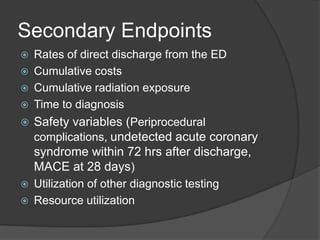
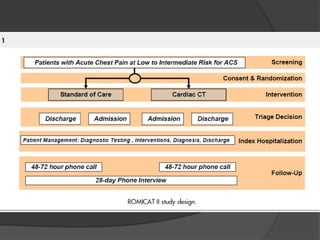
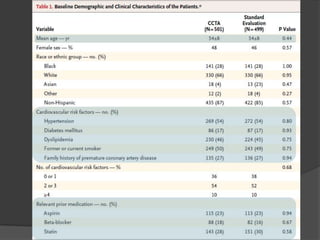
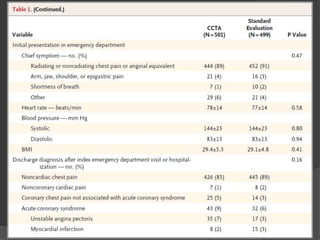
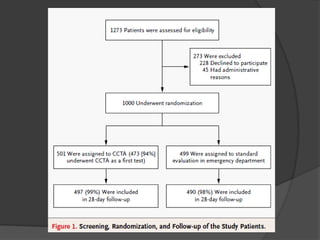
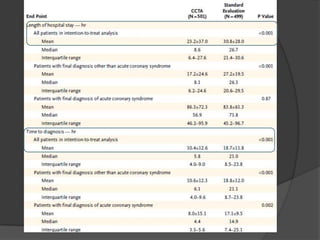
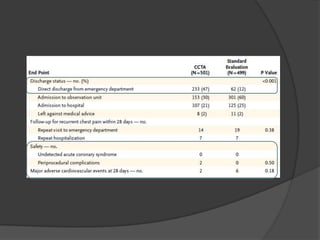
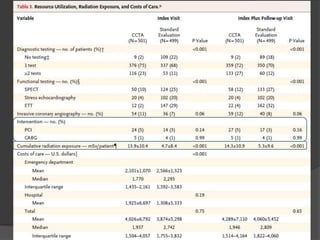
This study aims to evaluate whether an evaluation strategy incorporating early cardiac CT angiography (CCTA) improves clinical decision making compared to standard evaluation for patients presenting to the emergency department with acute chest pain suggestive of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) but without diagnostic ECG changes or positive troponin. The study is a randomized controlled trial that assigns eligible patients aged 40-74 years to either the CCTA or standard evaluation groups. The primary outcome is length of hospital stay, with secondary outcomes including rates of direct emergency department discharge, costs, radiation exposure, time to diagnosis, and safety/adverse events.