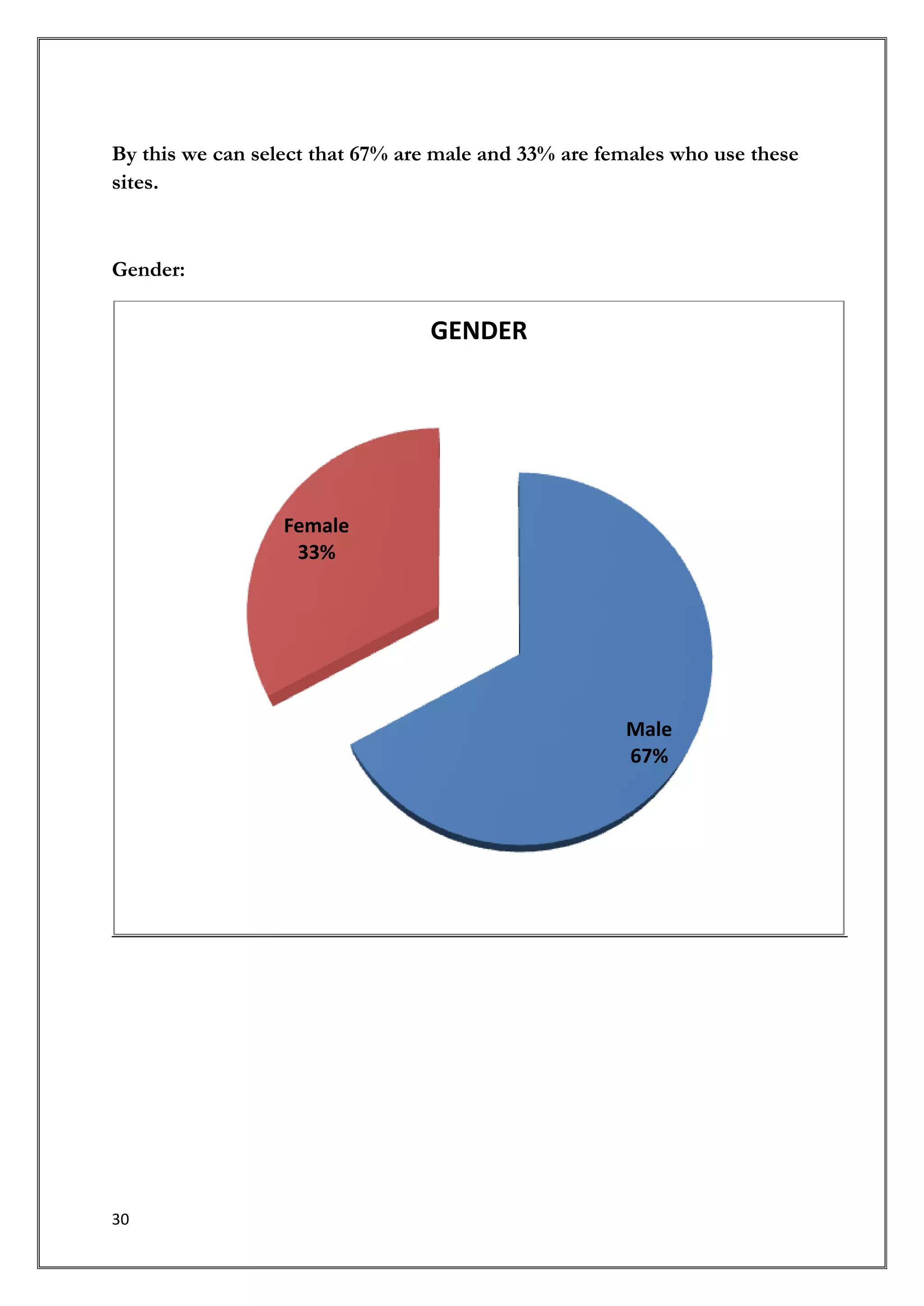
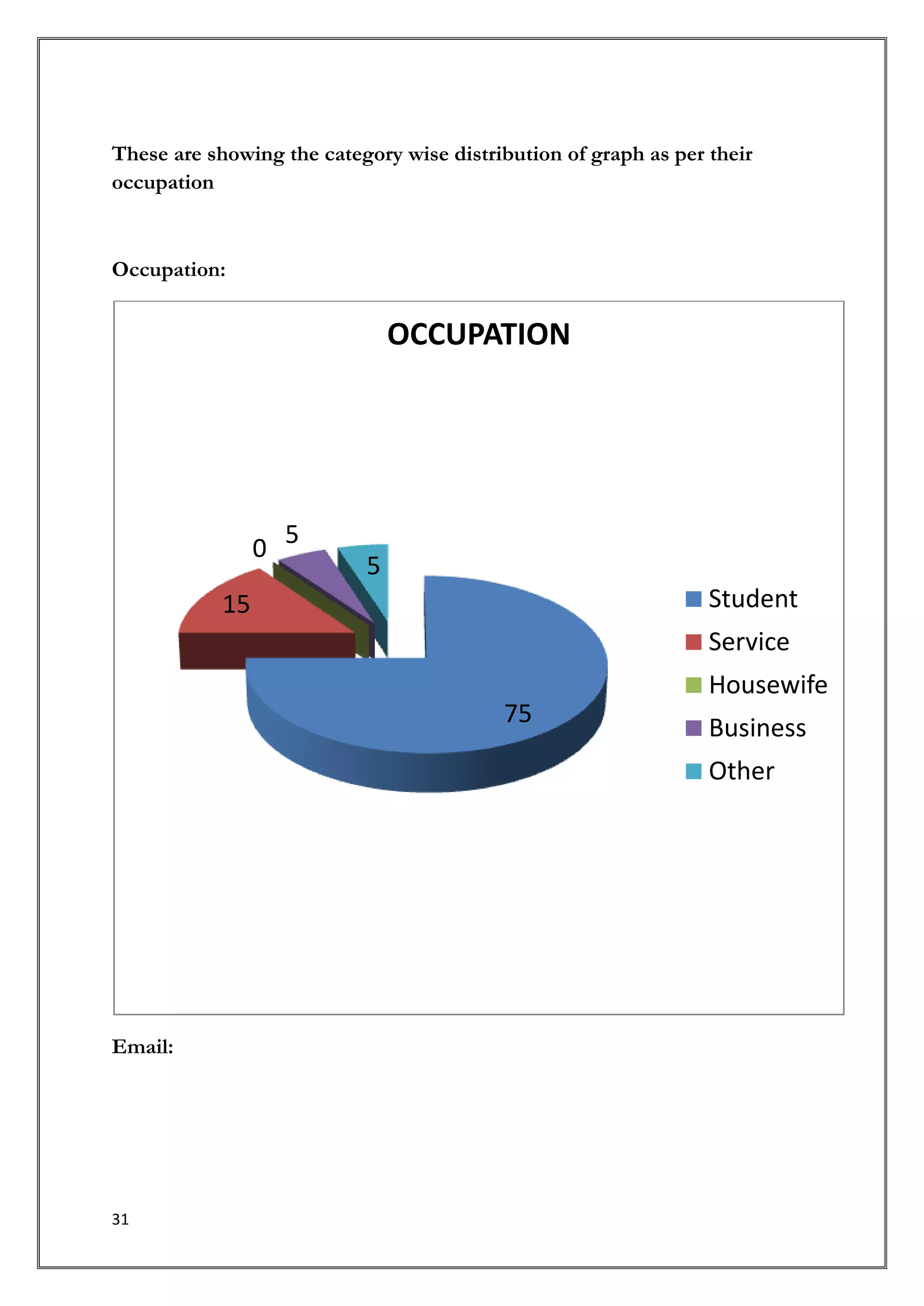
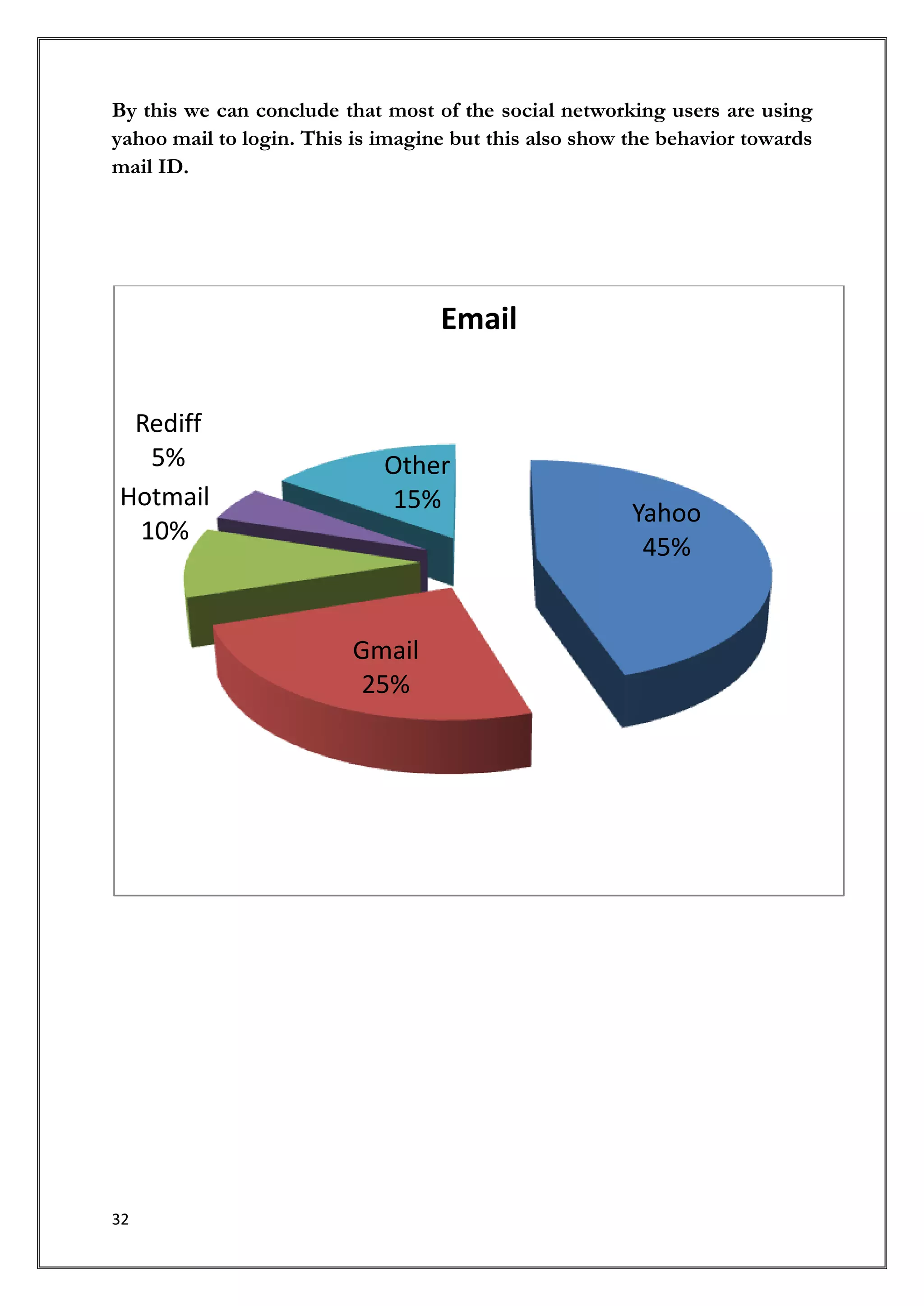
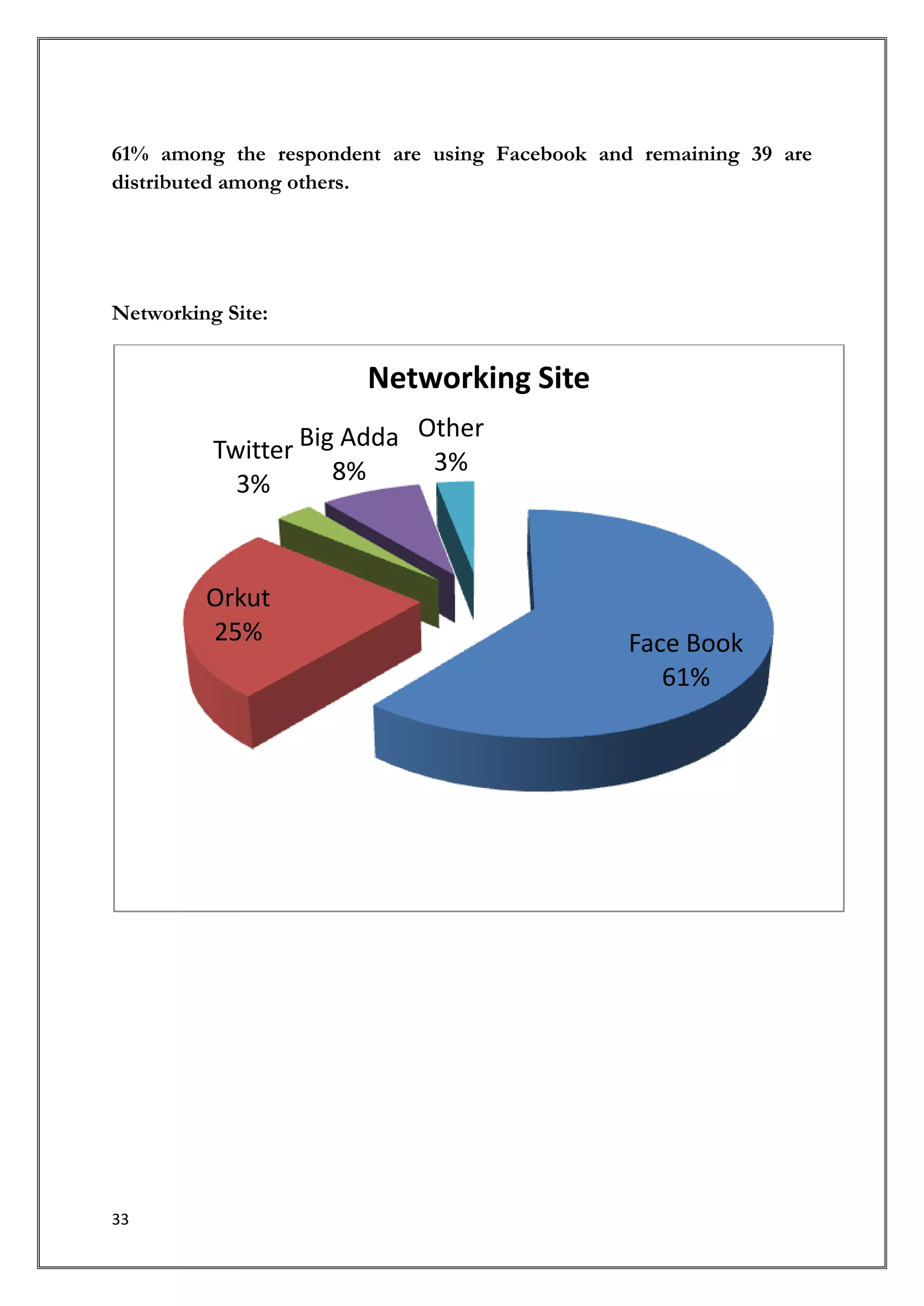
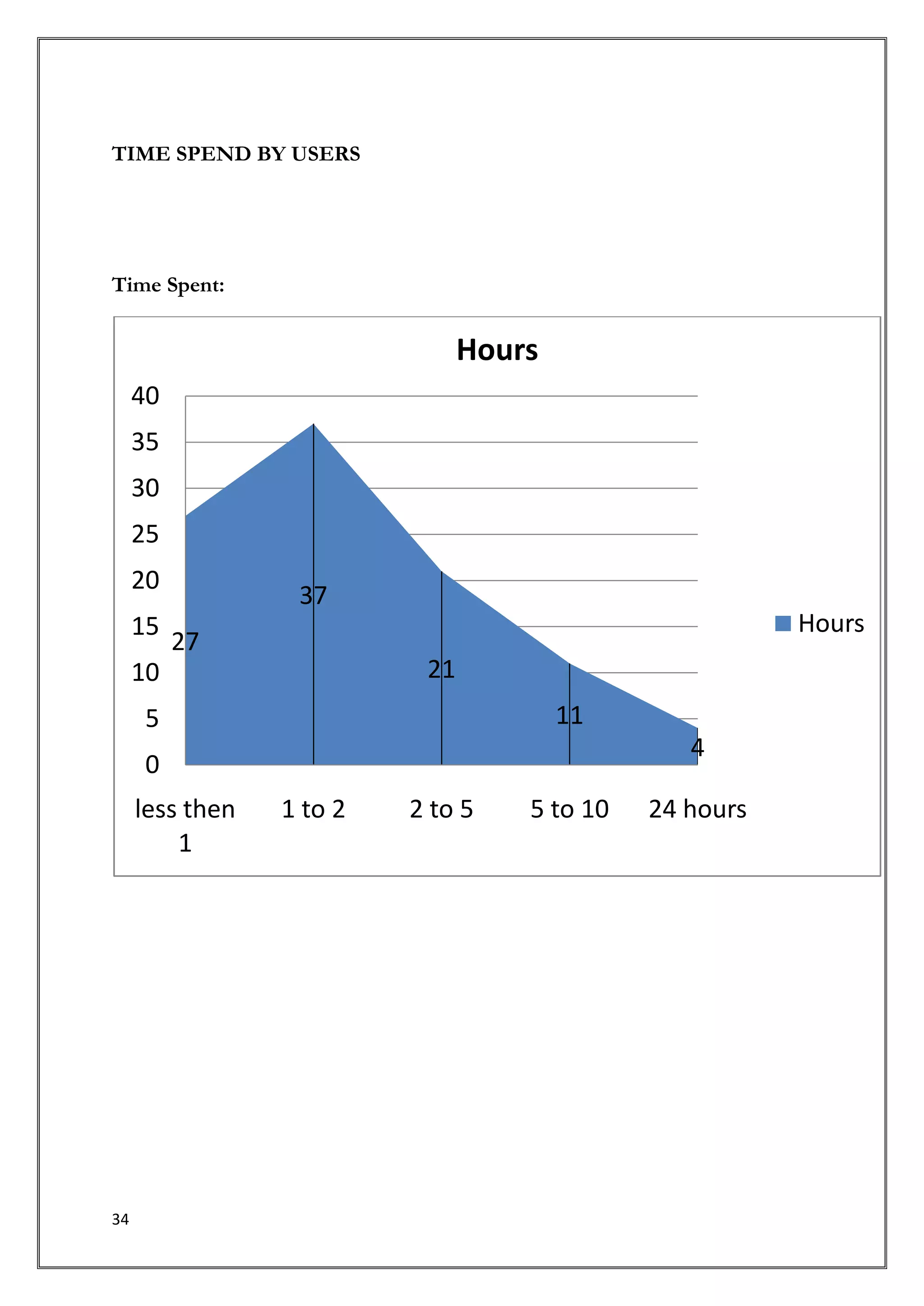
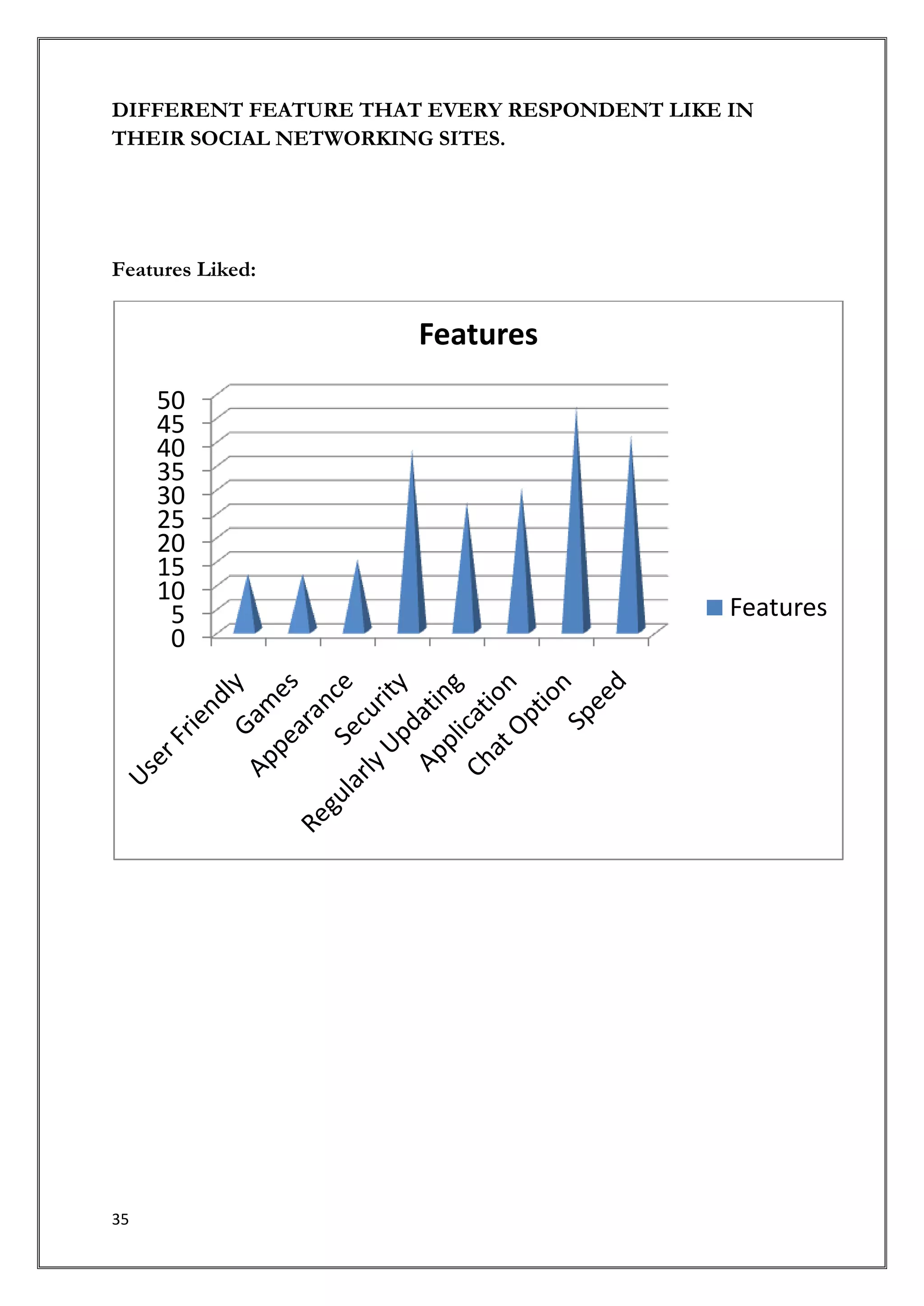
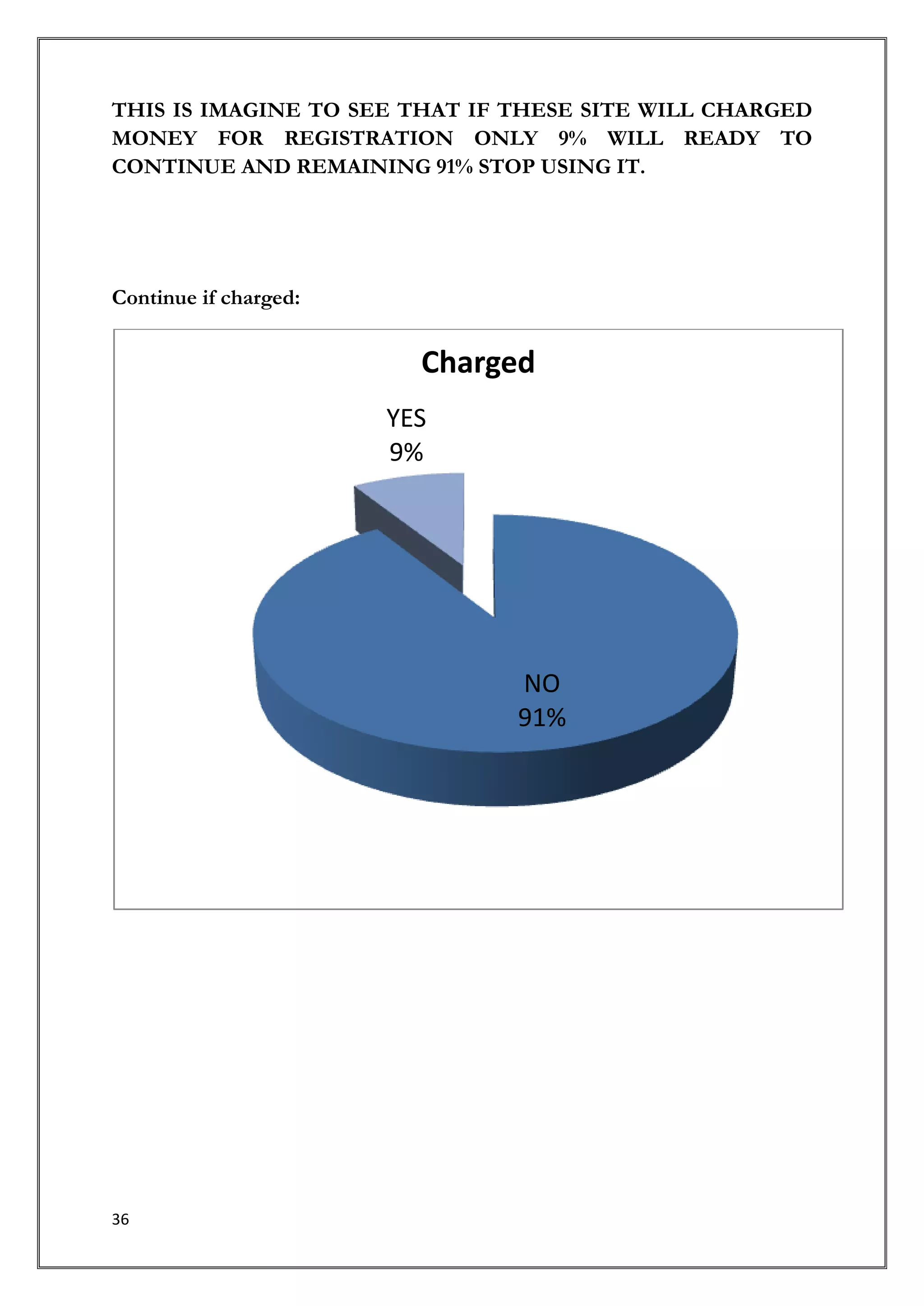
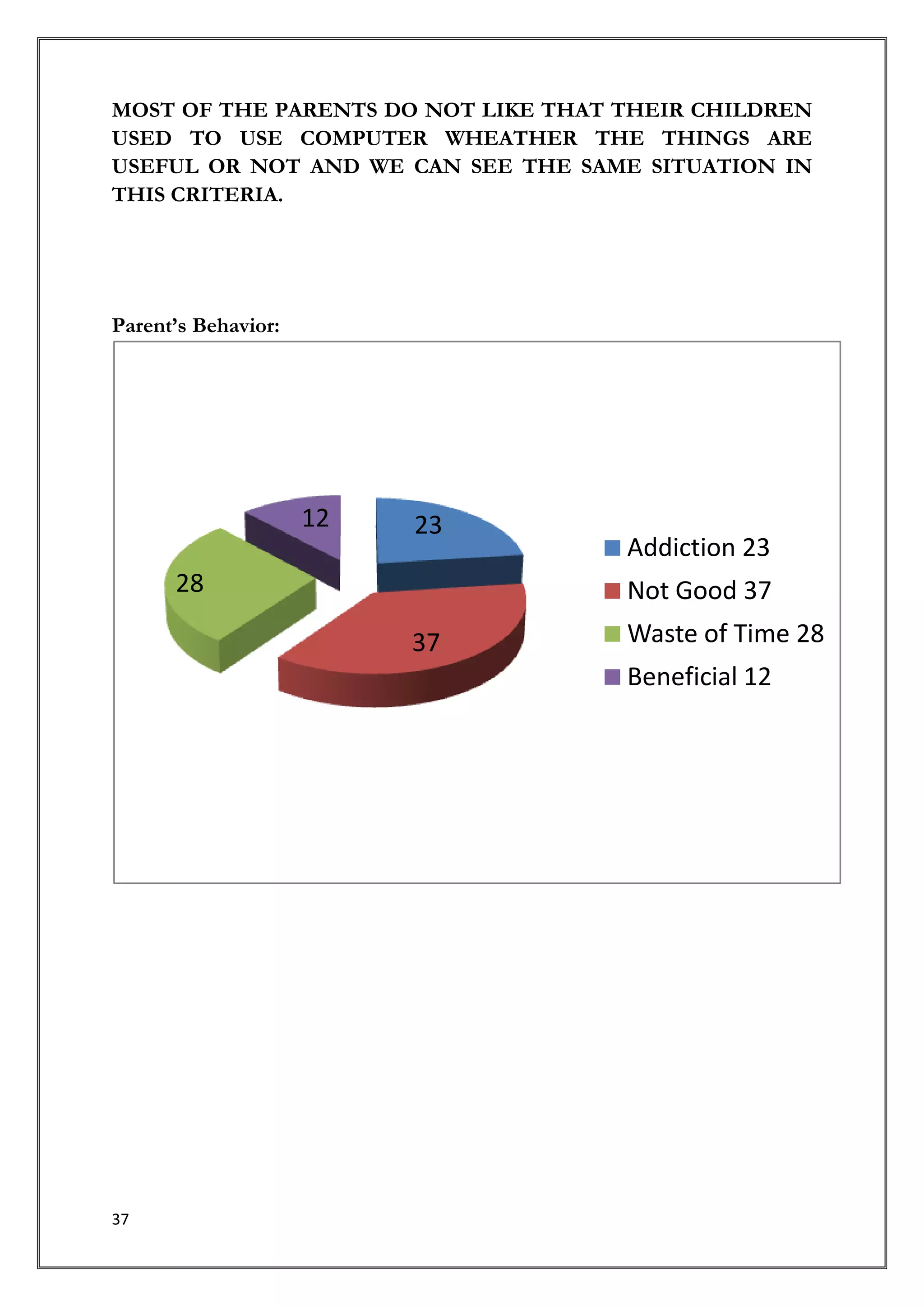
This document provides an introduction and overview of a research study on consumer behavior towards social networking sites. It was submitted by 5 students to their professor for review. The study aims to understand how consumers think, feel, and make decisions regarding social media by examining psychological and environmental factors of influence. It will analyze major social networking players, how they generate income, and marketing strategies. Primary research through questionnaires and interviews will be conducted to gather data and make recommendations.