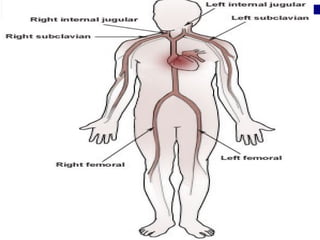
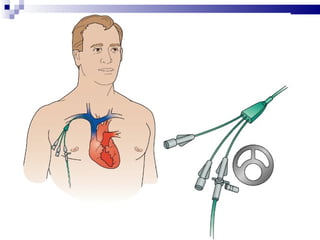
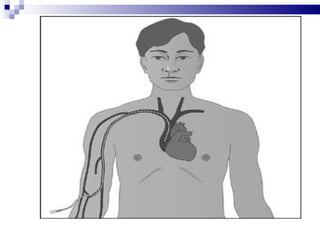
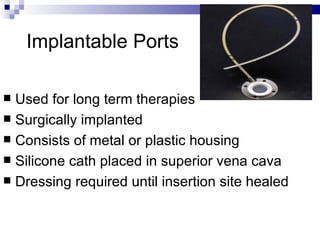
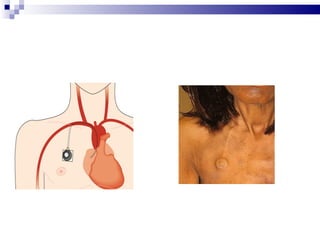
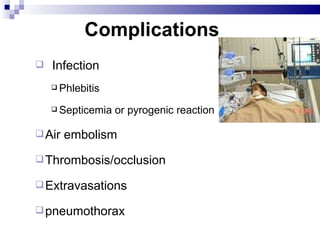
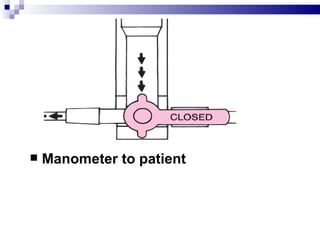
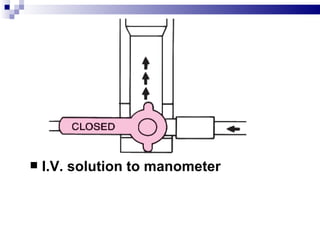
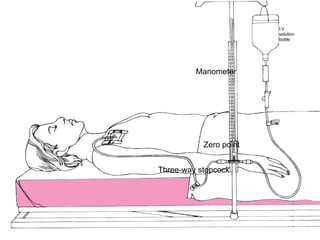
Central venous pressure (CVP) describes the blood pressure in the thoracic vena cava near the right atrium. Normal CVP ranges from 0-15 cm H2O depending on measurement point. CVP is affected by factors like volume status, respiration, and heart function. Central venous catheters are used to monitor CVP and administer IV medications and fluids long-term. Types include non-tunneled short term catheters and tunneled or implanted ports for longer term use. Nurses must properly insert, maintain, and discontinue central lines to prevent complications and ensure accurate CVP readings.