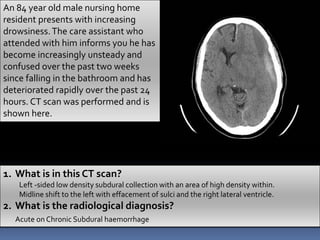
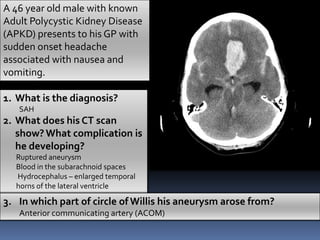
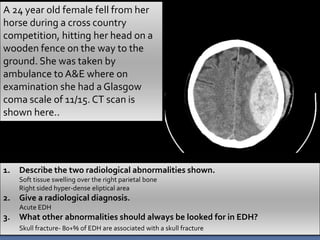
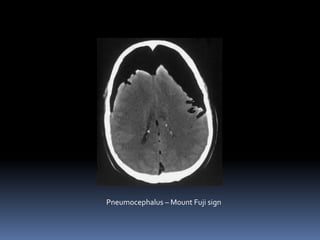
An 84-year-old male nursing home resident presented with increasing drowsiness and confusion over the past two weeks. A CT scan showed a left-sided low density subdural collection with a high density area, and midline shift to the left. The radiological diagnosis was acute on chronic subdural haemorrhage.