Recommended
PPTX
PPTX
Cell as basic unit of life ppt 88 slides
PDF
cellandcelltheory-190324140633.pdf
PPT
Cells: Cell Theory and Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells.ppt
PPTX
PPT
Basic information and characteristics of cells
PPTX
PPT
3524734.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.ppt
PPT
cell theory.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.ppt
PPTX
cell biology class__ introduction to cell biology and histroy.pptx
PPT
Cell theory power point 2
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
CLASS IX THE CELL.pptx for exam preparation.
PPTX
CLASS IX "THE CELL" pptx. Topper notes.
PPTX
prokaryotes and eukaryotes.pptx
PPTX
prokaryotes and eukaryotes.pptx
PPT
PPTX
Cells and cell theory Biology For Engineers
PPT
prokaryote_vs_eukaryote-DEMOjvuv bl hc.ppt
PPT
Prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
PDF
Cell-Theory-lesson 1,13,-14, (1).ppt.xxx
PDF
Lecture 1 Introduction to Cell Structure and Composition.pdf
PPT
PPT
PPT
chapter07_section01_edit.ppt
PPT
PPTX
PDF
p - Block Handwritten Notes PDF Download - Irfanullah Mehar - World of Wisdom...
PDF
이영욱 교수님의 물리학회 발표자료 전채_20251120.pdf
More Related Content
PPTX
PPTX
Cell as basic unit of life ppt 88 slides
PDF
cellandcelltheory-190324140633.pdf
PPT
Cells: Cell Theory and Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells.ppt
PPTX
PPT
Basic information and characteristics of cells
PPTX
PPT
3524734.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.ppt
Similar to Cell and cells types: Differente types of cells
PPT
cell theory.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.pptcell theory.ppt
PPTX
cell biology class__ introduction to cell biology and histroy.pptx
PPT
Cell theory power point 2
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
CLASS IX THE CELL.pptx for exam preparation.
PPTX
CLASS IX "THE CELL" pptx. Topper notes.
PPTX
prokaryotes and eukaryotes.pptx
PPTX
prokaryotes and eukaryotes.pptx
PPT
PPTX
Cells and cell theory Biology For Engineers
PPT
prokaryote_vs_eukaryote-DEMOjvuv bl hc.ppt
PPT
Prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
PDF
Cell-Theory-lesson 1,13,-14, (1).ppt.xxx
PDF
Lecture 1 Introduction to Cell Structure and Composition.pdf
PPT
PPT
PPT
chapter07_section01_edit.ppt
PPT
PPTX
Recently uploaded
PDF
p - Block Handwritten Notes PDF Download - Irfanullah Mehar - World of Wisdom...
PDF
이영욱 교수님의 물리학회 발표자료 전채_20251120.pdf
PPTX
Cell Transport Powerpoint.pptx for high school students
PDF
Rapid diagnosis and contamination of seafood and aquaculture products
PPT
ch7_Acids&Bases.ppt. acid and bases , reactions of acids and bases, equilibri...
PDF
Synthetic Biology - Future and Alpplication
PDF
Bioinorganic Chemistry - PDF Notes Hindi Medium - Irfanullah Mehar - JJ Sir C...
PPTX
Chapter I Hematologic Disorders Pharmacotherapy (1).pptx
PDF
s - Block Handwritten Notes PDF - Irfanullah Mehar - JJ Sir Chemistry - World...
PPTX
SCIENCE 9 Q4 Module2 MOMENTUM AND IMPULSE
PPTX
HUBUNGAN EKOLOGI DENGAN KONSERVASI .pptx
PPTX
Cell cycle ( mitosis and meiosis)Msc.pptx
PPTX
FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR fracture with treatment
PDF
Detection of an NH3 Absorption Band at 2.2μm on Europa
PPTX
Mass selection is one of the oldest methods of plant breeding Commonly use_20...
PPTX
Presentation - Why Earth is the only living planet
PPTX
VIRULENCE FACTOR OF BACTERIA: STRUCTURAL ELEMENT, ENZYMES, TOXINS...
PPTX
Gene Editing_ Rewriting the Code of Life.pptx
PDF
Factors affecting Plant Health – Edaphic factors and Biotic Factors
PDF
Control and Coordination - Short Notes (Prashant Kirad) (1).pdf
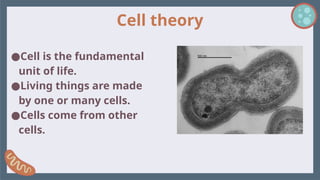
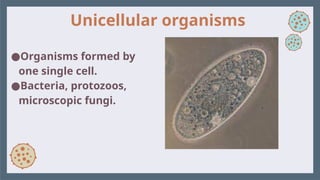
Cell and cells types: Differente types of cells 1. 2. Cell theory
●Cell is the fundamental
unit of life.
●Living things are made
by one or many cells.
●Cells come from other
cells.
9. ●Cells can specialize and
organize to form complex
organisms.
●Cell -> Tissue -> Organs ->
Systems -> Organisms.
Pluricellular organisms
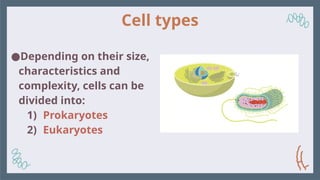
11. 12. Cell types
●Depending on their size,
characteristics and
complexity, cells can be
divided into:
1) Prokaryotes
2) Eukaryotes
13. Prokaryotes
●Exist since 3,500 million
years ago.
●Only living organisms
during 2,000 million
years.
●THEY DON’T HAVE
NUCLEUS!!!
●THEY DON´T HAVE
ORGANELLES!!!
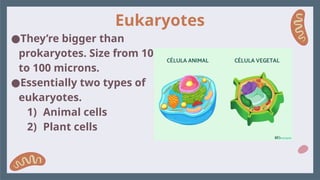
14. Eukaryotes
●Exist since 1,500 million
years ago.
●THEY HAVE NUCLEUS!!!
●THEY HAVE
ORGANELLES!!!
●They’re bigger than
prokaryotes. Size from 10
to 100 microns.
15. 16. Where do eukaryotes come from?
●Eukaryotes are
symbiotes!!!
●Increasing oxygen on
ancient Earth’s
atmosphere forced
organisms to cooperate.
●Eukaryotes formed by
endosymbiosis
●Mitochondria and
chloroplasts.