1. The document provides instructions for a chemistry exam consisting of 45 multiple choice items to be completed in 90 minutes. Students must shade their answers on an answer sheet corresponding to the item numbers.
2. Some key instructions include only marking one answer for each item, erasing any answers they wish to change, and working as quickly and carefully as possible. They may skip items and return to them later.
3. No working is to be done in the test booklet until instructed to begin. Calculators may be used but must be silent and non-programmable.



![- 8 -
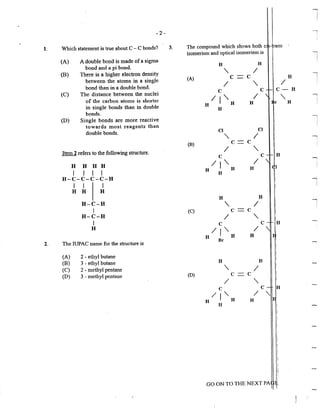
33.
34.
35.
Item 33 refers to the following fractions of
crude oil.
I.
II.
III.
IV.
Diesel
Petrol
Refinery gas
Kerosene
The correct order in tenns ofINCREASING
boiJing points is
(A) I, II, Ill, IV
(B) III,I,IV,II
(C) III, II, IV. I
(D) IV, II, I, Ill
Which of the following products is NOT
produced for commercial purposes by the
e]ectroJysis ofconcentrated brine?
(A) Chlorine
(B) Oxygen
(C) Hydrogen
(D) Sodium chlorate (V)
In the Bosch-Haber process, N., and H~ can
be obtained from X and Y respecti~eJy.
Which of the following pairs BEST
describes X and Y?
X y
(A) Ammonium salts Naphtha
(B) Ammonium salts Air
(C) Air Naphtha
(D) Air Ammonium salts
36. Which of the following statements does
NOT accurateJy describe a result ofethanol
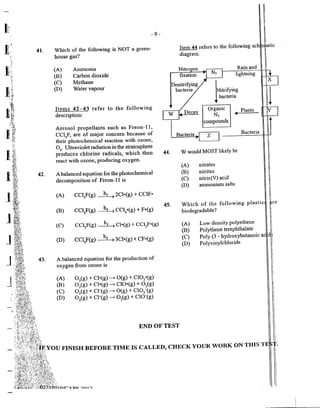
consumption?
(A) Digestion occurs in the stomach.
(B) Natural inhibitions are re]axed
(reduced).
(C) Oxidation occurs in the blood.
(D) Reaction time is reduced.
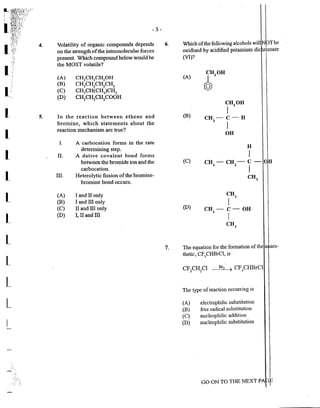
37.
38.
39.
40.
In the electrolysis of brine u ing the·
diaphragm cell, two by-produc s re
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
chlorine and oxygen
chlorine and sodium
hydrogen and mercury
hydrogen and sodium h
The presence ofphosphate ions ( . 4
J-) can
be detected using
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
ammonium molybdate
potassium hexacyano
solution
potassium thiocyanate s
sodiun1 thiosulphate
J
1
tion
I
l
ate(II)
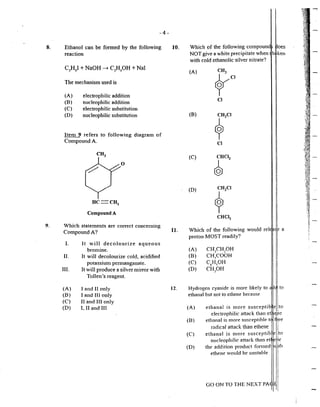
C d f l I I II I .
mnpoun s o · su P. 1~r sue 1 .as. s~ p 11tes
are used as food additives. This 1 l1
.ecause
they I
I
(A) improve the flavour of ft i
(B) help to enhance the colo ~f food
(C) inhibit the oxidation ofun a: trated
(D)
fats
help to preserve the
dehydration
Which of the following
sulphuric acid'?
I. Fet1ilizer
n. Paint
IIJ. Fibre
IV. Detergent
(A) I. II and Ill only
(B) 1, Ill and lV only
(C) II, Ill and JV only
(D) L 11, JH and JV
GO ON TO THE NEXT P Cftf.
by
use
-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012-160926163202/85/CAPE-Chemistry-Unit-2-Paper-1-2012-8-320.jpg)