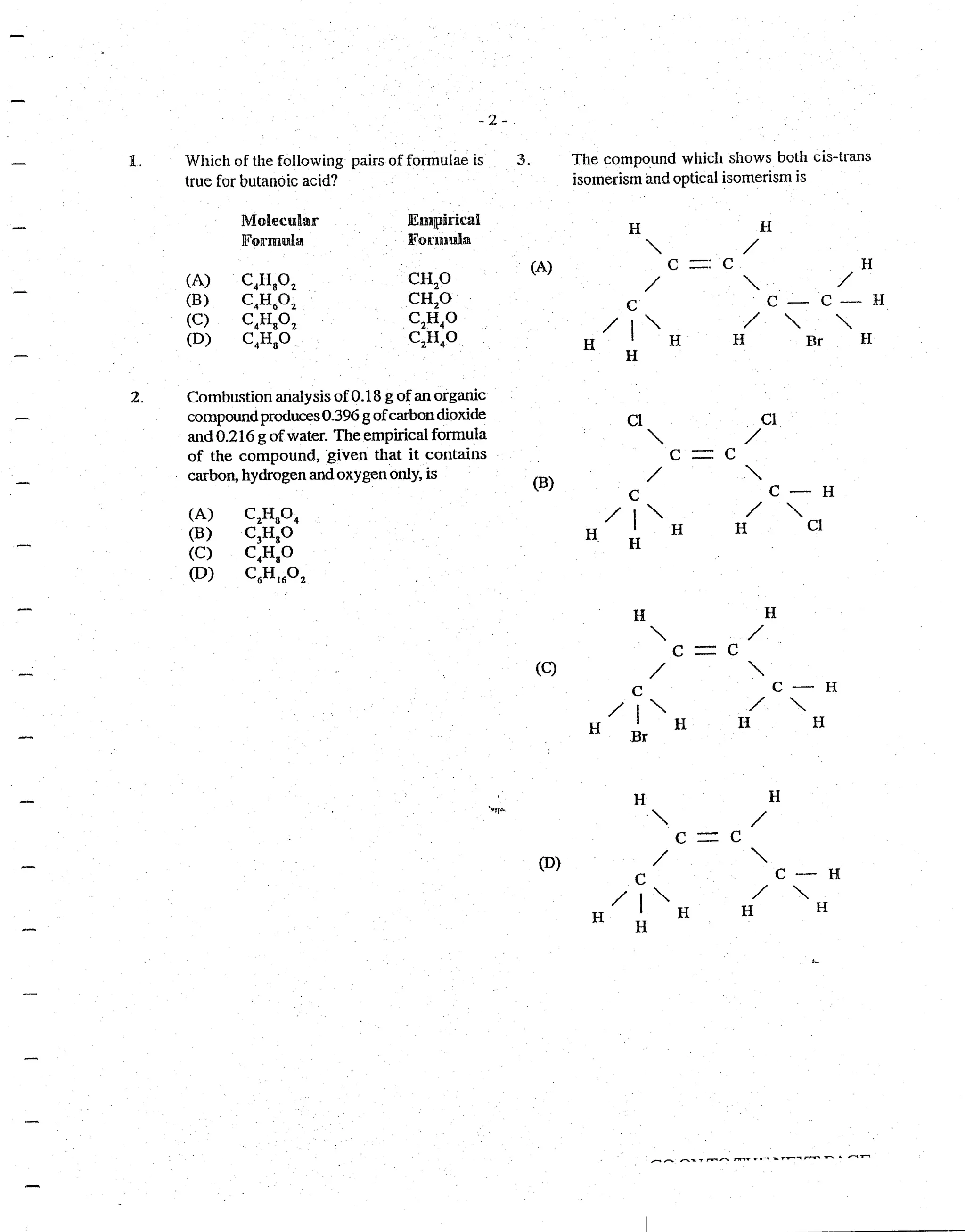
This document contains a chemistry test with 45 multiple choice questions covering various topics in organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, analytical chemistry and environmental chemistry. Some of the questions test understanding of fundamental concepts like chemical formulas, reaction mechanisms, spectroscopy techniques and chemical analysis. Other questions require applying this conceptual understanding to solve problems involving stoichiometry, equilibrium, acid-base reactions and other chemical calculations. The test evaluates a wide range of essential chemistry knowledge.


![16.
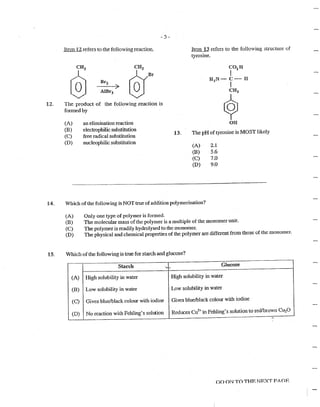
17.
13.
19.
-6-
Which of the following sets of titration
readings is the MOST precise?
(A) 25.1 25.5 25.1 25.2
(B) 24.9 24.5 25.2 25.4
(C) 25.0 25.0 24.9 24.8
(D) 25.0 24.5 24.8 24.6
Which of the following is NOTa property of
a primary standard?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Does not undergo hydrolysis
Low relative molecular mass
Obtainable in a pure state
Very soluble in water
What is the concentration (tnol dm-3) of an
aqueous solution that contains 63.3g of
K3
Fe(CN)6
in 1.0 dm3
of solution? [The
relative formula mass ofiSFe(CN)5
is 329.2.]
(A) 1.92 x 1o-1
(B) 2.95 X 1()4
(C) 3.11 X l0-3
(D) 5.77 X lo-1
Naturally occurring Element X has four
isotopes: 50
X, 52
:X, 53
X and 54
X. They hav~
percentage abundance of4.31, 83.76, 9.55/··
and 2.38 respectively.
What is the relative atomic tnass of X?
(A) 52.00
(JB) 52.06
(C) 52.25
(D) 53.00
20.
21.
22.
Treatment ofa 10.00 g sample containing a
chloride salt with ex:cess silver nitrate solution
produces 8.08 g ofsilver chloride.
(Ag= 108, Cl = 35.5)
The expression for the percentage ofchloride
in the sample is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
35.5Xl0.00 xlOO
108X8.08
35.5x8.08 x
100
108><10.00
35.5xlO.OO xlOO
143.5x8.08
35.5x8.08 ><lOO
143.5xl0.00
A compound absorbs light offrequency 940
MHz. The wavelength. in em. of the light
absorbed is (c = 3.0 x 108
m s·1
)
(A) 31.91
(B) 31.91 X lQ-2
(C) 31.91 X lo-1
(D) 31.91 X 1()"
Which two fean.u·es BEST describe ultraviolet
radiation?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Long wavelength and high energy
Long wavelength and low frequency
Shortwavelength and hlgh frequency
Short wavelength and low energy
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-160926163157/85/CAPE-Chemistry-Unit-2-Paper-1-2010-5-320.jpg)
![-7-
23. vVhich ofthe following alkenes has the wavelength ofmaximtun absorption, A.max ?
24.
25.
26.
(A)o (B)o~
~· /}
(C)o (D)o
Which ofthe following equations goven1s the
determination ofan unknown compound, X,
in a solution by UVNIS spectroscopy?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
log10
(I/1) = E c L
1ogiO (IIlo) = E c L
log10
(!0
/I) =E L [X]
1og10
(I/10
) = E L [X]
Which of the following pairs do NOT absorb
infrared radiation?
I. H2
0 and HI
II. H2
and Cl2
III. Nl-13
and HBr
IV. CH4
and Br2
(A) I and III only
(B) I and IV only
(C) II and III only
(D) II and IV only
Which of the following species is NOT a·,,.~
significant fragment from the mass spectrum
ofethanol?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
C2
H5
0H+
CzHs+
CH3
+
OH+
27.
28.
Which of the following is NOT a stationary
phase used in chromatography?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Alumina
Cellulose
Silicagel
Starch
Item 28 refers to the following information.
Sample X is a mixture of substances. X was
separated into its components using paper
chromatography simultaneously with
individual samples of e, f, g and h. The
chromatograph produced is shown below.
Sample X e f g h
Which substances are MOST likely present
in Sample X?
(A) e, f, g
(B) e,f, h
(C) e,g,h
(D) e, f, g, h](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-160926163157/85/CAPE-Chemistry-Unit-2-Paper-1-2010-6-320.jpg)