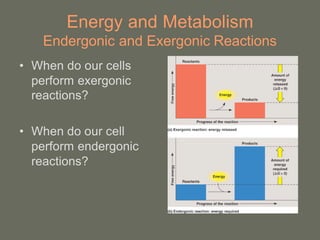
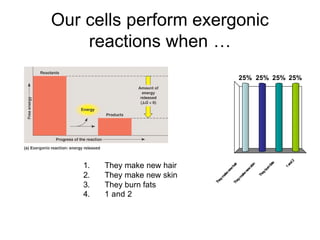
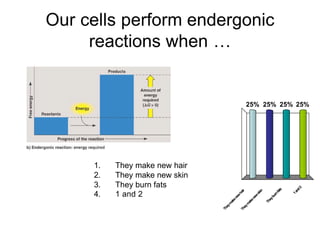
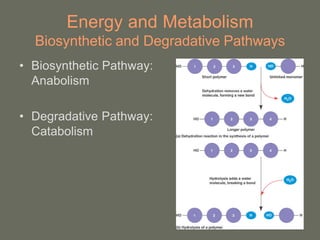
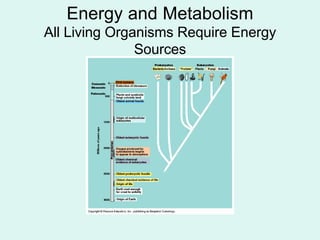
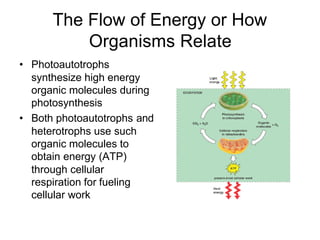
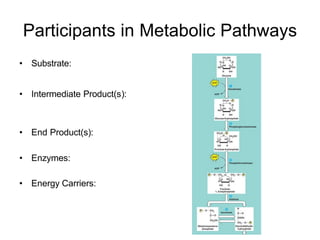
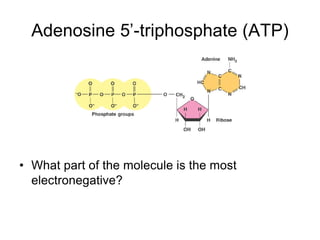
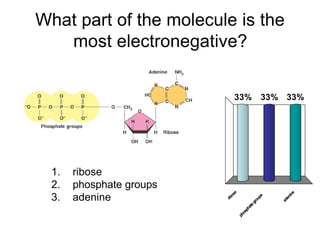
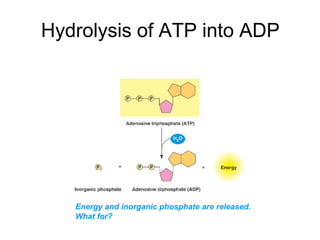
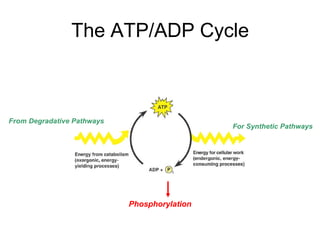
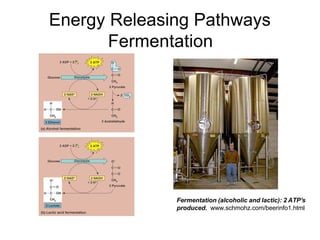
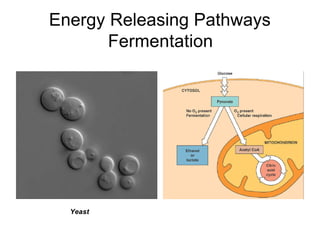
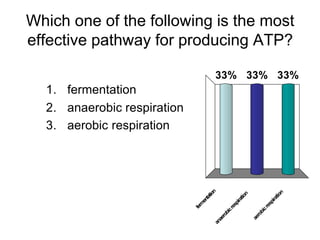
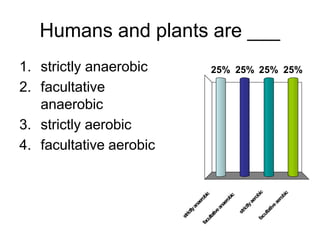
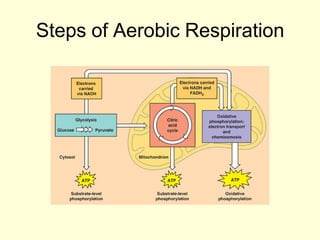
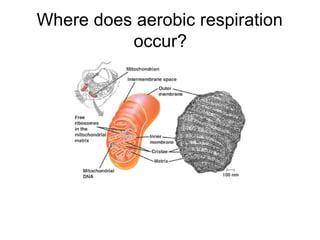
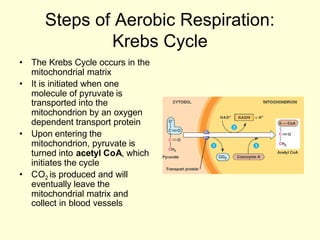
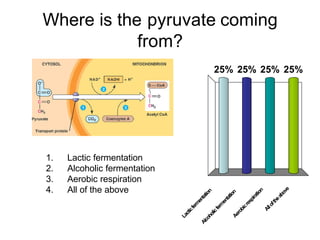
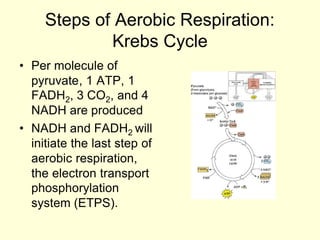
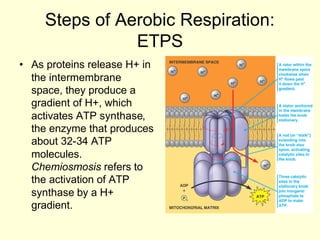
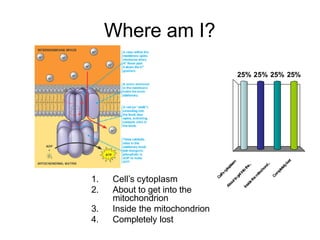
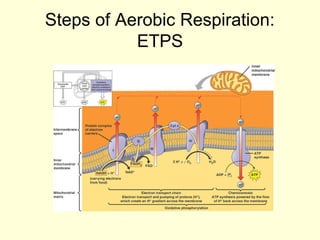
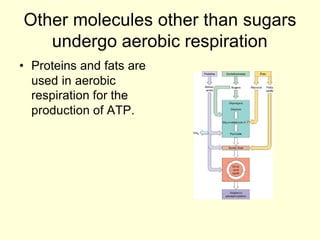
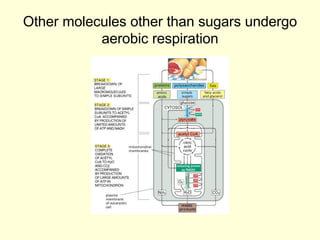
Cells perform exergonic reactions like aerobic respiration to obtain energy in the form of ATP, which powers endergonic processes like biosynthesis. During aerobic respiration, glucose and other molecules like fats are broken down through glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain to generate large amounts of ATP via chemiosmosis. Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria and produces approximately 36 ATP per glucose molecule.