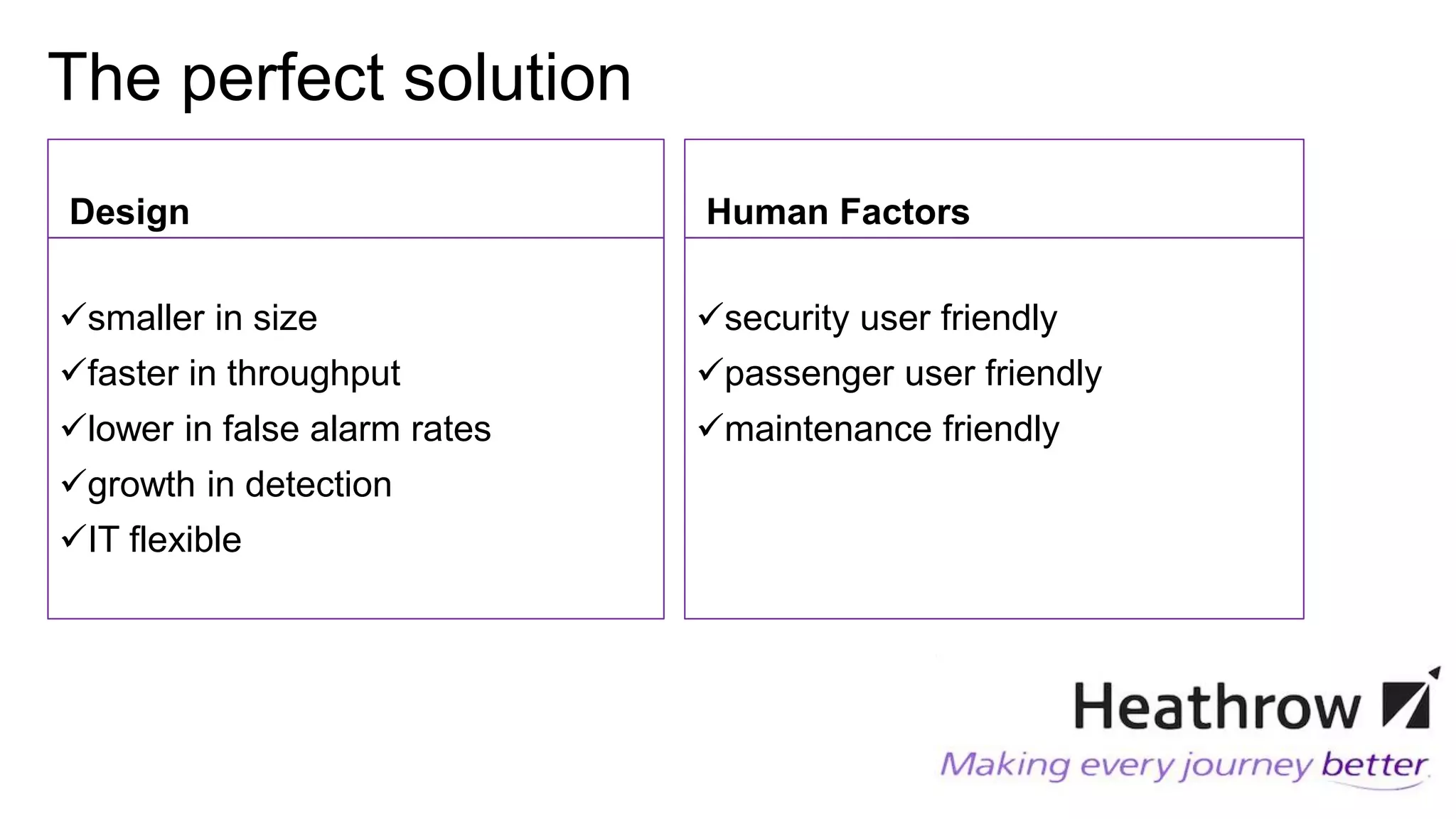
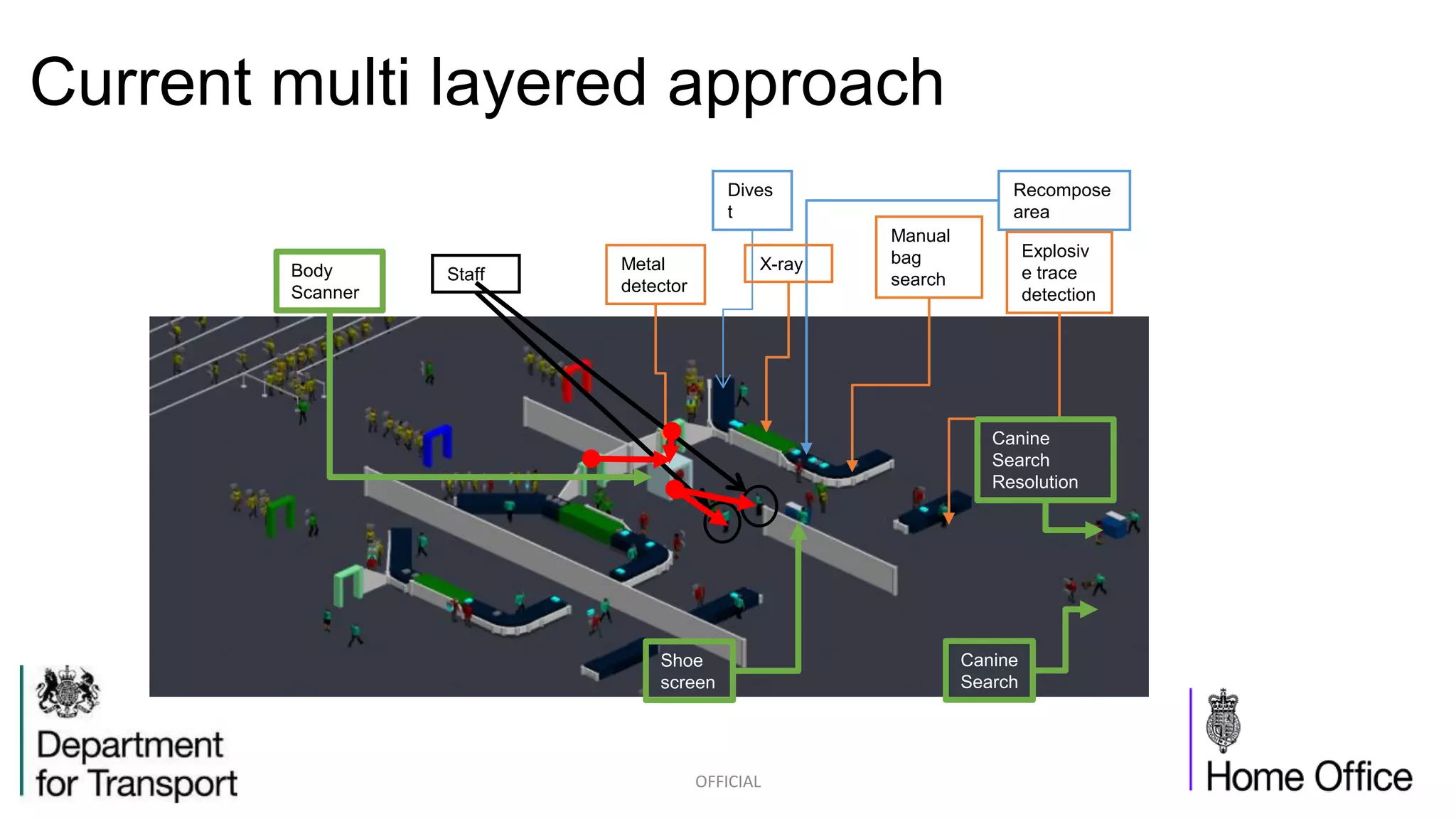
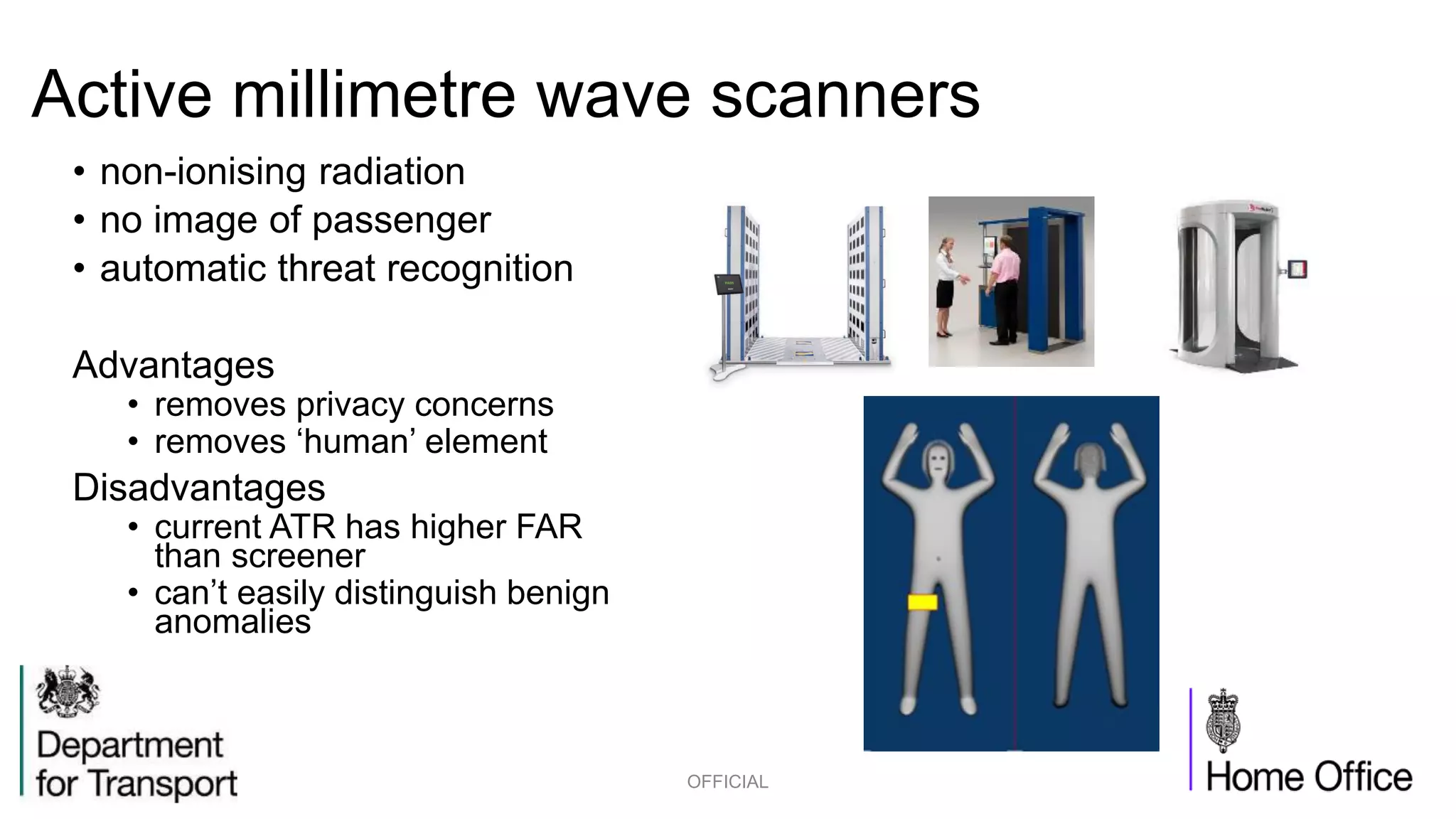
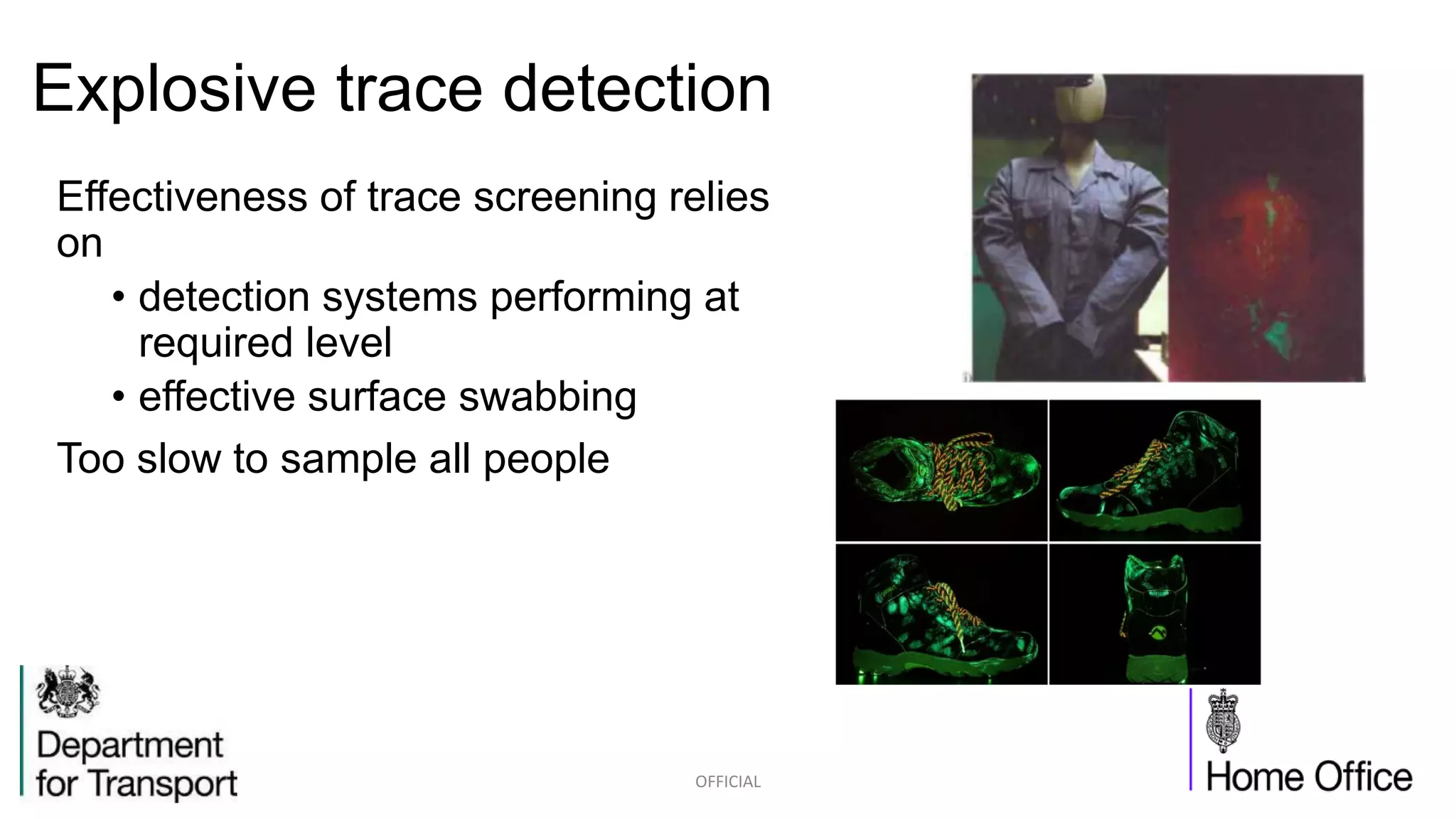
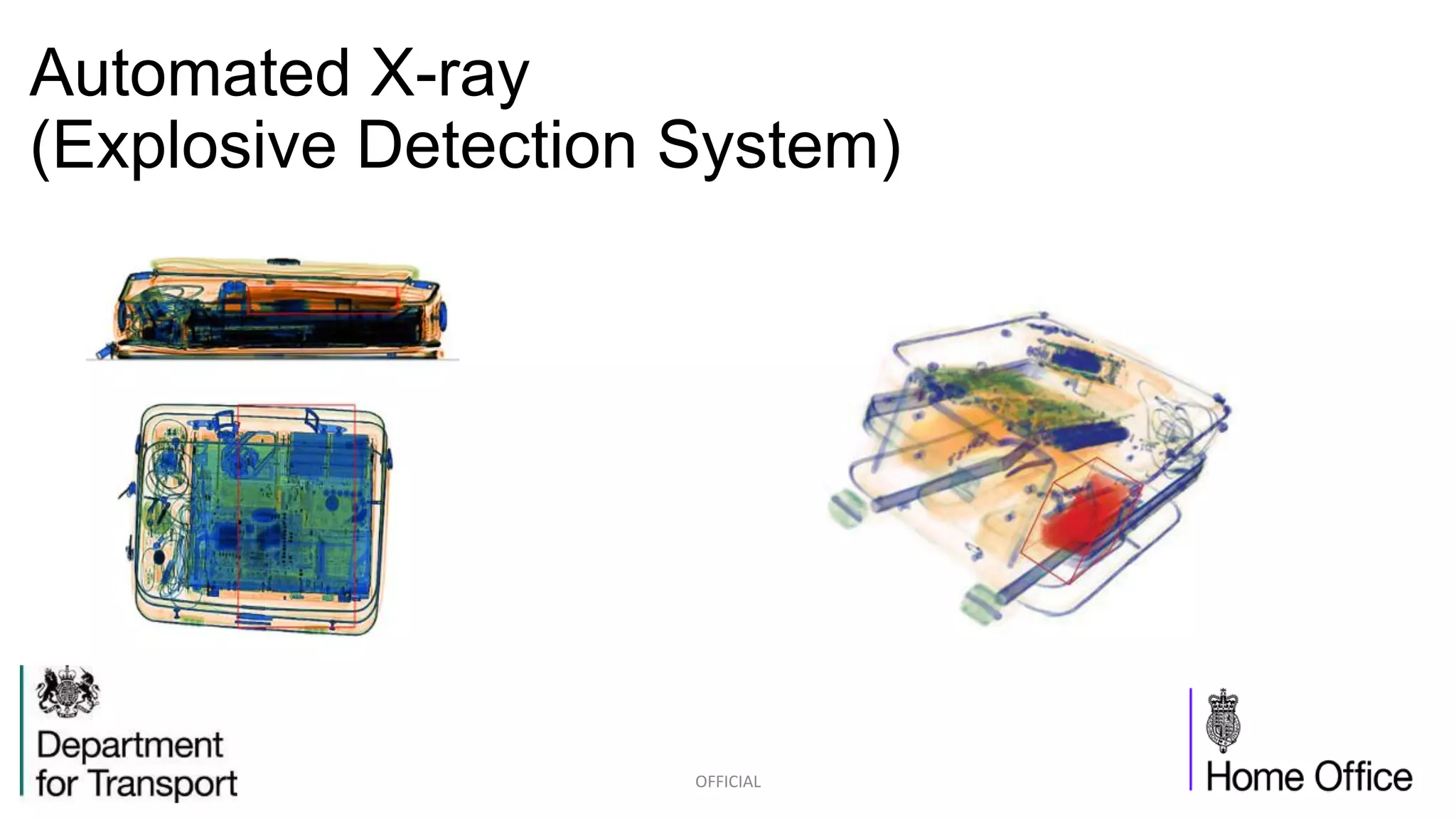
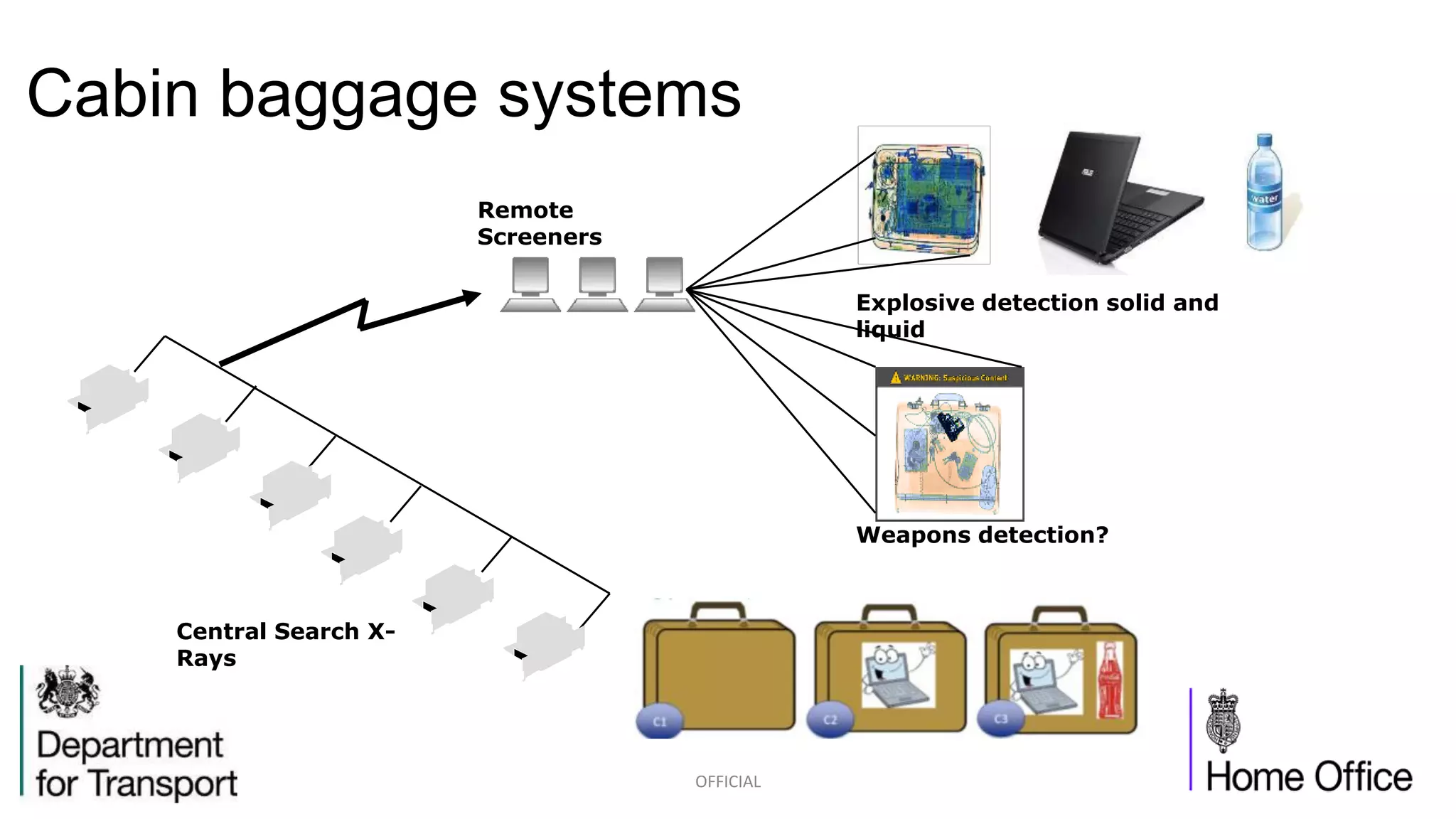
The competition briefing outlines the challenges and requirements for enhancing airport security focusing on screening passengers, hand baggage, and hold baggage amid increasing threats. Key objectives include developing smaller, faster, and more effective detection technologies that are user-friendly for both passengers and screeners, while reducing false alarm rates. Various technology challenges and detection methods such as explosive trace detection, canine searches, and automated systems are discussed to improve security efficiency and passenger experience.