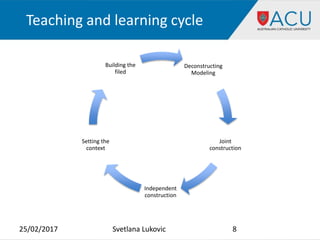
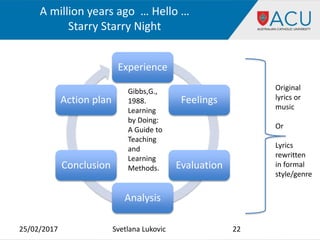
The document discusses using music and art in teaching English for academic purposes. It describes incorporating art topics into student presentations and assessments to practice language skills. Students presented on artists and artworks from their own cultures. Music was also used, such as having students rewrite song lyrics in a more academic style. Specific language areas that can be taught using music and art include vocabulary, grammar, writing skills such as reflection, and developing critical thinking. The purpose is to create a more engaging and motivating learning environment through multimodal techniques.