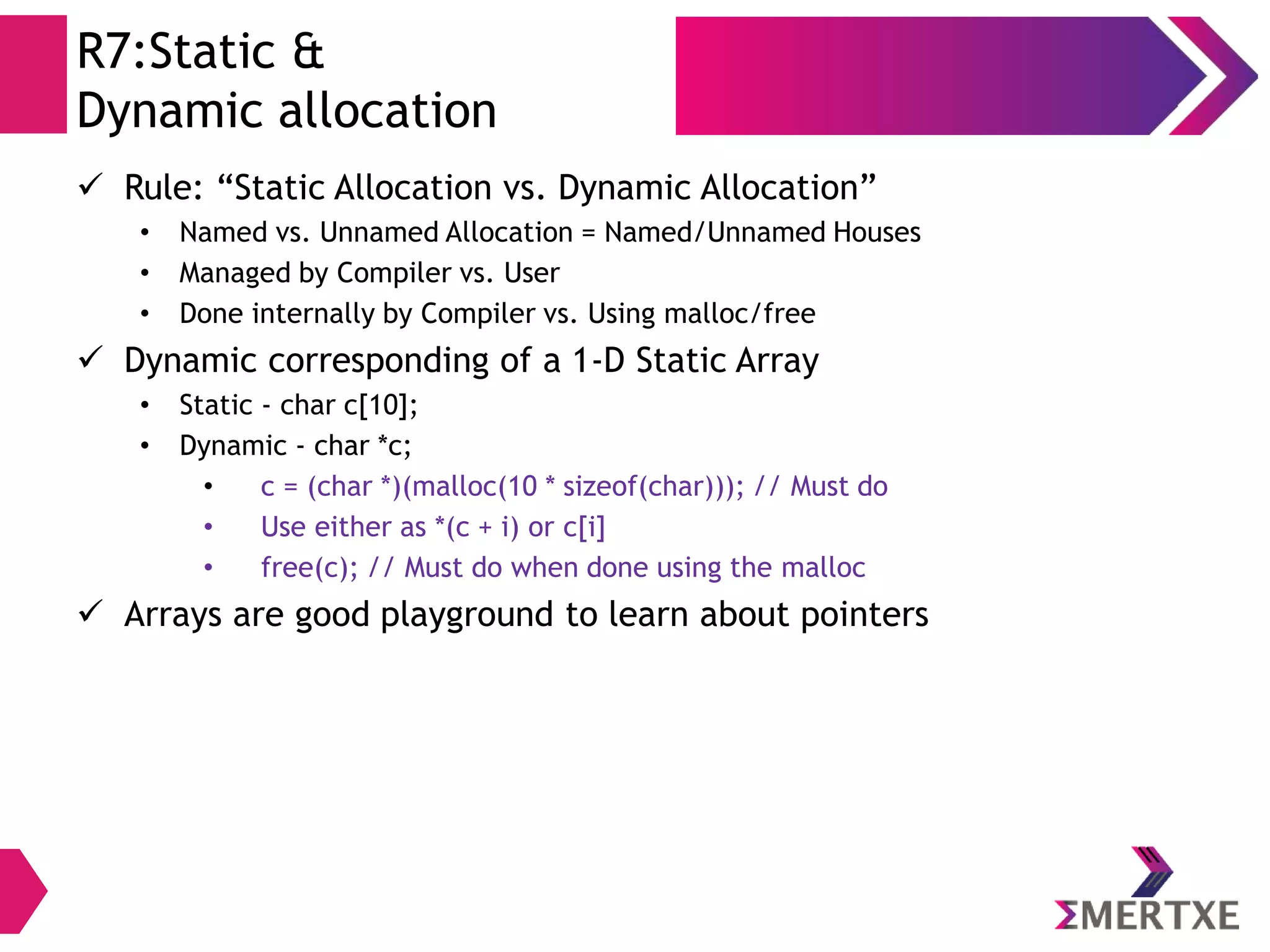
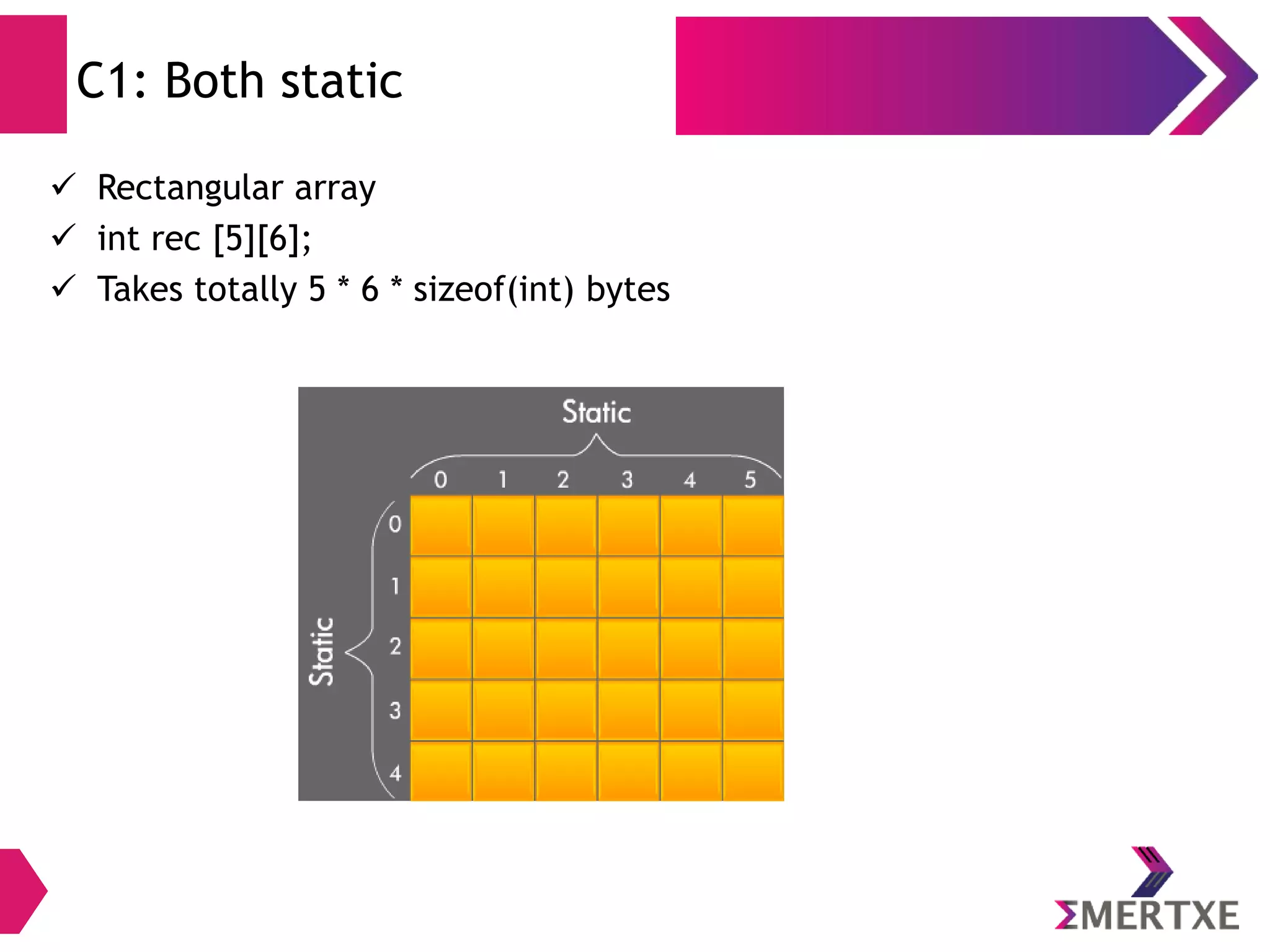
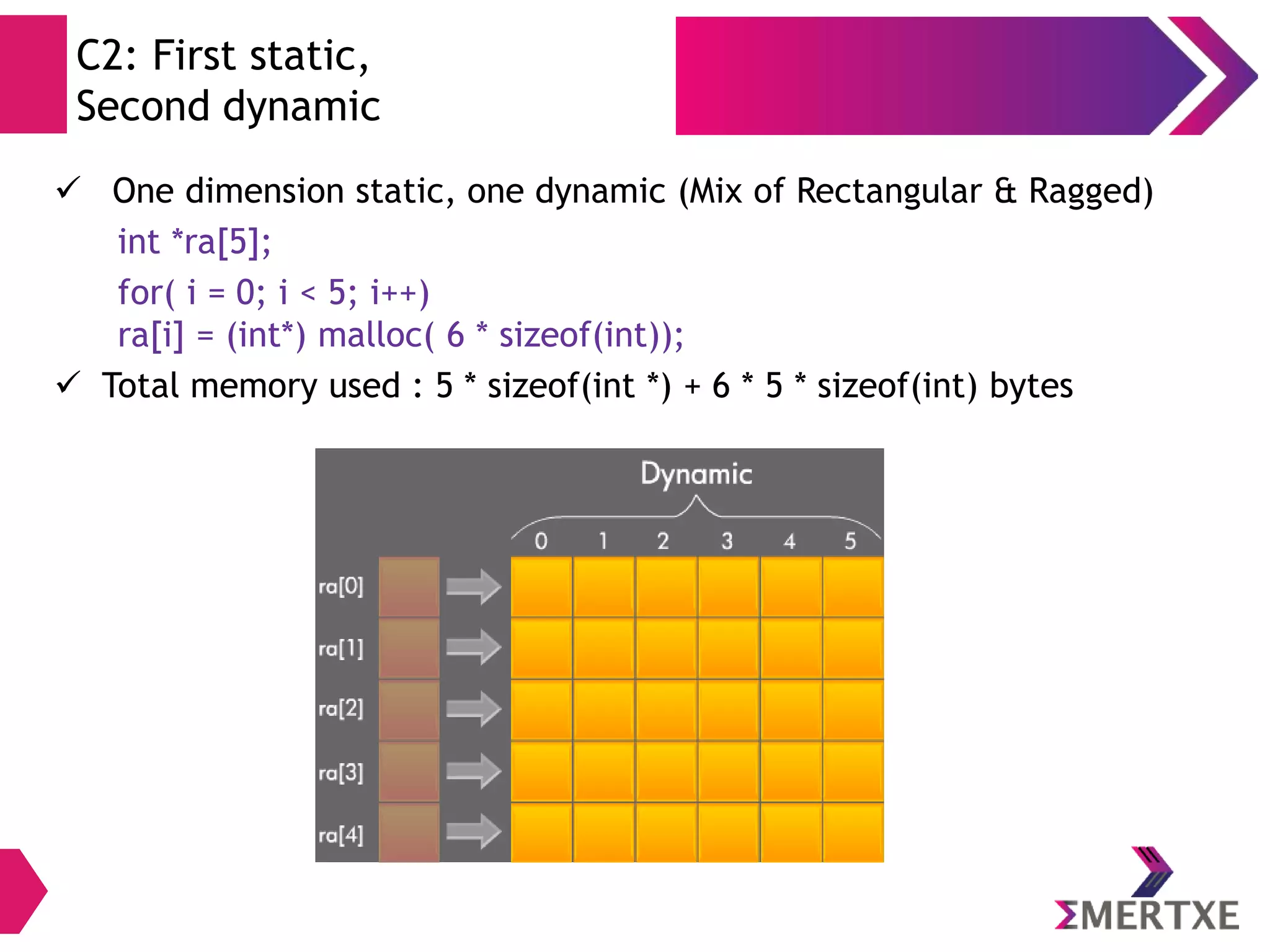
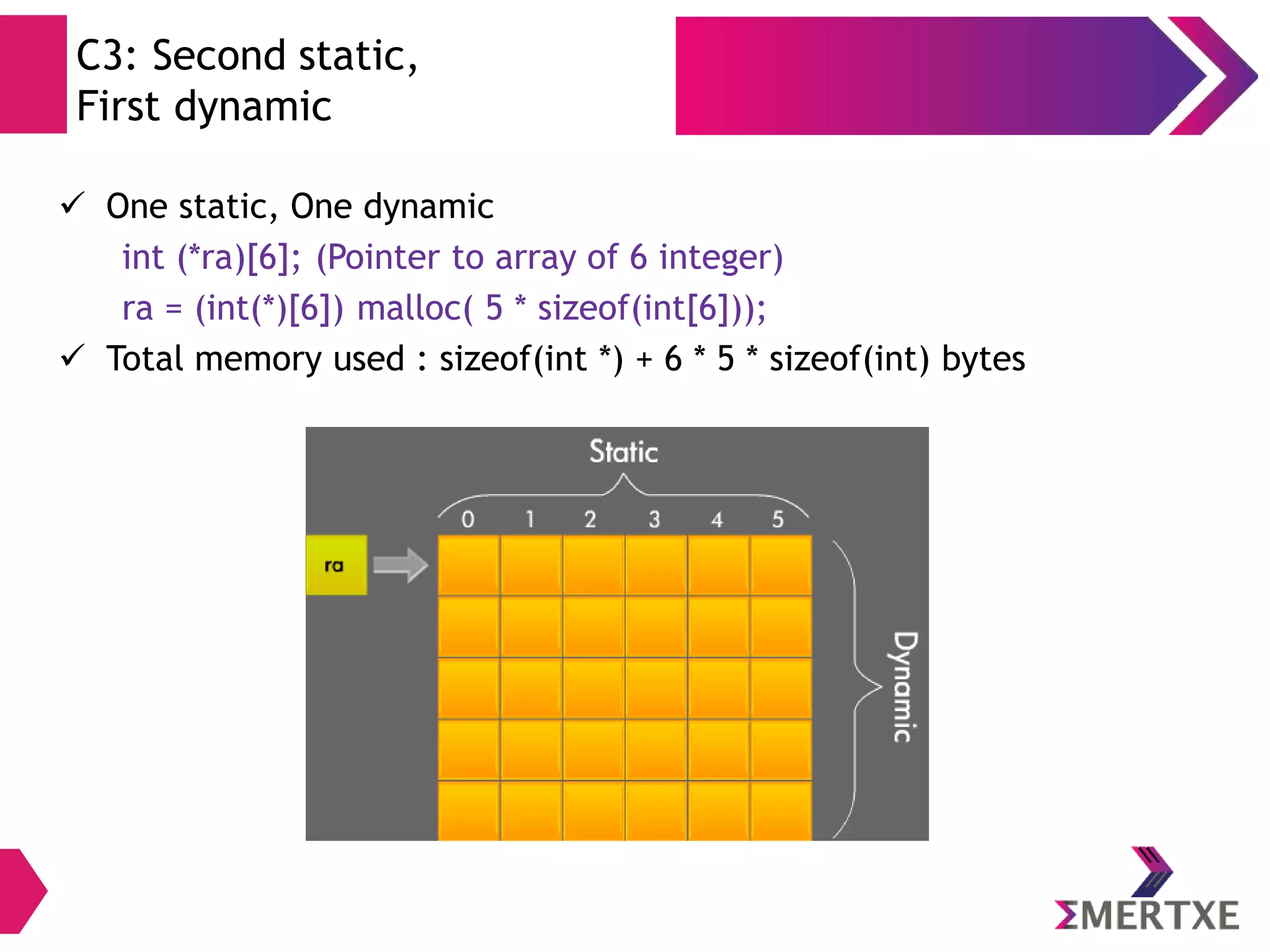
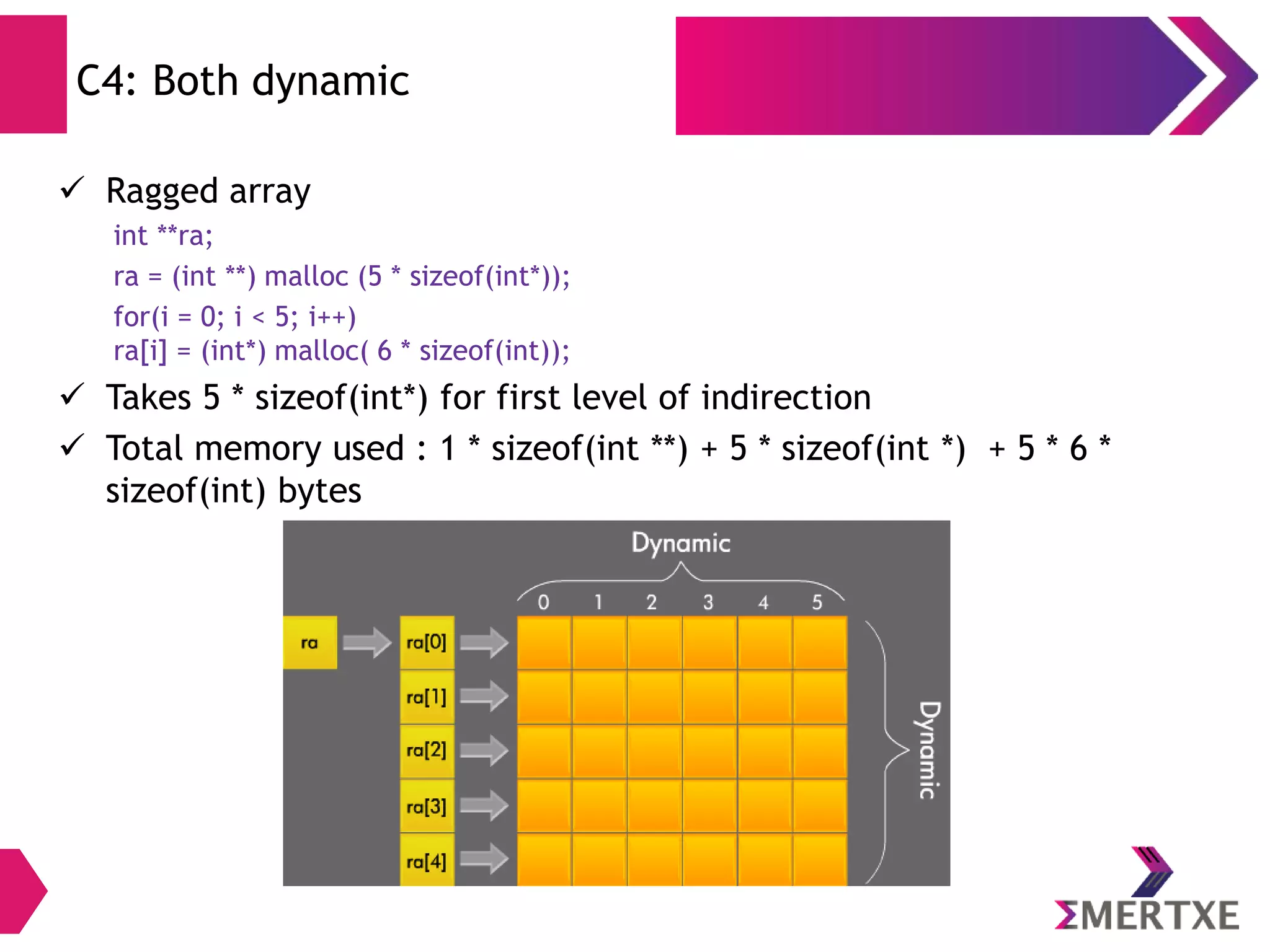
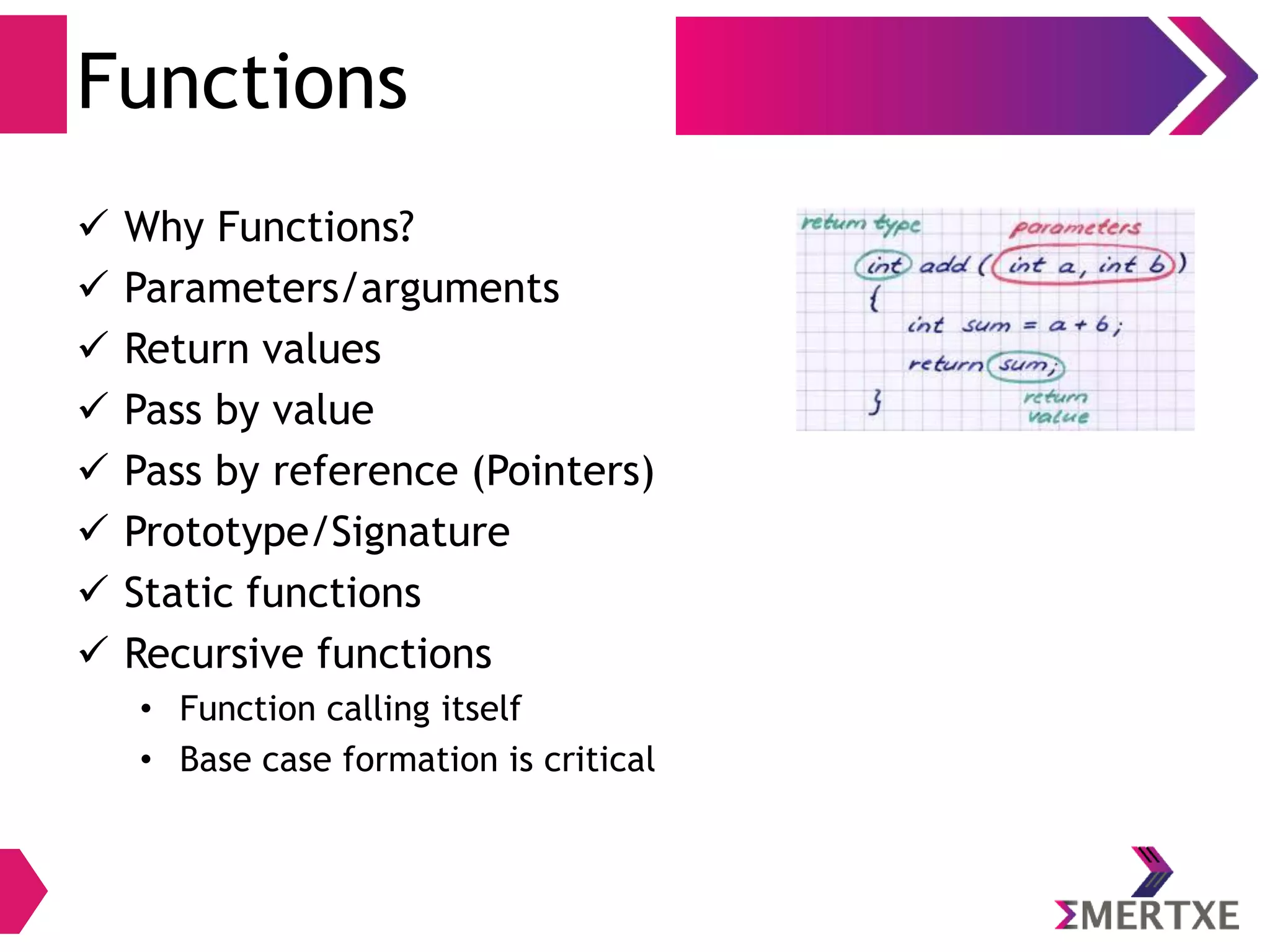
The document discusses the importance of functions in embedded C programming, emphasizing their reusability, modularity, and ease of debugging. It explains parameters, arguments, and return values, alongside different passing mechanisms such as pass-by-value and pass-by-reference, and provides examples and exercises. Additionally, it covers arrays, their declaration and memory allocation, as well as variadic and recursive functions.




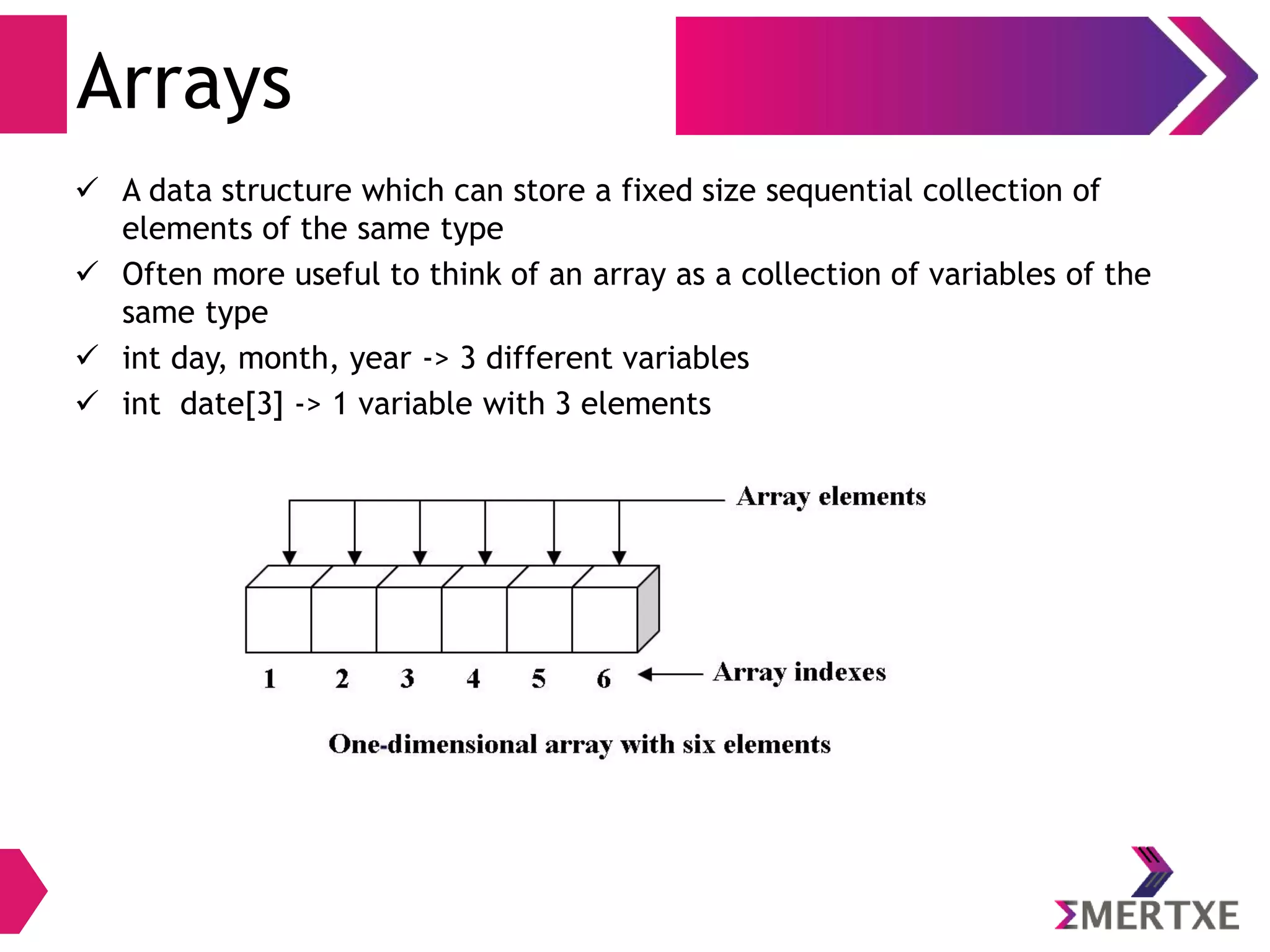



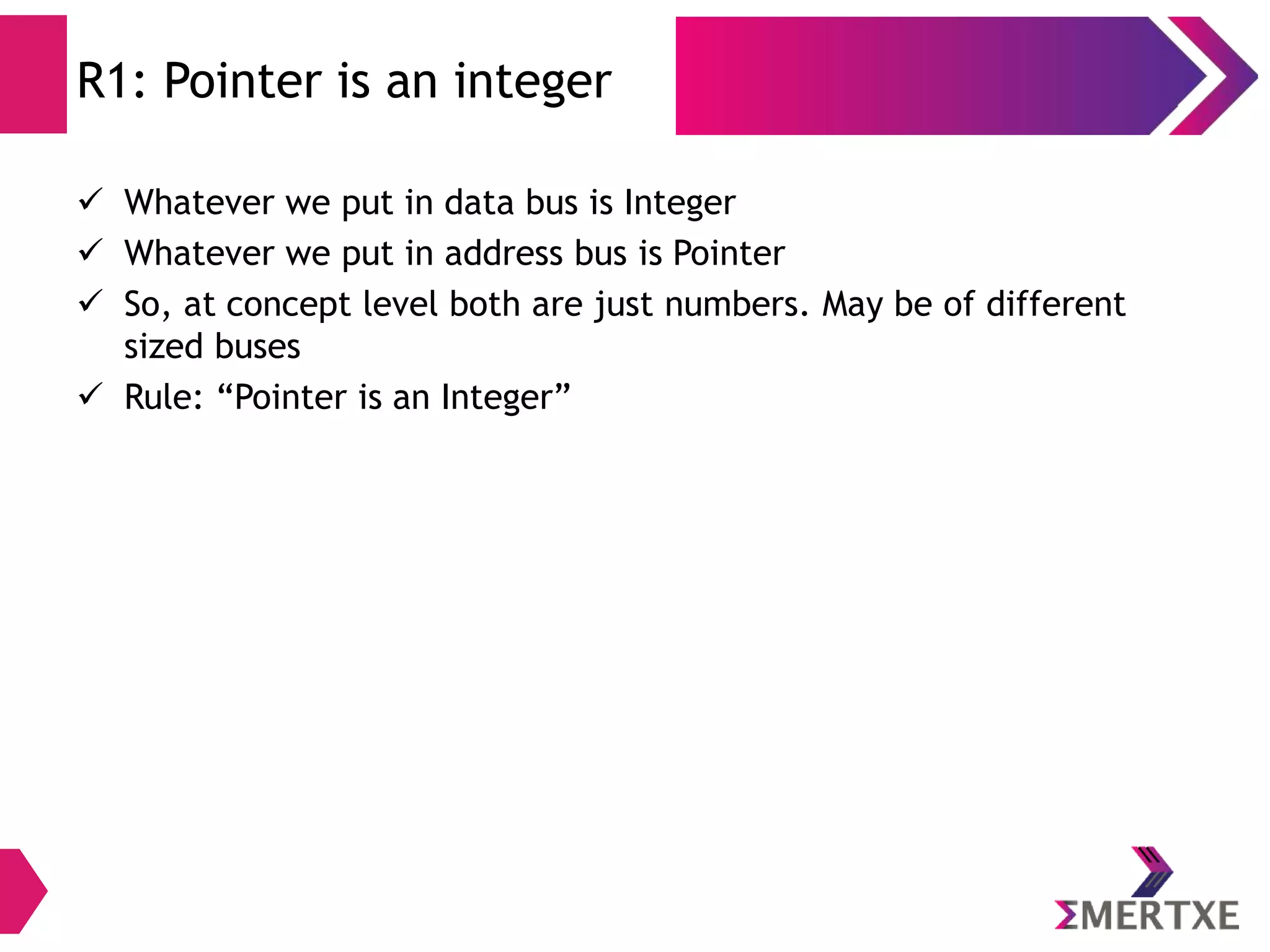

![Array: Declaration
Syntax
type arrayName [ SIZE ];
Example
To declare an array to store ages of 5 people
int age[ 5 ];
Total Memory
Total Memory = SIZE * sizeof(dataType)
= 5 * sizeof( int ) // Assuming sizeof(int) = 4
= 5 * 4
= 20 bytes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-refresher-day2-140322125752-phpapp01/75/C-Programming-Refresher-Part-II-17-2048.jpg)
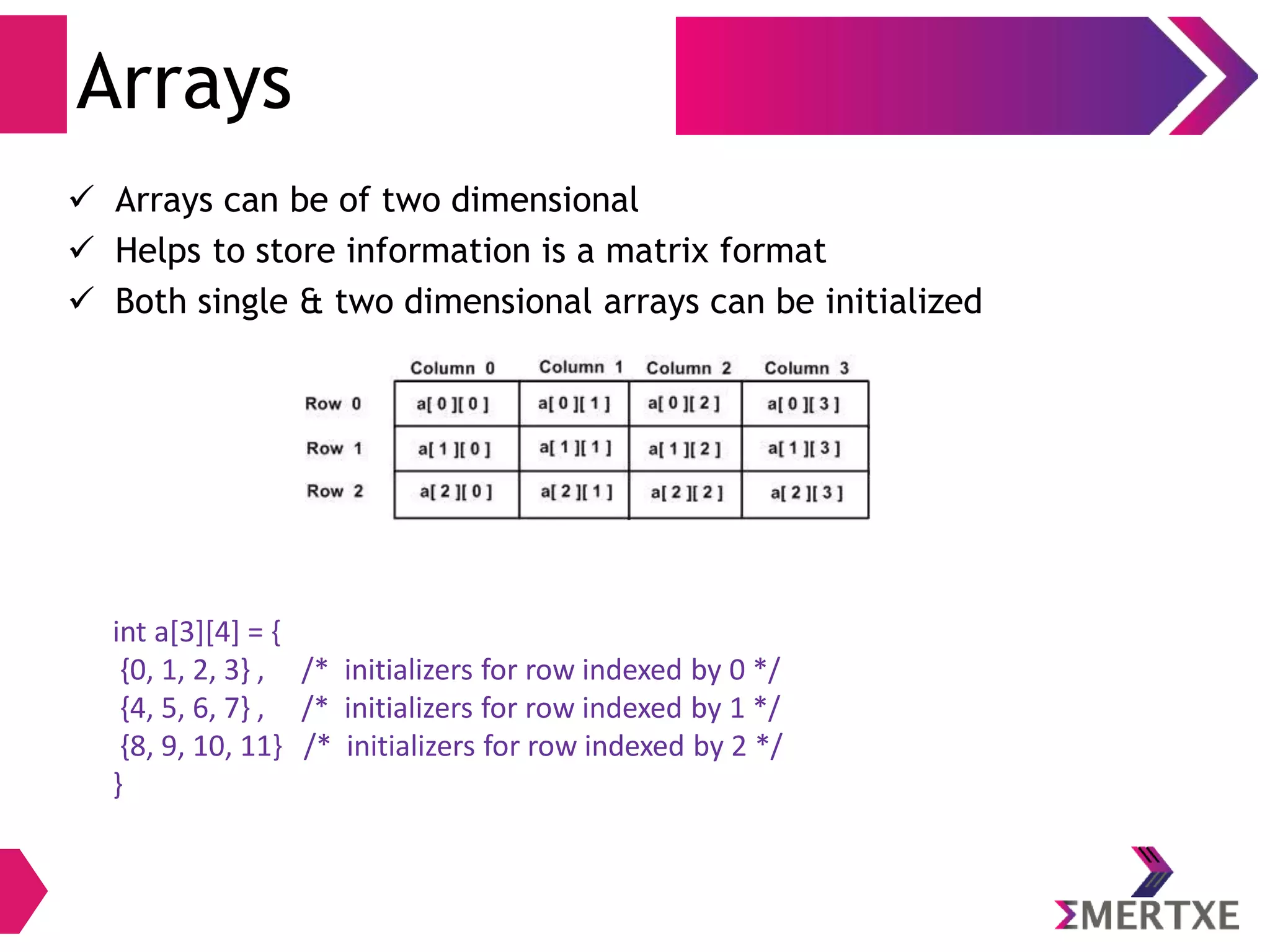
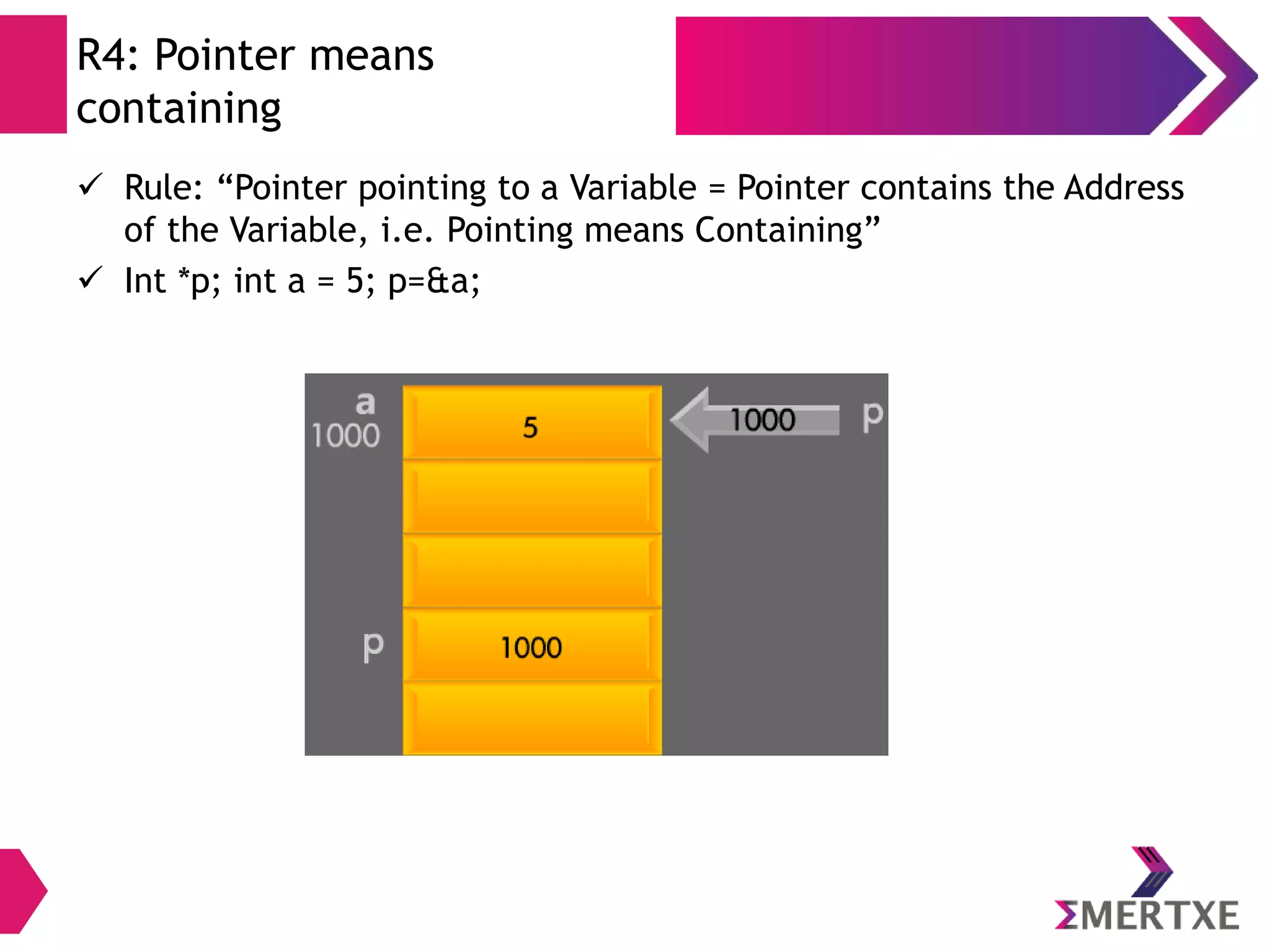
![Array: Definition
Example
To declare an array to store ages of 5 people
int age[ 5 ] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
Memory Allocation
10 20 30 40 50
age[0]
age[4]
age[3]
age[2]
age[1]
100 104 108 112 116
DIY : Write a program to add all the elements of the array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-refresher-day2-140322125752-phpapp01/75/C-Programming-Refresher-Part-II-18-2048.jpg)