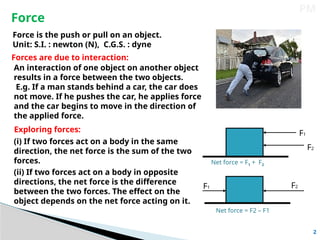
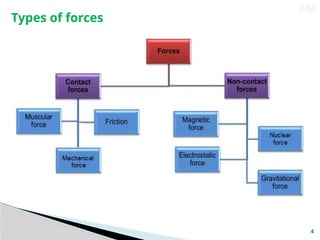
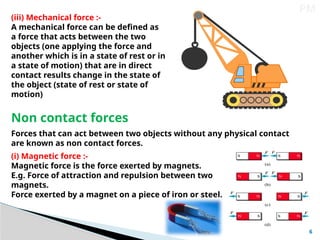
El documento explica que la fuerza es un empuje o tirón aplicado a un objeto, y se mide en newtons. Se clasifica en fuerzas de contacto, como la fuerza muscular y la fricción, y fuerzas no de contacto, como la magnética y la gravitacional. También se aborda el concepto de presión como la fuerza por unidad de área, destacando cómo varía en líquidos y gases, así como la presión atmosférica en la superficie terrestre.