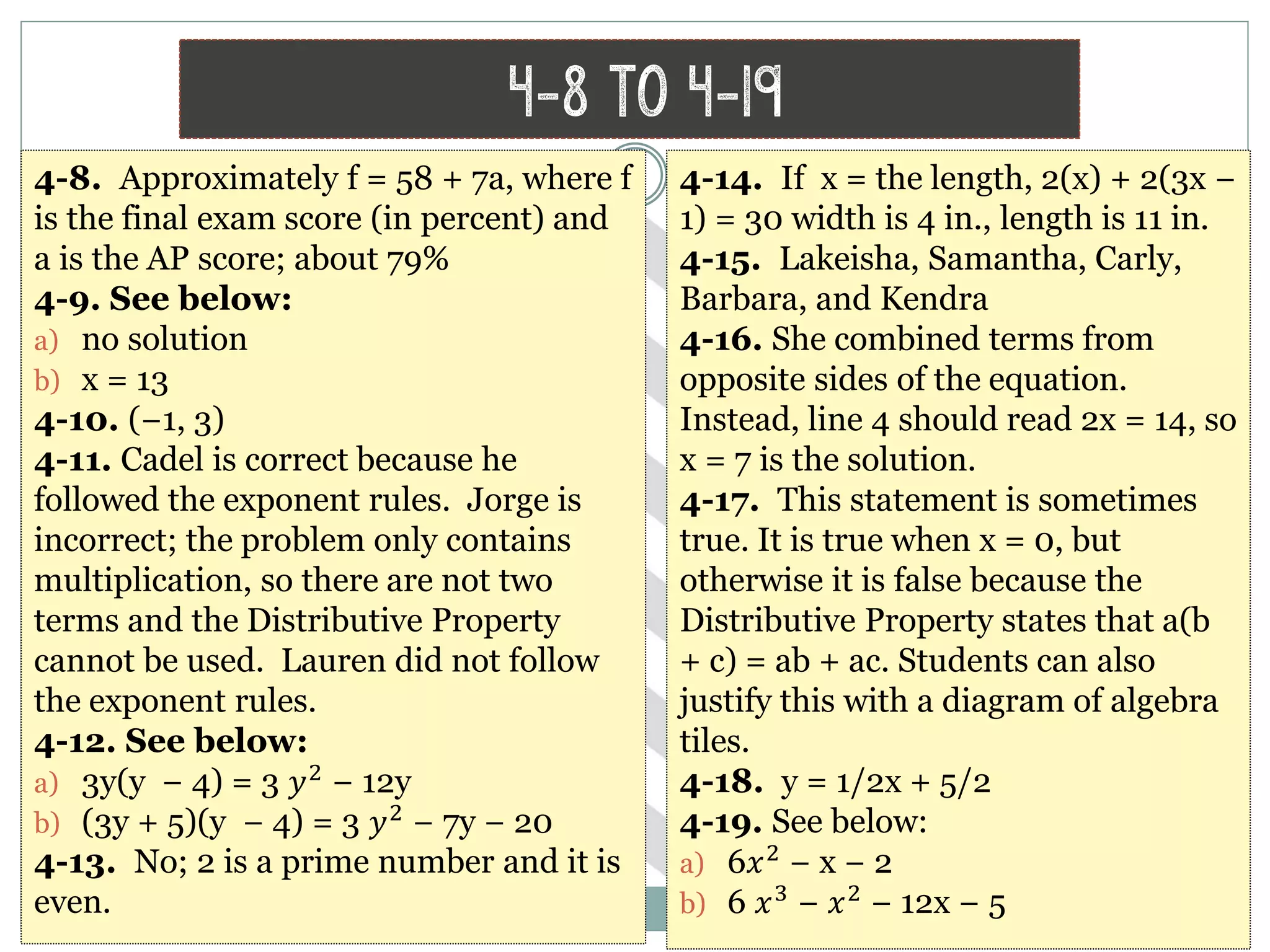
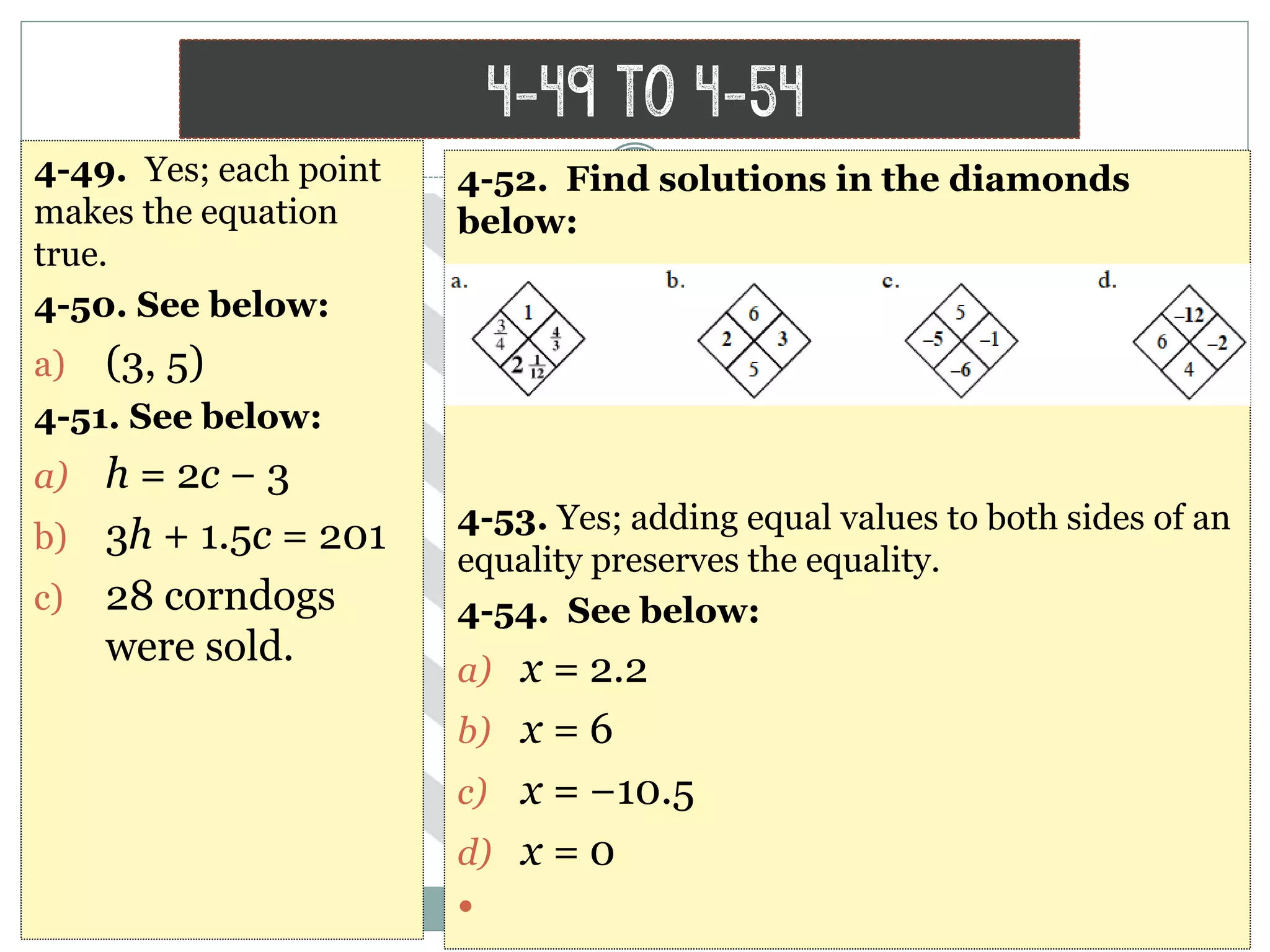
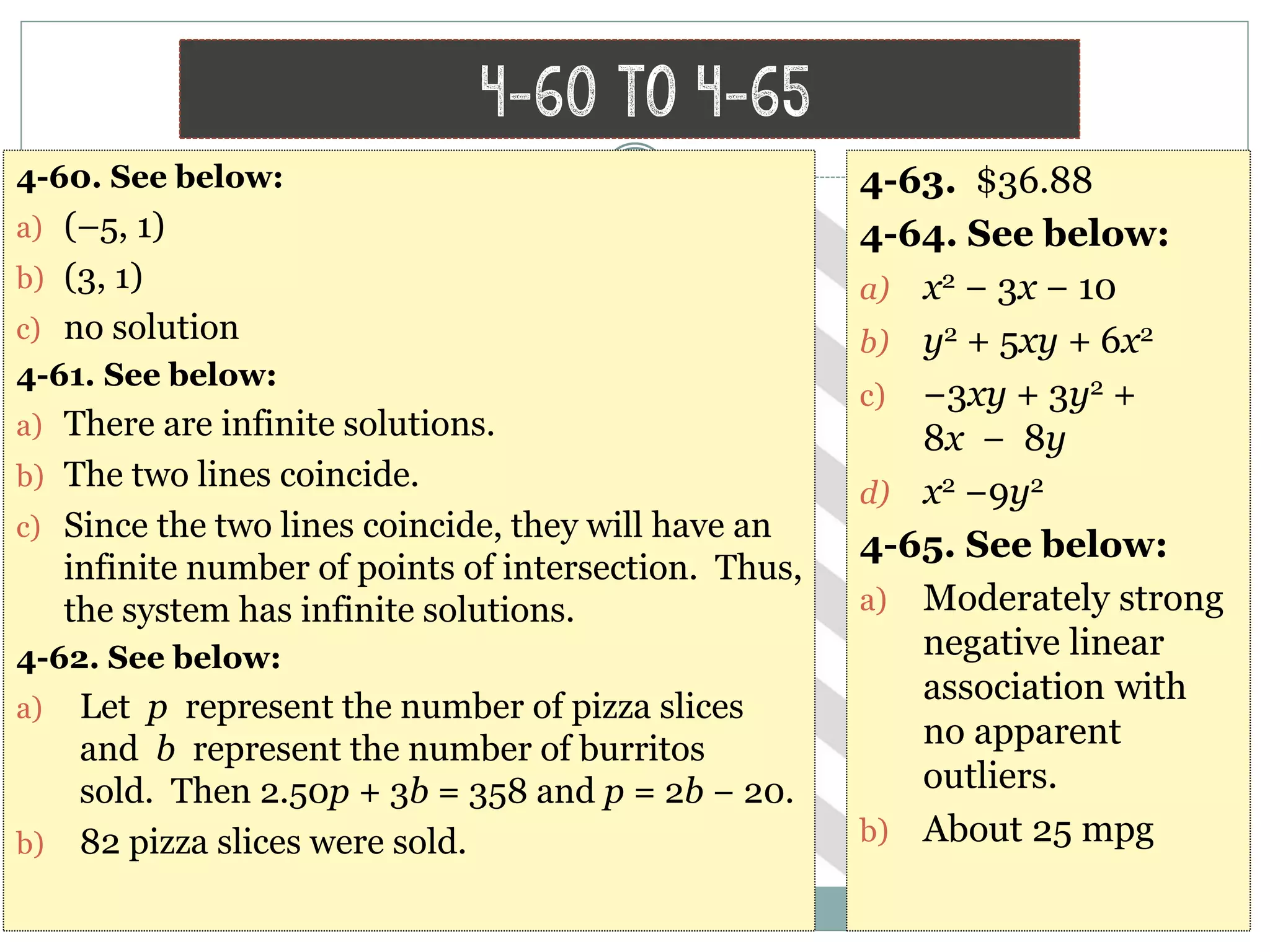
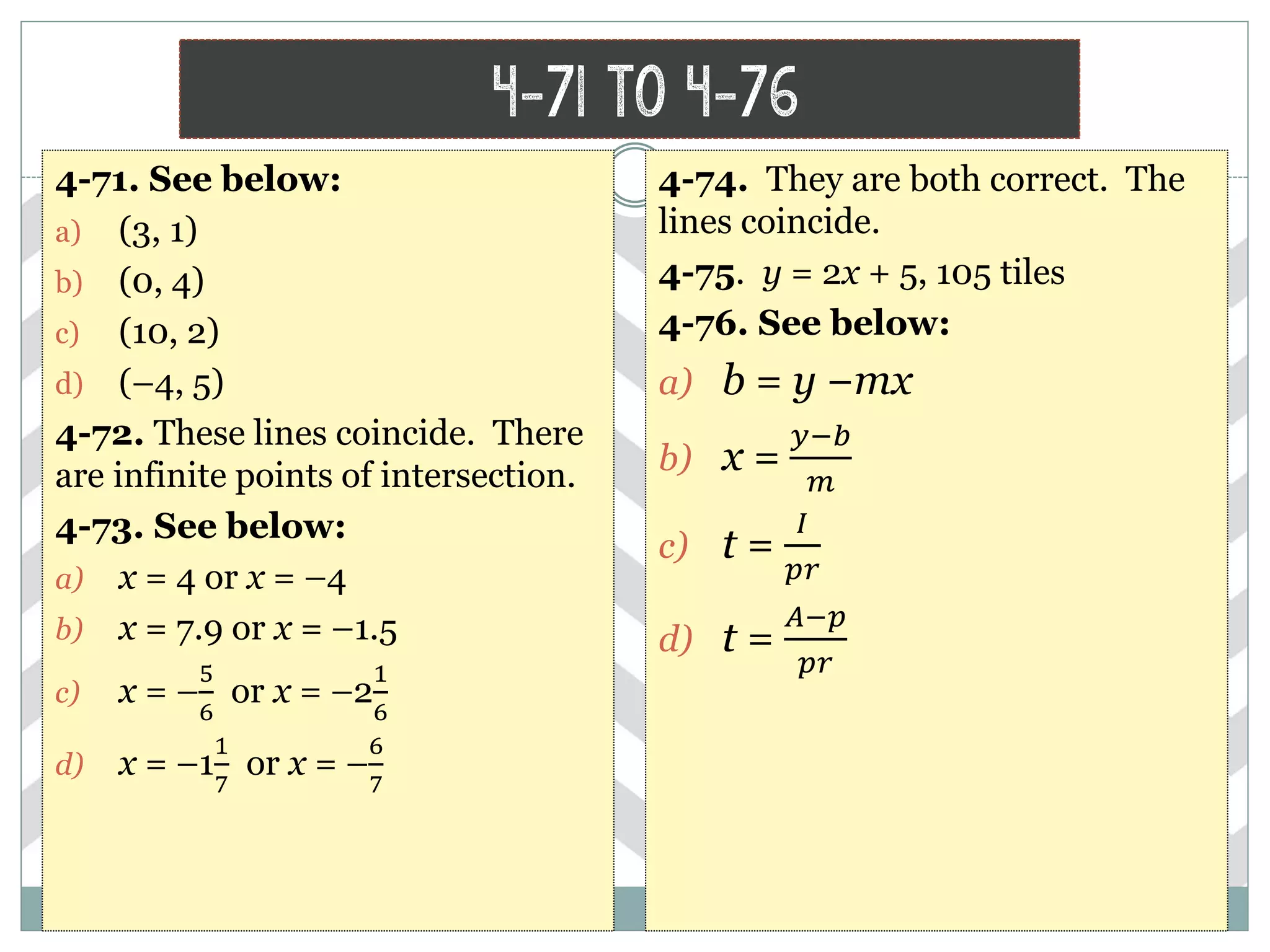
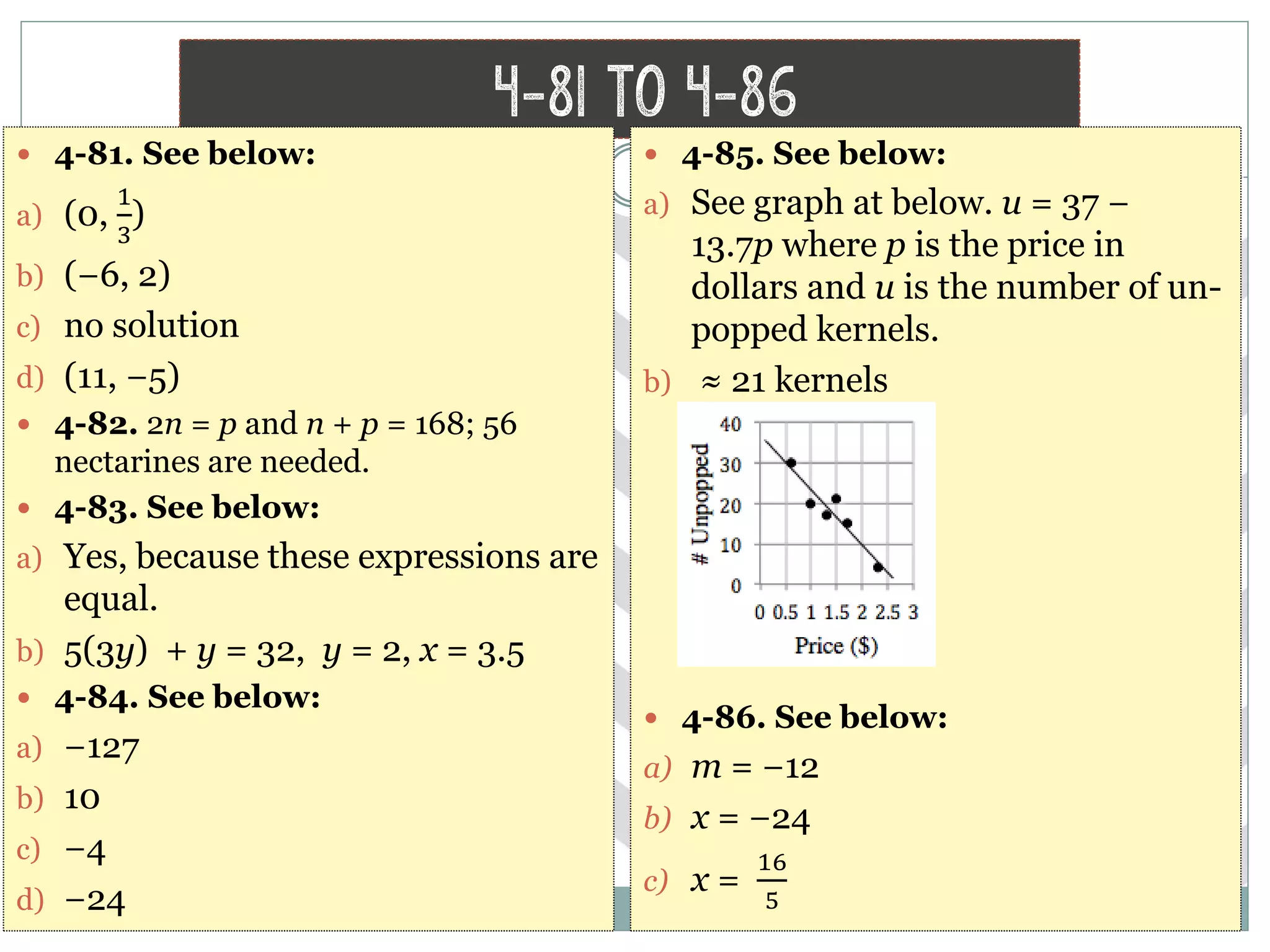
This document contains math problems and solutions from a high school algebra 1 textbook. It covers topics like systems of equations, functions, exponents, distributions, graphs, and word problems. The problems are presented along with the step-by-step work or solutions. Key concepts covered include solving linear equations, evaluating expressions, identifying functions, graphing lines, and applying algebraic rules and properties.