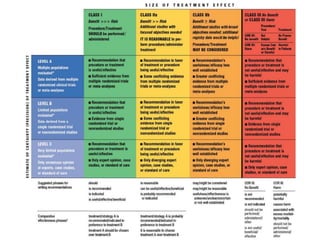
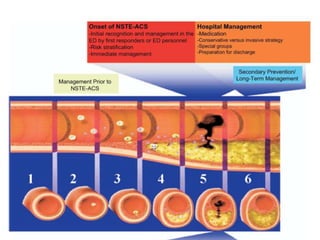
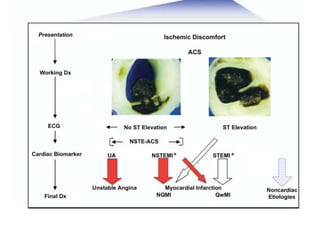
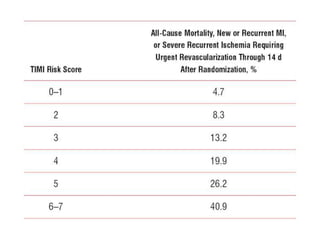
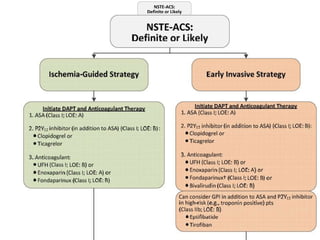
This document provides guidelines for the management of patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes (NSTE-ACS). It recommends performing an early ECG and serial troponin tests to assess risk. For high-risk patients, an immediate invasive strategy within 2 hours is recommended. For low-risk patients, an ischemia-guided strategy is recommended initially. For intermediate-risk patients, an early invasive strategy within 24 hours is suggested. Standard therapies include aspirin, P2Y12 inhibitors, anticoagulants, beta-blockers, nitrates, and renin-angiotensin system inhibitors.

















![GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors
GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor [Eptifibatide
(Integrilin) or tirofiban (Aggrastat)] in
patients treated with an early invasive
strategy and dual anti-platelet therapy
(DAPT) with intermediate/high-risk
features (e.g., positive troponin) (Class
IIb)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-160114222441/85/cardio-24-320.jpg)




![Ischemia-guided strategy
Low-risk score (e.g., TIMI [0 or 1], GRACE
[<109])
Low-risk Tn-negative female patients
Patient or clinician preference in the
absence of high-risk features](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-160114222441/85/cardio-30-320.jpg)

