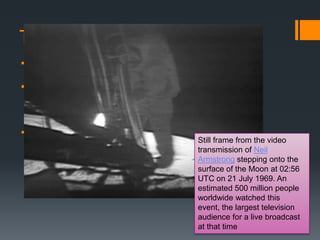
Canada promoted world peace in several ways during the Cold War era:
1) Canadians developed peaceful nuclear technology and nuclear reactors to provide energy while limiting nuclear proliferation. Atomic Energy of Canada Ltd was established to regulate nuclear research.
2) Canada successfully launched scientific satellites like Alouette 1, advancing space research without engaging in the military space race between the US and USSR.
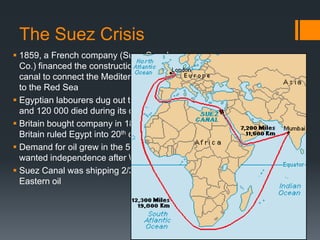
3) During the 1956 Suez Crisis, Canadian minister Lester B. Pearson helped resolve the conflict through persuasive diplomacy and the establishment of the first UN peacekeeping force, winning him the Nobel Peace Prize.