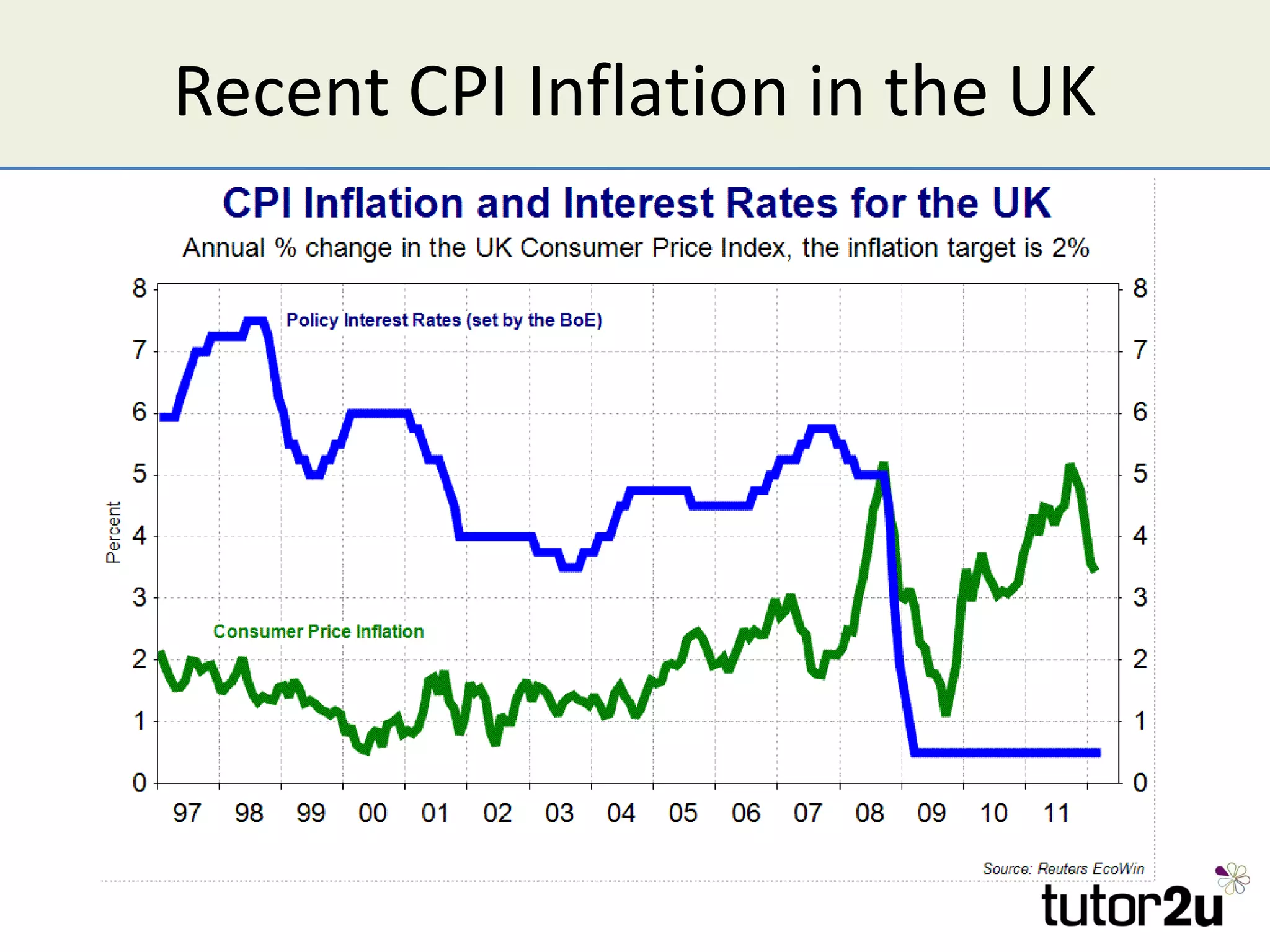
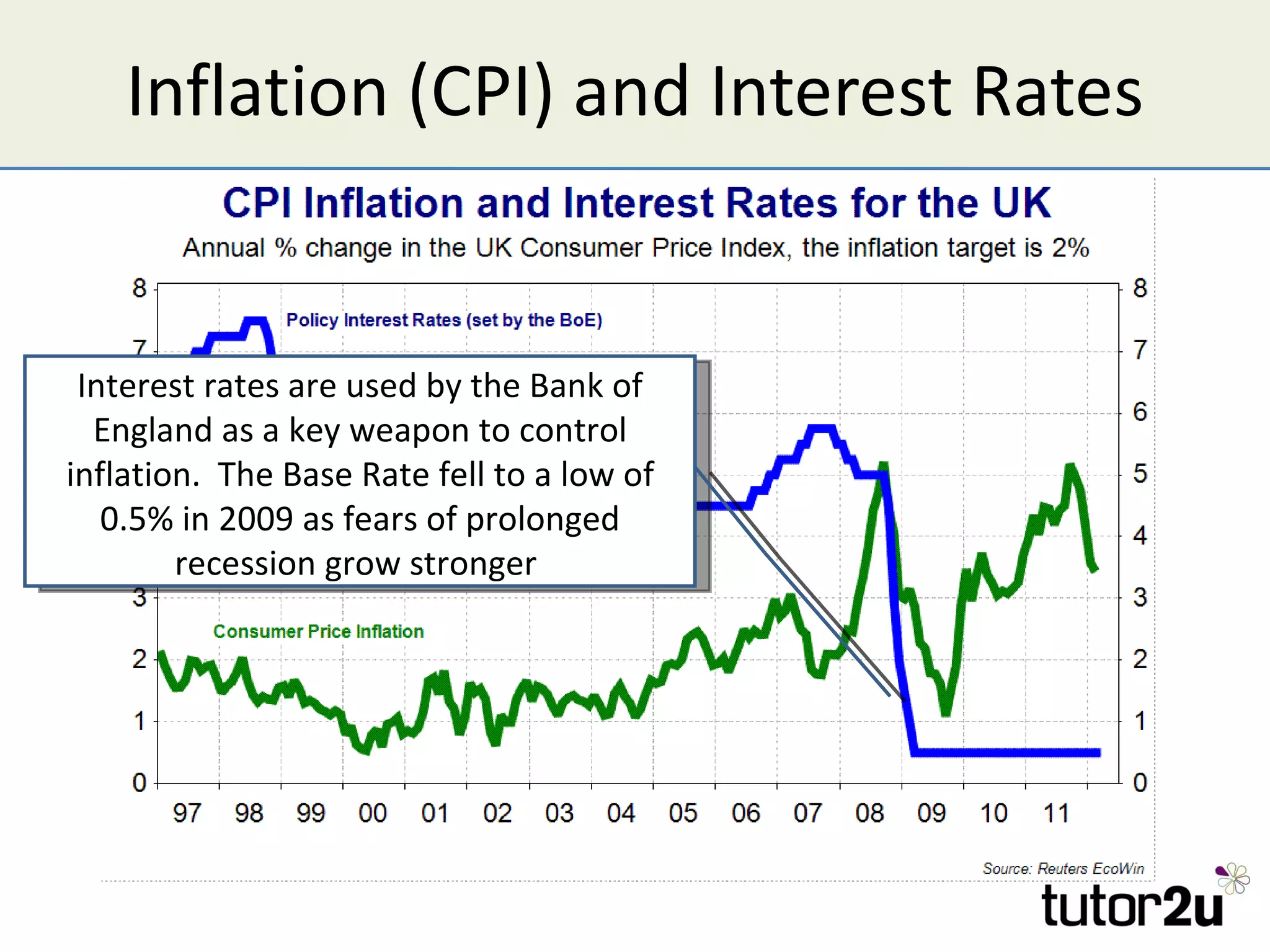
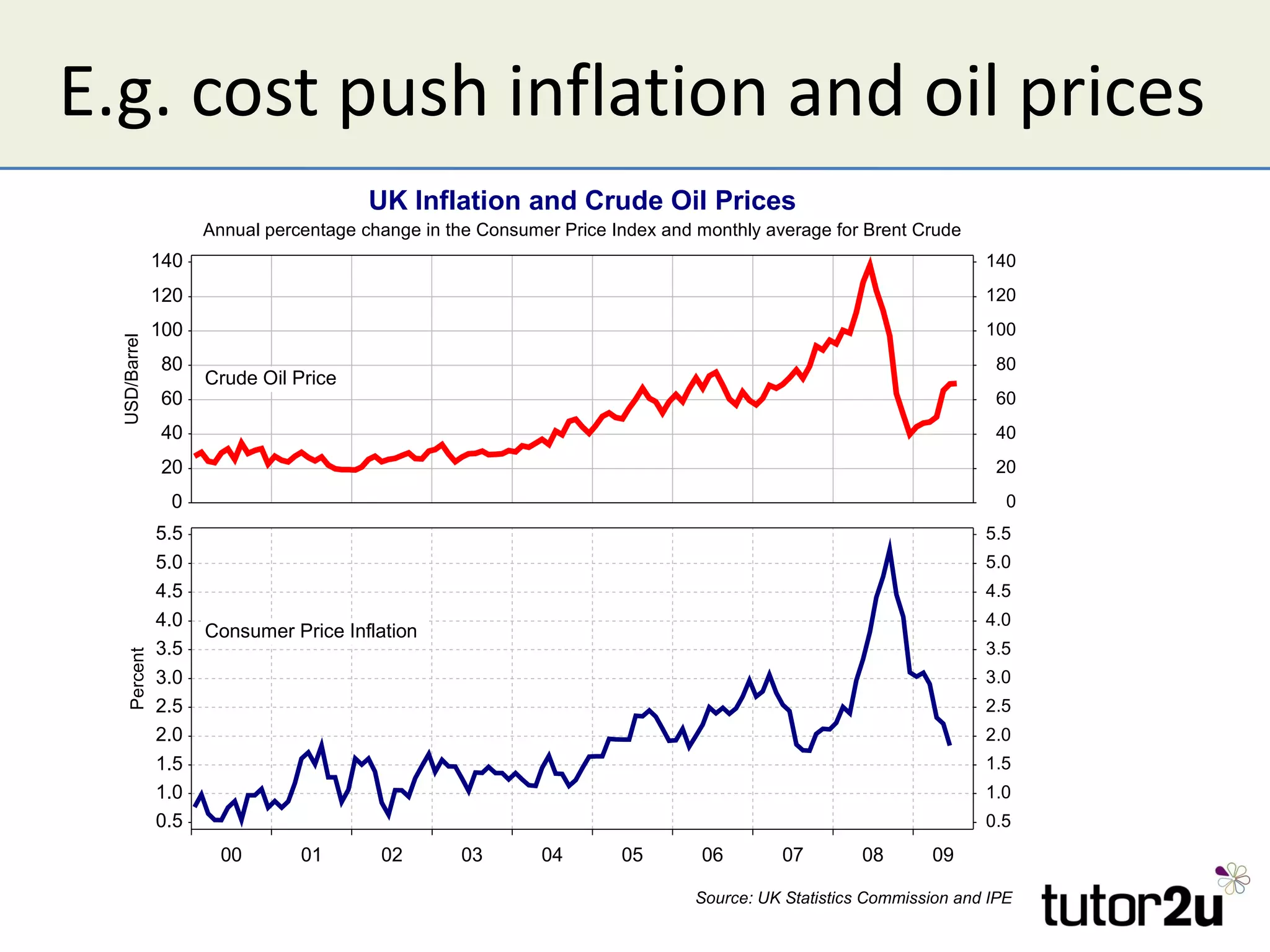
Inflation is defined as a sustained increase in the average price level within an economy, primarily measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) with a targeted rate of 2% in the UK. Causes of inflation include demand-pull, where excess demand leads to price increases, and cost-push, resulting from rising production costs. Inflation has various impacts, including eroding purchasing power, affecting savings and wages, and potentially leading to higher unemployment and economic instability.