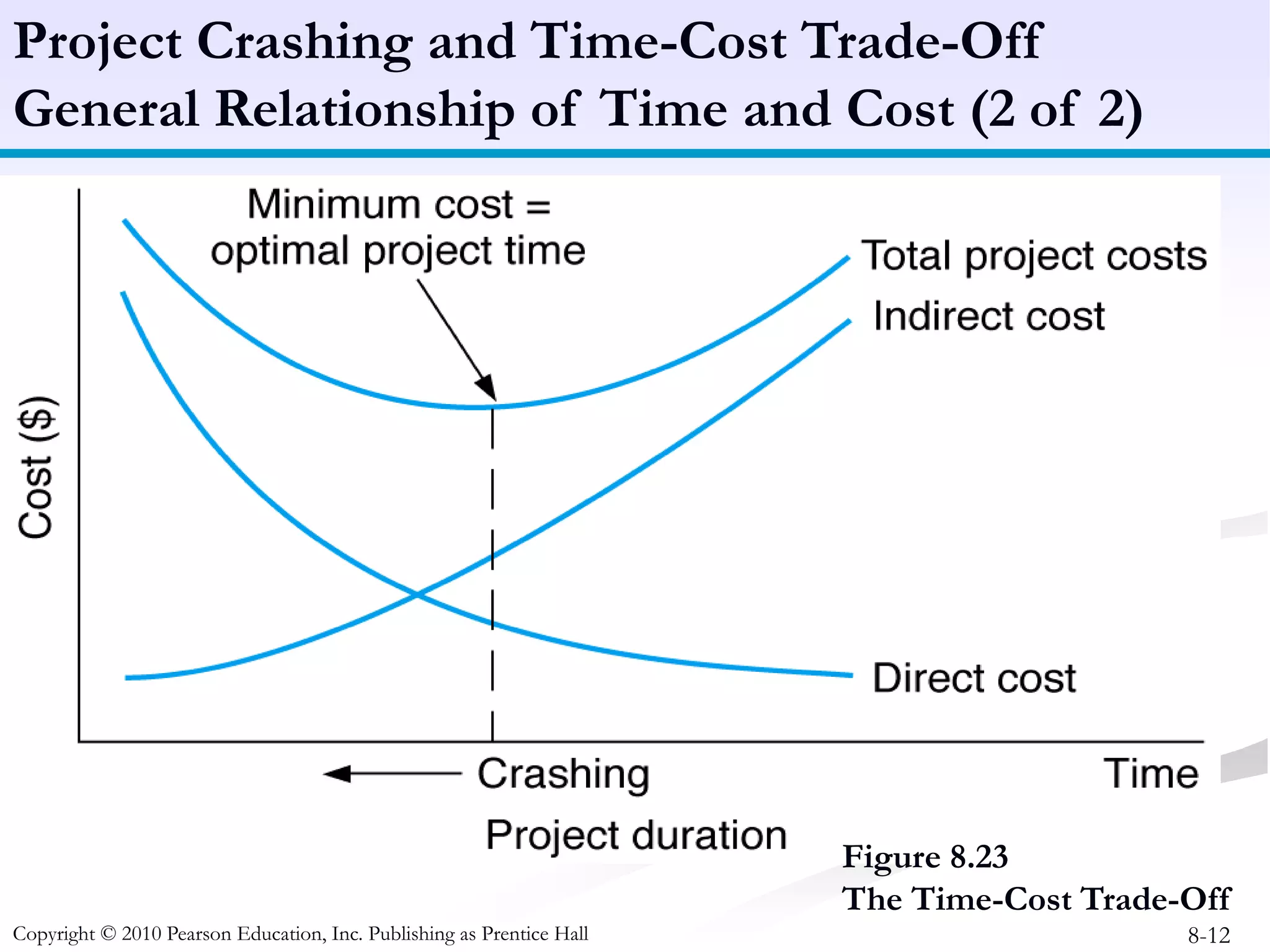
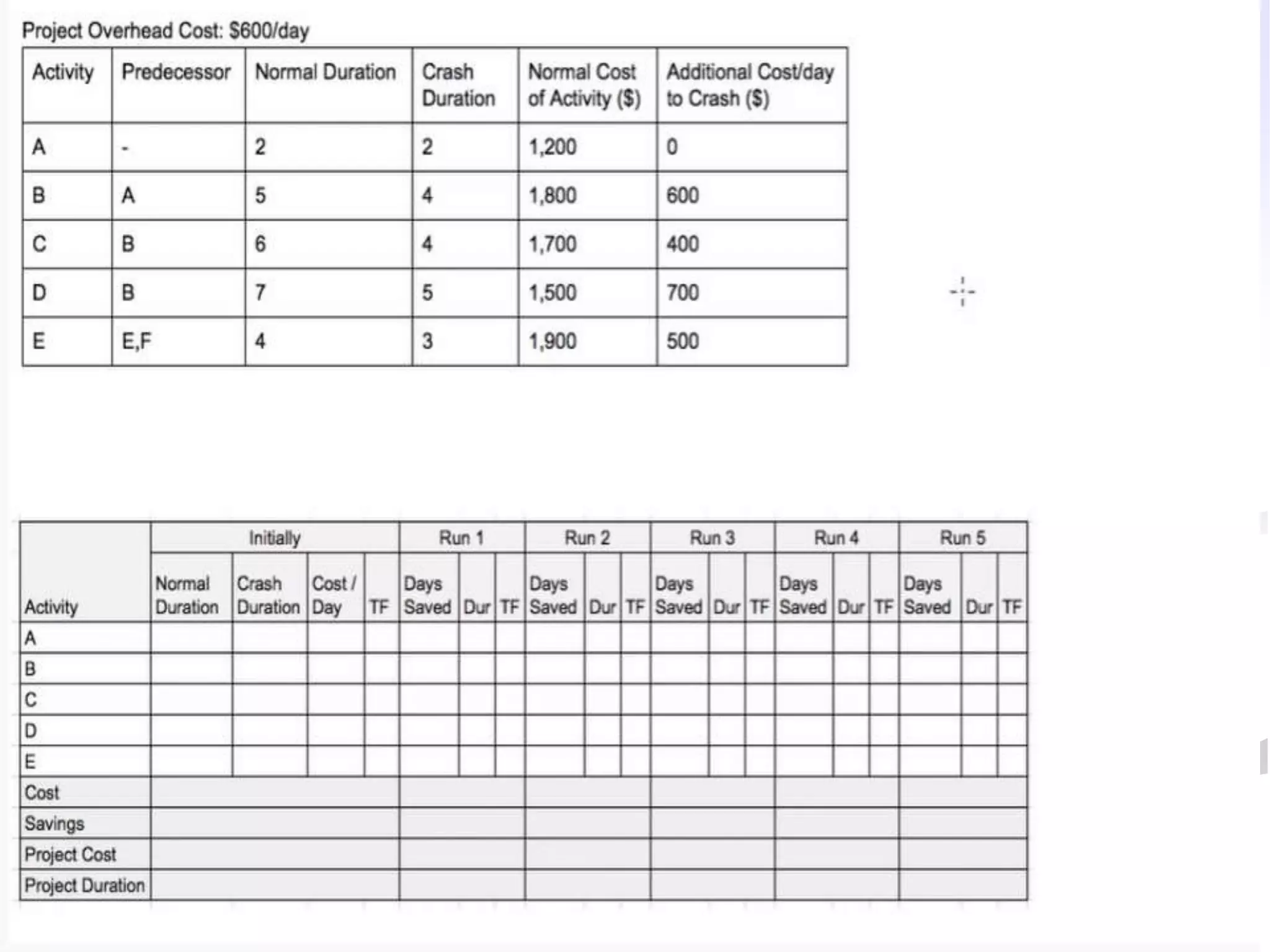
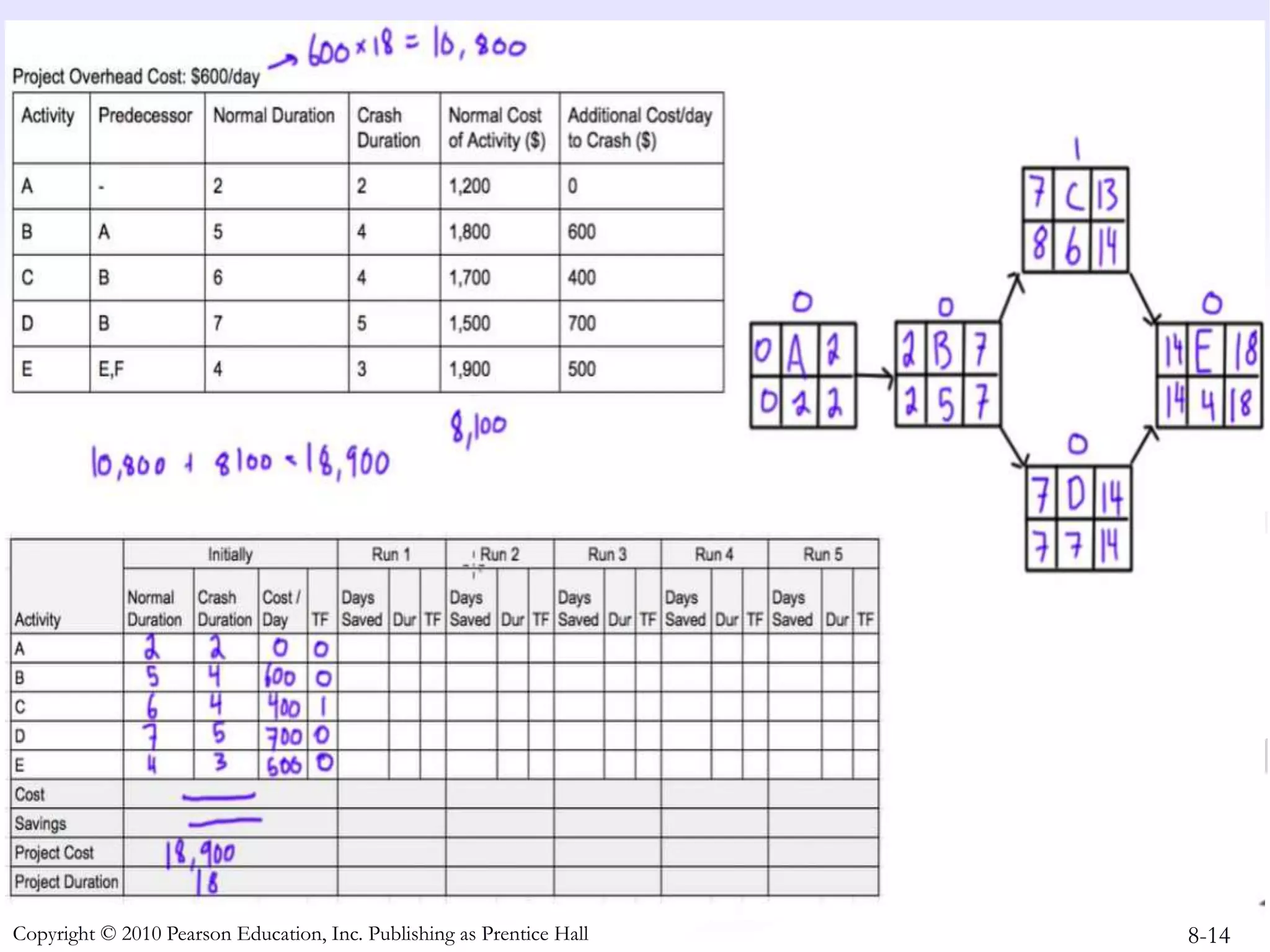
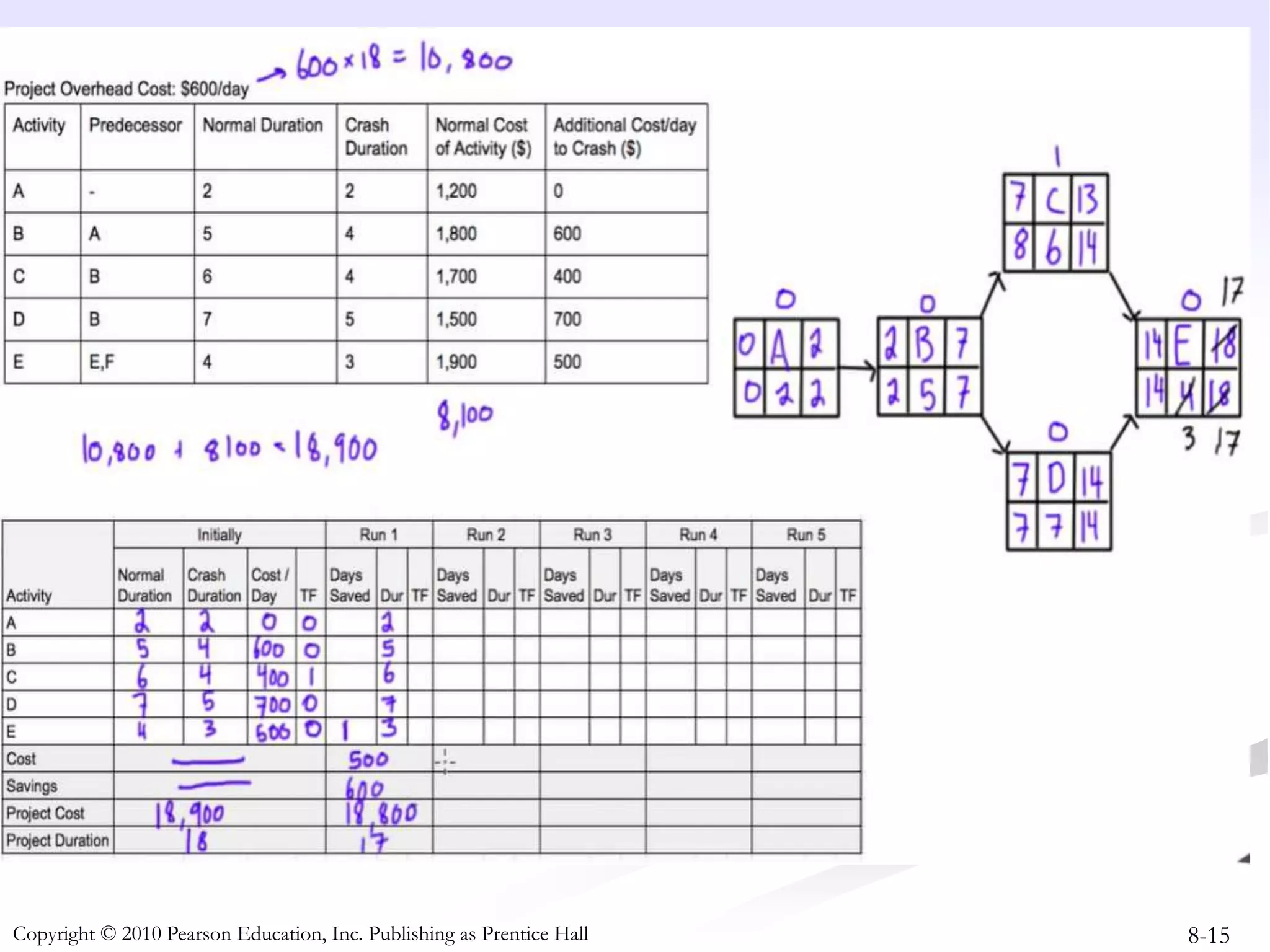
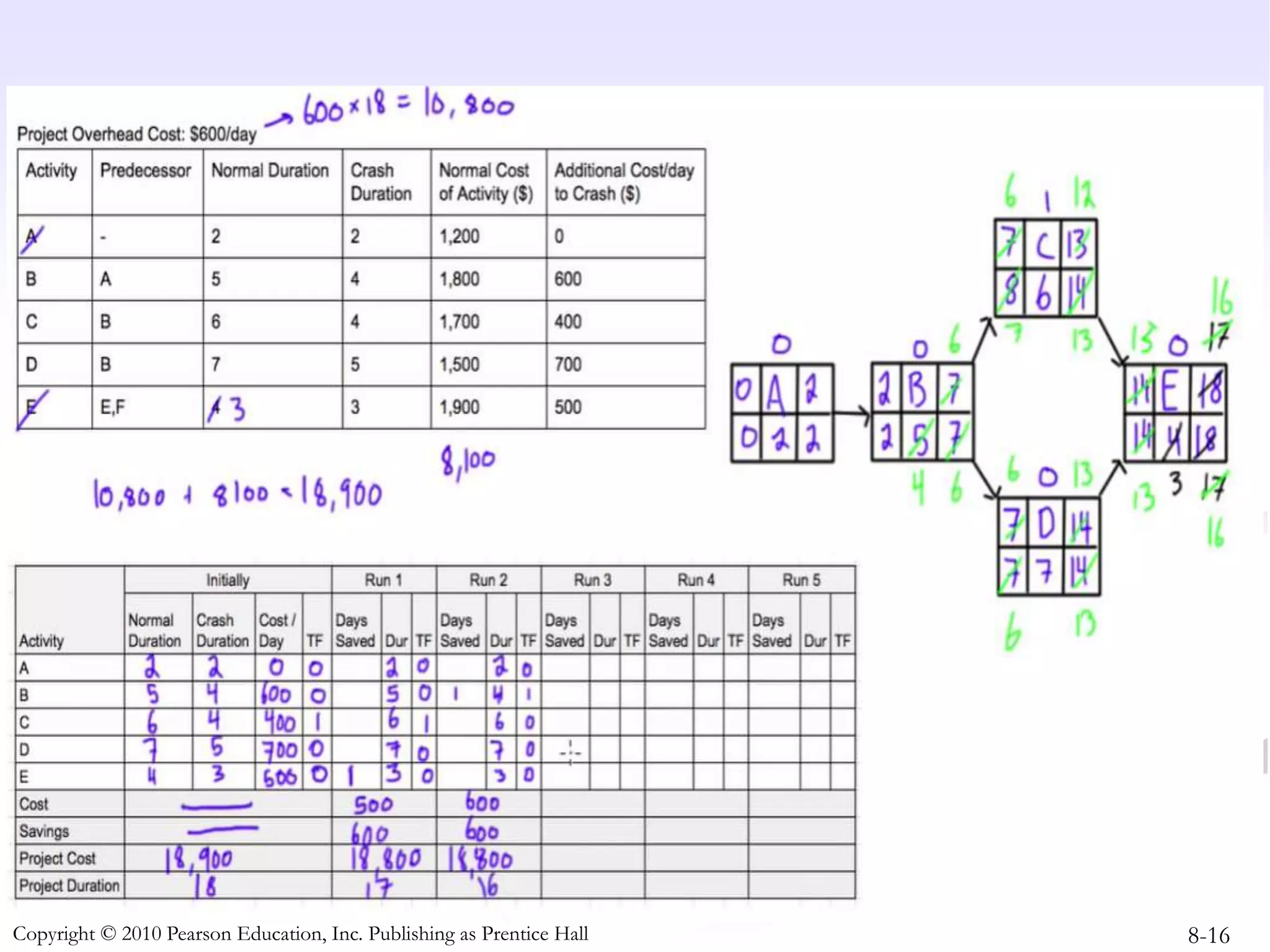
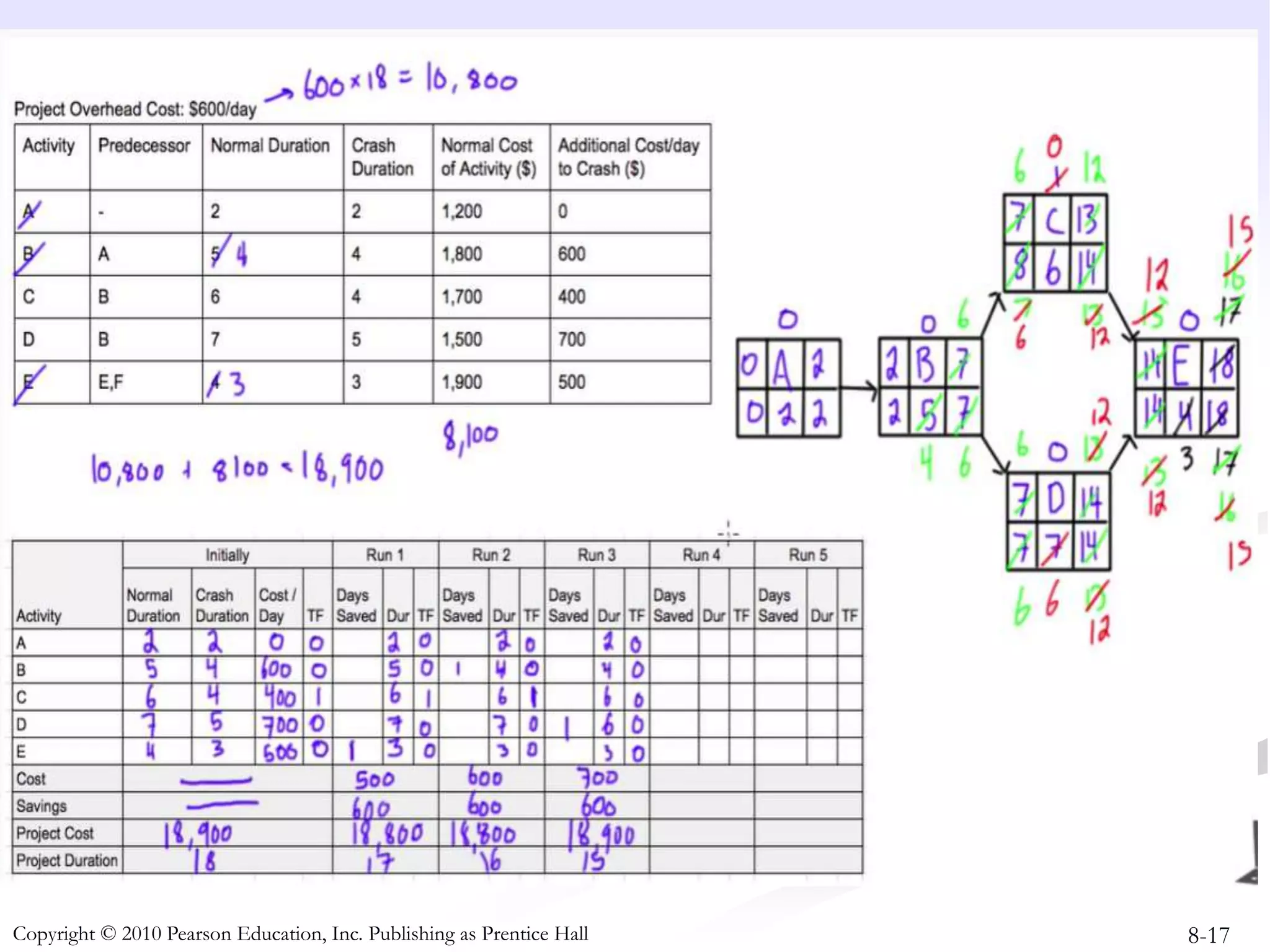
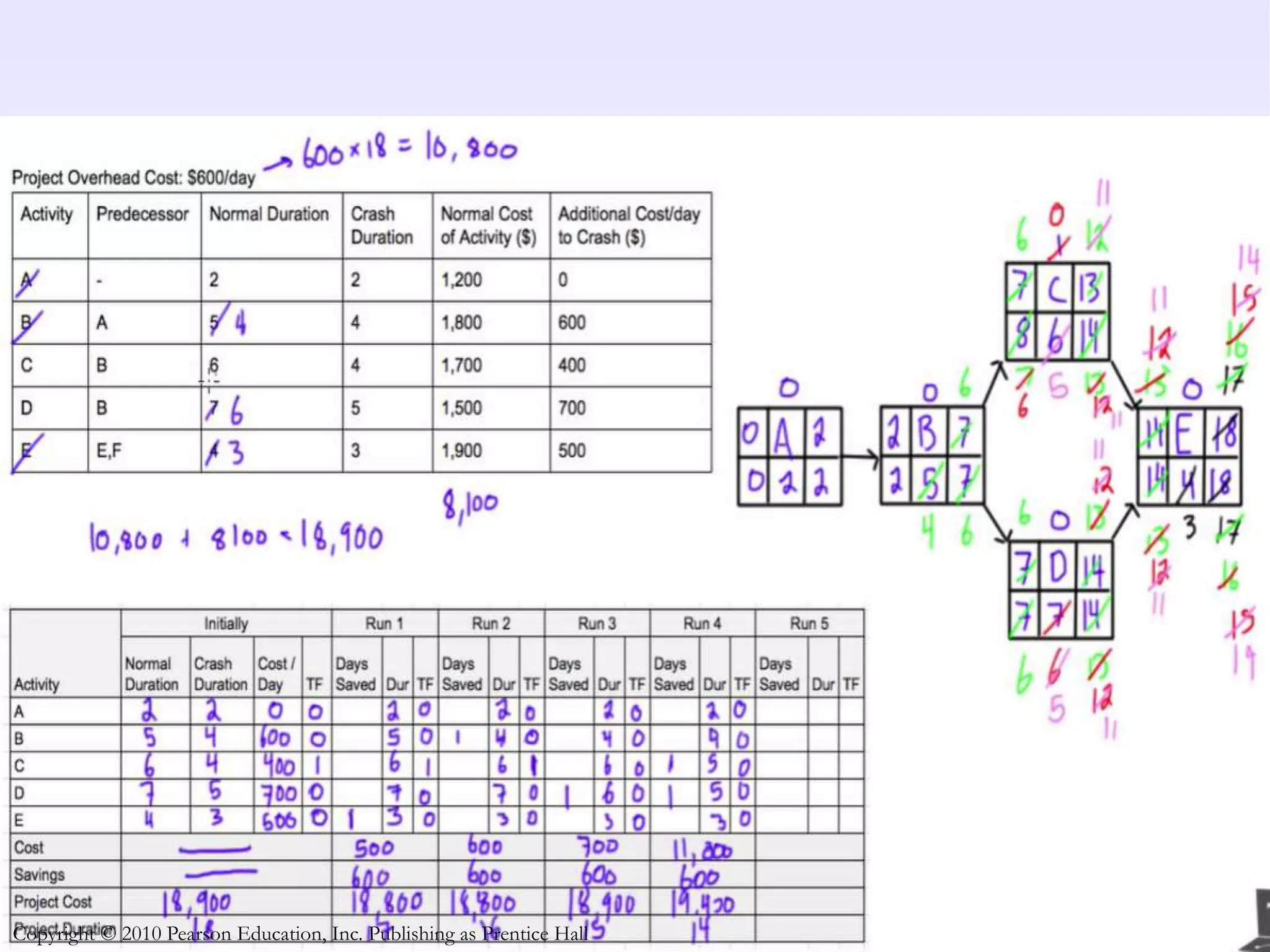
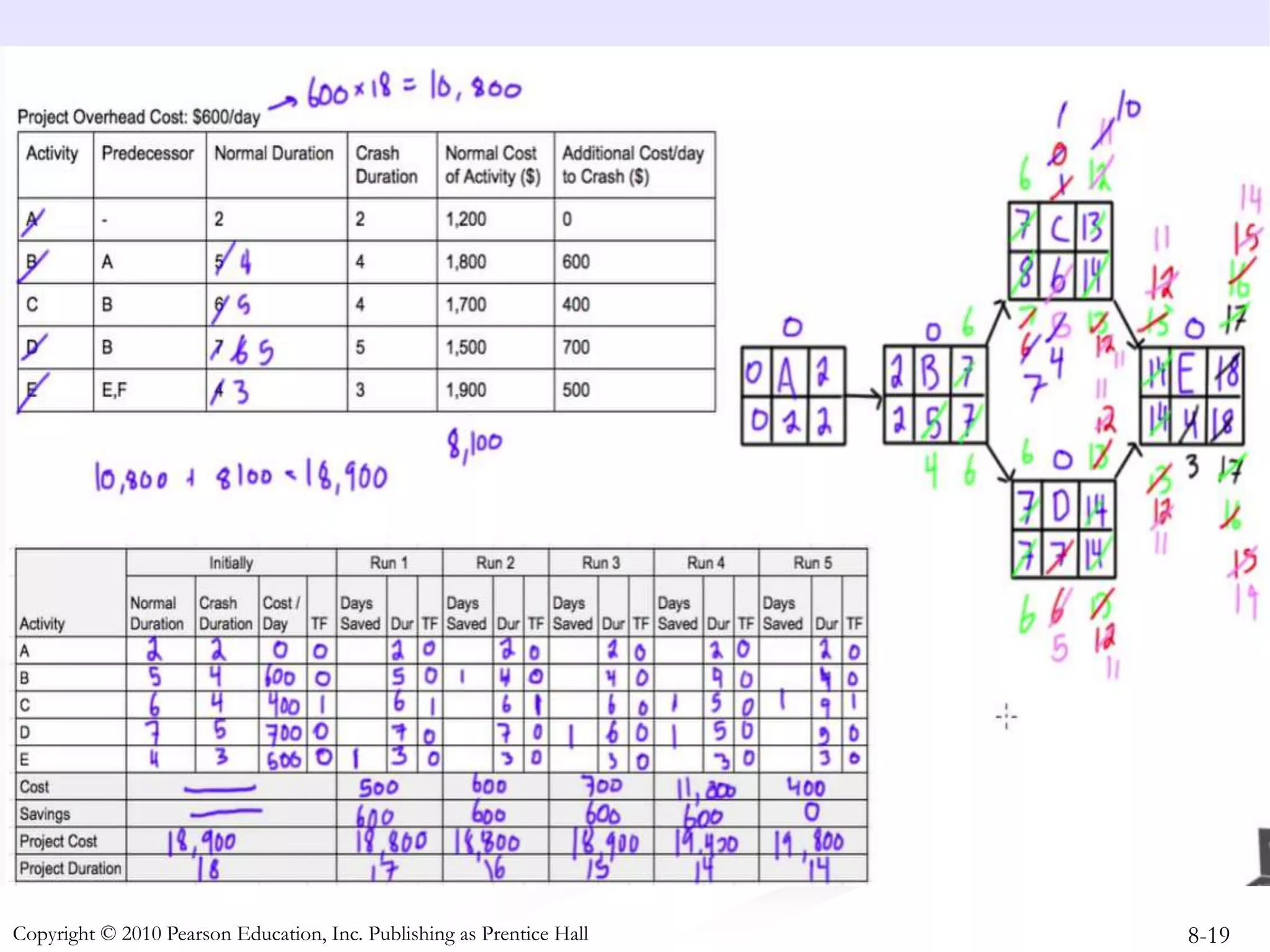
This document discusses project crashing techniques to reduce a project's completion time. It begins by introducing the concept of project crashing by allocating more resources to critical activities. An example is then provided to illustrate how crashing can shorten the critical path duration. However, crashing has a trade-off of increasing costs. The relationship between time and cost is examined, showing that crashing incurs a linear increase in expense as completion time decreases. Methods for determining the optimal balance of time versus cost when crashing a project are explored.