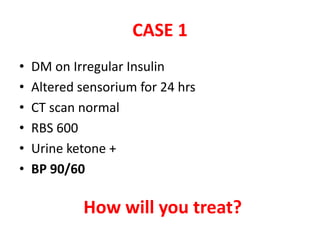
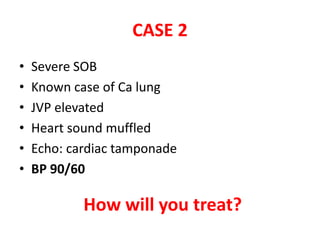
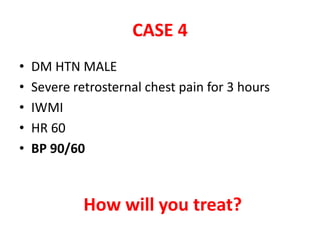
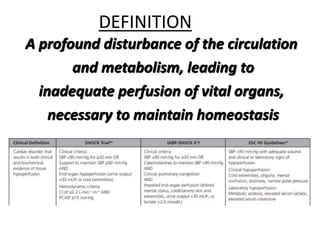
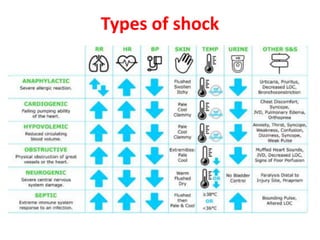
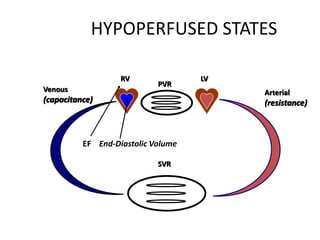
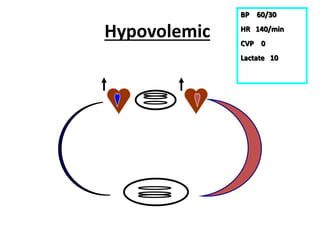
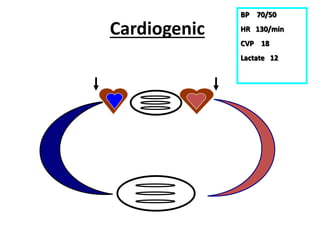
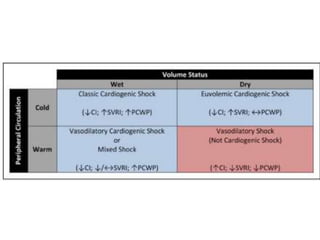
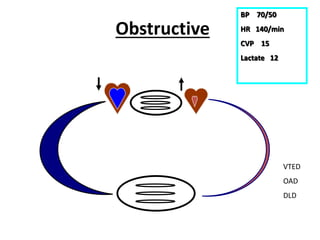
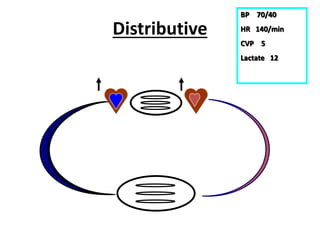
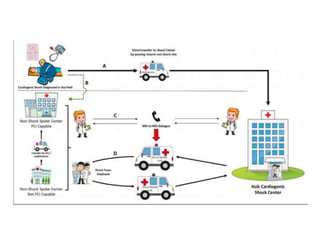
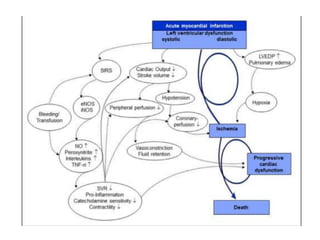
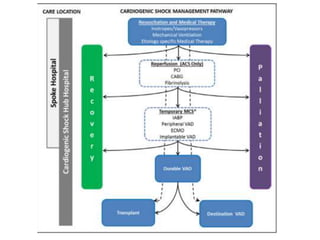
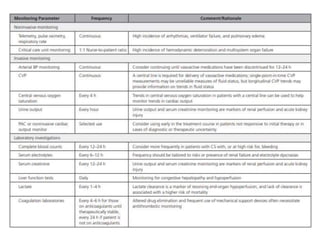
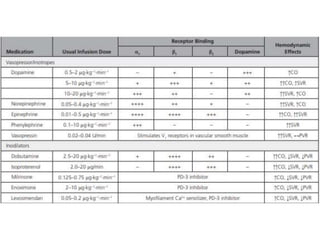
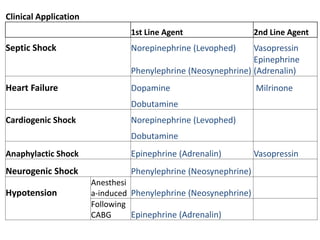
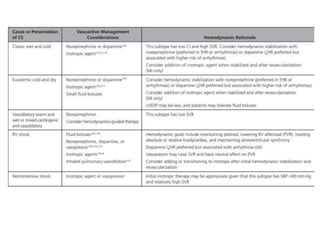
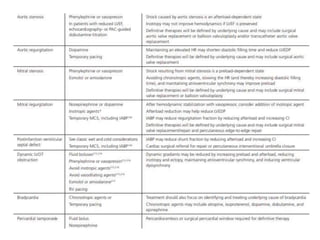
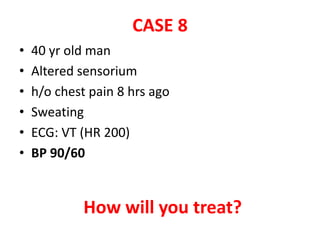
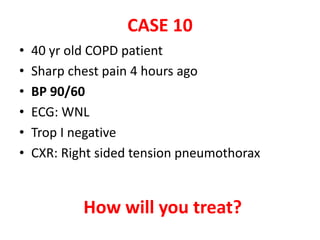
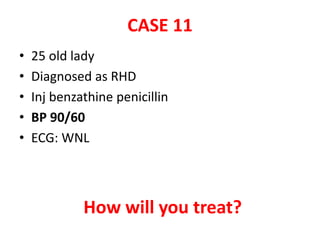
This document discusses circulatory failure and shock, presenting 12 case studies. It defines shock as a profound disturbance of circulation and metabolism leading to inadequate organ perfusion. It describes types of shock including hypovolemic, cardiogenic, obstructive, and distributive shock. Clinical signs of shock are listed. First and second line agents for treating different types of shock are provided, including fluids, vasopressors, inotropes, and other medications. The case studies present patients in shock from various causes and ask how each would be treated.