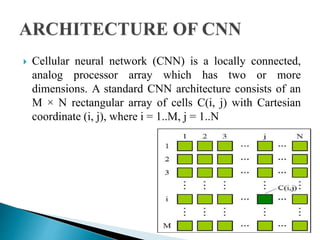
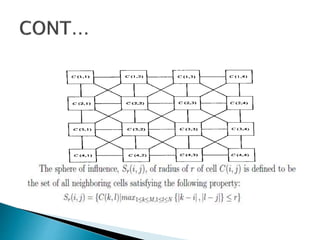
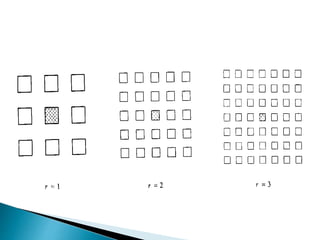
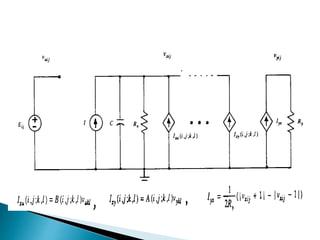
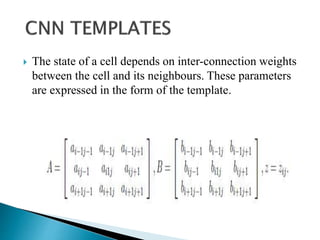
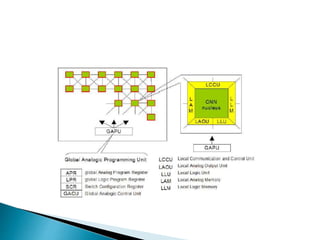
Cellular Neural Networks (CNNs) are a revolutionary computing paradigm that allows for analog parallel processing similar to neural networks but where each processing unit only communicates with its nearest neighbors. CNNs consist of arrays of identical nonlinear dynamic units arranged in a grid where each unit receives input from neighboring units. The CNN Universal Machine (CNN-UM) was the first programmable analog processor array computer with its own language and operating system that was as powerful as a supercomputer for image processing applications. CNNs show promise for applications such as high-speed target recognition, visual inspection, and the development of artificial senses through cheap sensor arrays.