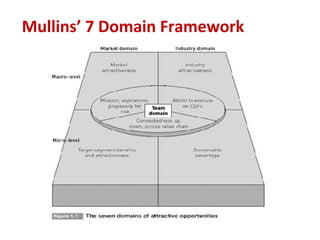
Creativity is the ability to develop new ideas and look at problems in new ways, while innovation is applying creative solutions to problems. Barriers to creativity include focusing on one answer, logic over imagination, rigidly following rules, fear of mistakes, specialization, and believing you are not creative. Good opportunities have customers willing to buy a product that solves their needs, in a large enough market, where entry is possible and you can differentiate yourself.