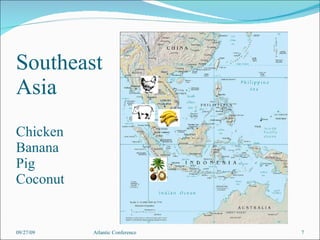
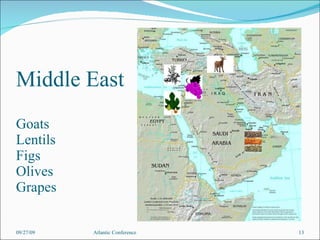
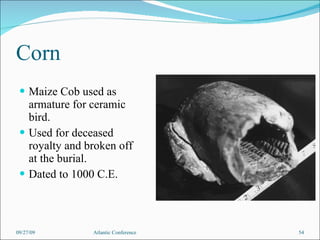
The document discusses the complex history of food and plant domestication leading to modern breakfast items, highlighting the significant contributions of tropical civilizations before European exploration. It emphasizes that various species were transported across oceans pre-1492, showing a rich exchange of agricultural and cultural knowledge. The analysis aims to shift the understanding of Euro-ethnocentrism by recognizing the integral roles played by non-European peoples in shaping global food practices.