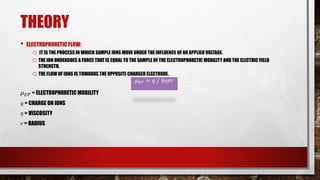
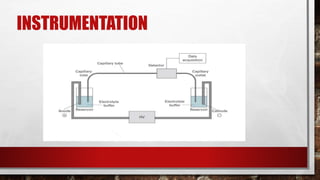
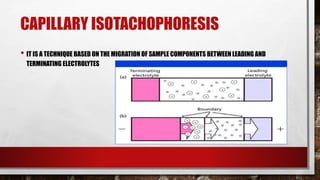
Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate molecules according to their size and charge by applying an electric field to move them through a medium. Capillary electrophoresis improves on traditional electrophoresis by using a narrow capillary tube instead of a slab gel. Molecules migrate through the capillary at different rates depending on their charge and size. The electric field causes positively and negatively charged molecules to move in opposite directions. Capillary electrophoresis has applications in genetic analysis, pharmaceutical analysis, and protein characterization due to its high efficiency, small sample size requirements, and ability to automate.