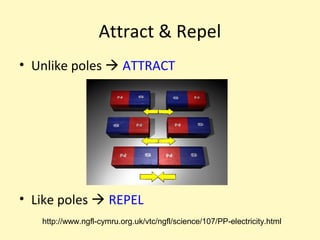
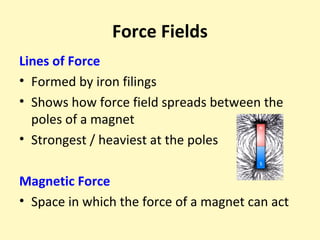
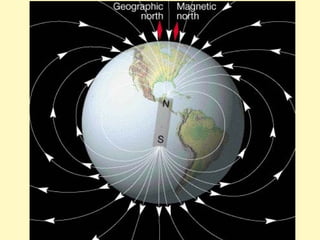
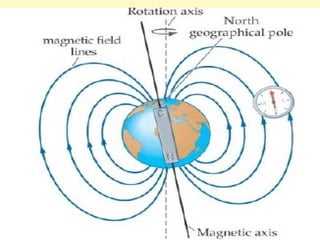
This document provides information about the properties and behavior of magnets. It explains that magnets attract certain metals like iron and steel, and that their force is strongest at their poles. It also describes how opposite poles attract each other while like poles repel. The document notes that magnetism causes the northern lights and allows compasses to work by aligning with Earth's magnetic field.