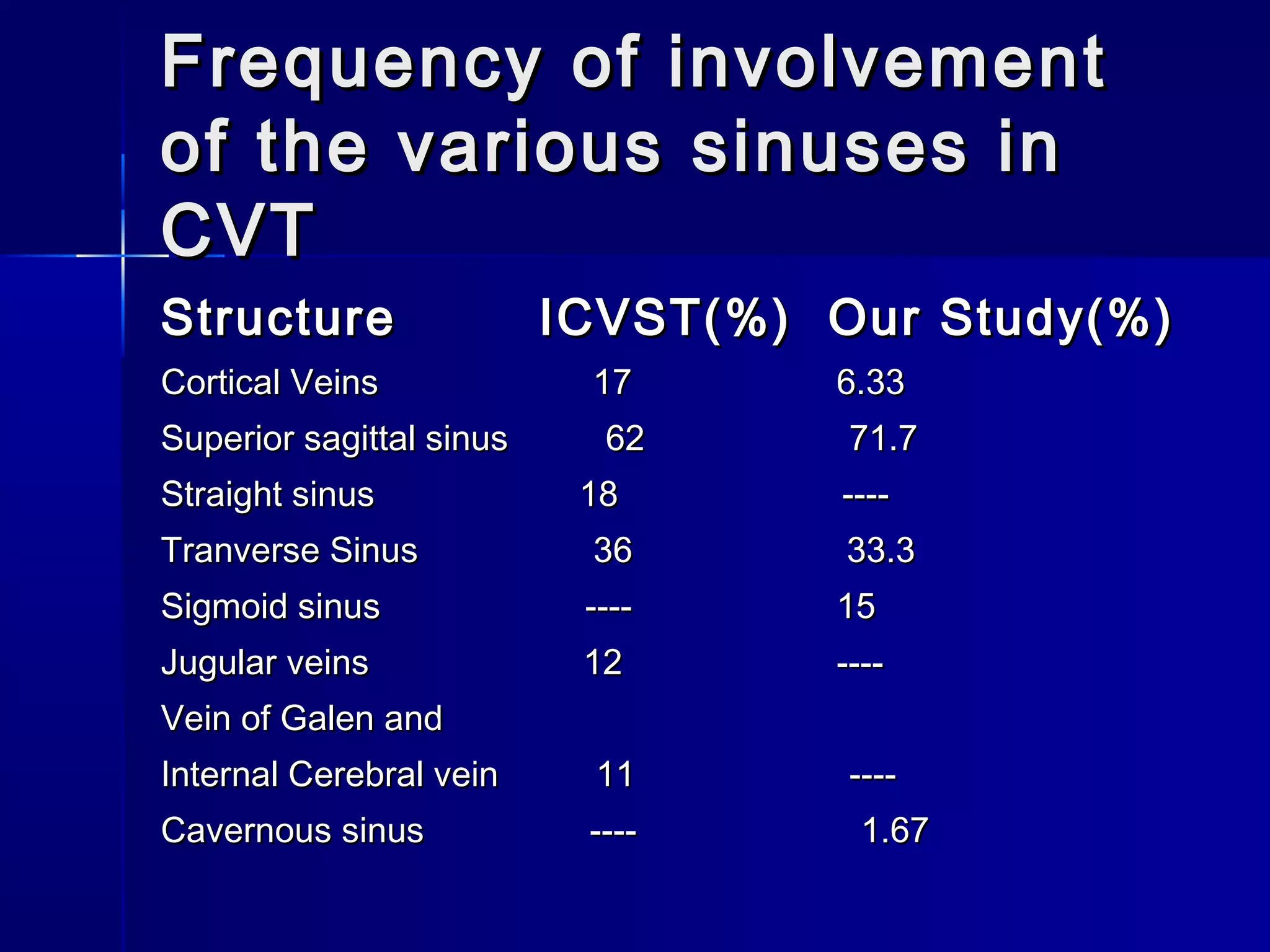
This document discusses cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), including its history, major venous drainage pathways of the cranium, aetiology, neurological features, frequency of sinus involvement, and investigations. It provides details on the dural sinuses, superficial and deep cerebral veins, dural veins, scalp veins, and cervical veins that drain the brain. Common causes of CVT include oral contraceptives, pregnancy, hematological/immunological abnormalities, infections, and malignancy. Headache and focal neurological deficits are frequent symptoms, while impaired consciousness and seizures also occur. Imaging studies like CT, MRI, and angiography along with lumbar puncture are used to diagnose CVT.