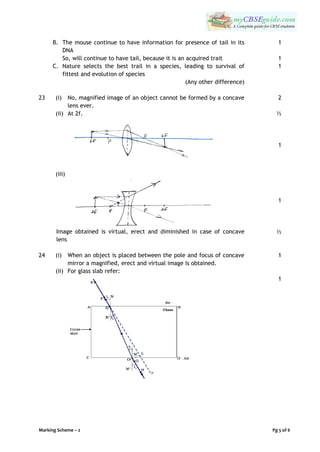
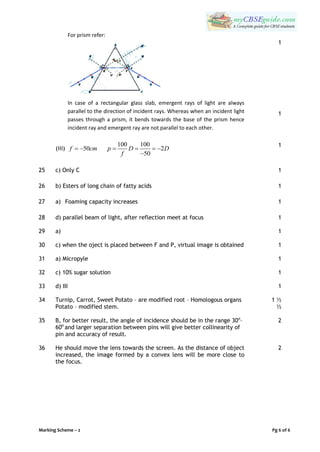
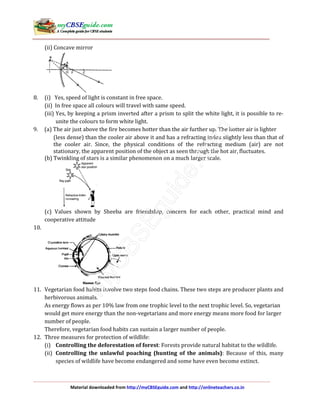
The document provides the instructions and questions for a sample science exam for Class 10. It has two sections - Section A with multiple choice, short answer, and long answer questions and Section B focusing on practical skills. The instructions specify the number of marks, word limits, and expected answer types for each question. Various science topics are covered, including biology, chemistry, and physics concepts.