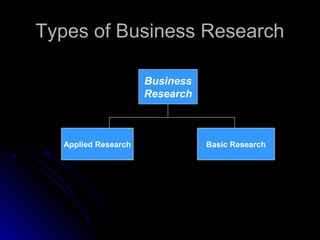
This document provides an introduction to business research. It defines business research and discusses the types of business research, including applied and basic research. The importance of research for managers in decision making is explained. Managers must identify problems, recognize relevant factors, know how to gather and use information to make effective decisions. Hiring internal or external researchers involves tradeoffs. Ethical conduct is important throughout the research process from data collection to dissemination of results.