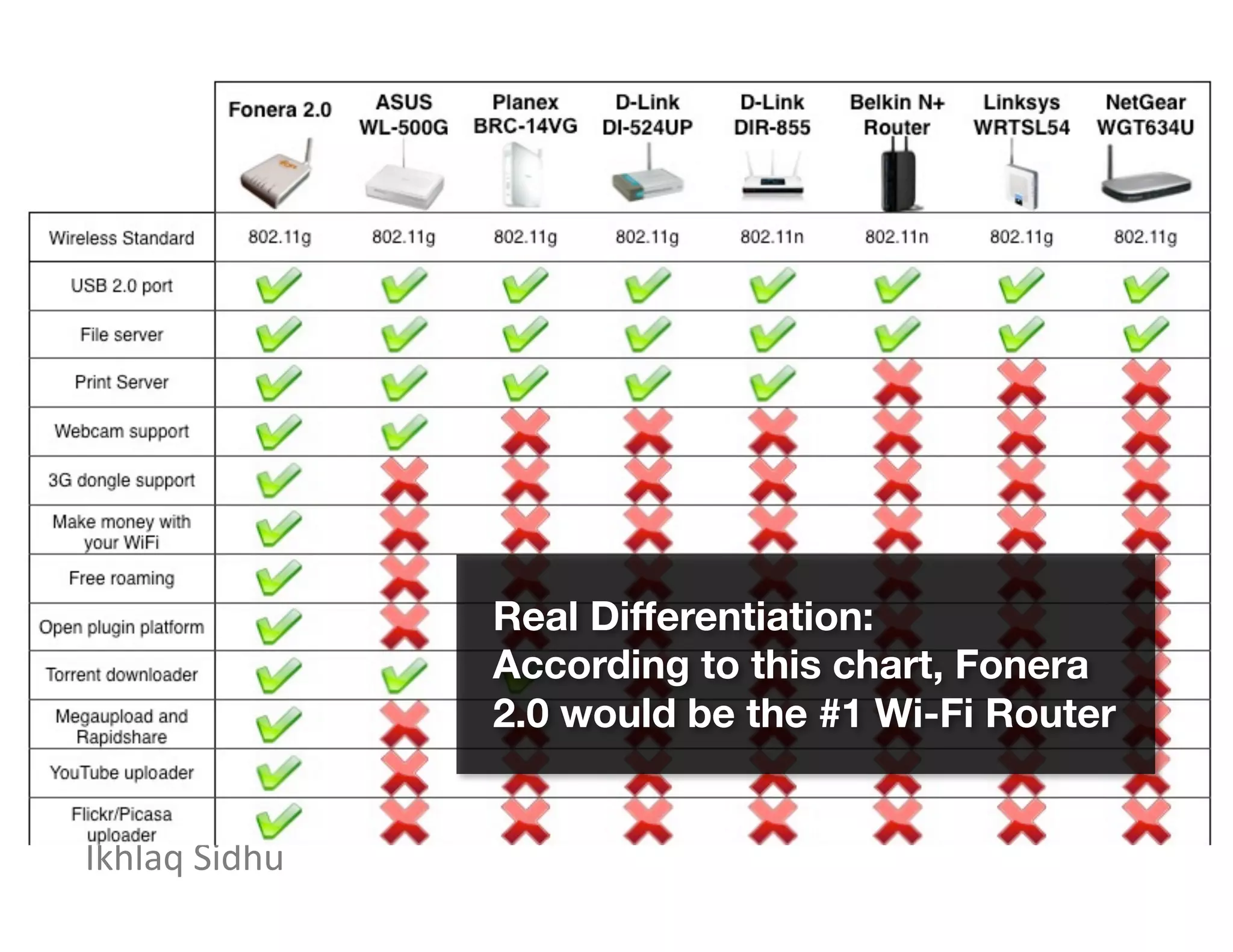
This document discusses business models and business design. It provides advice on developing an effective business model, including:
- Define a clear value proposition that can be quantified in terms of costs, price, and value created.
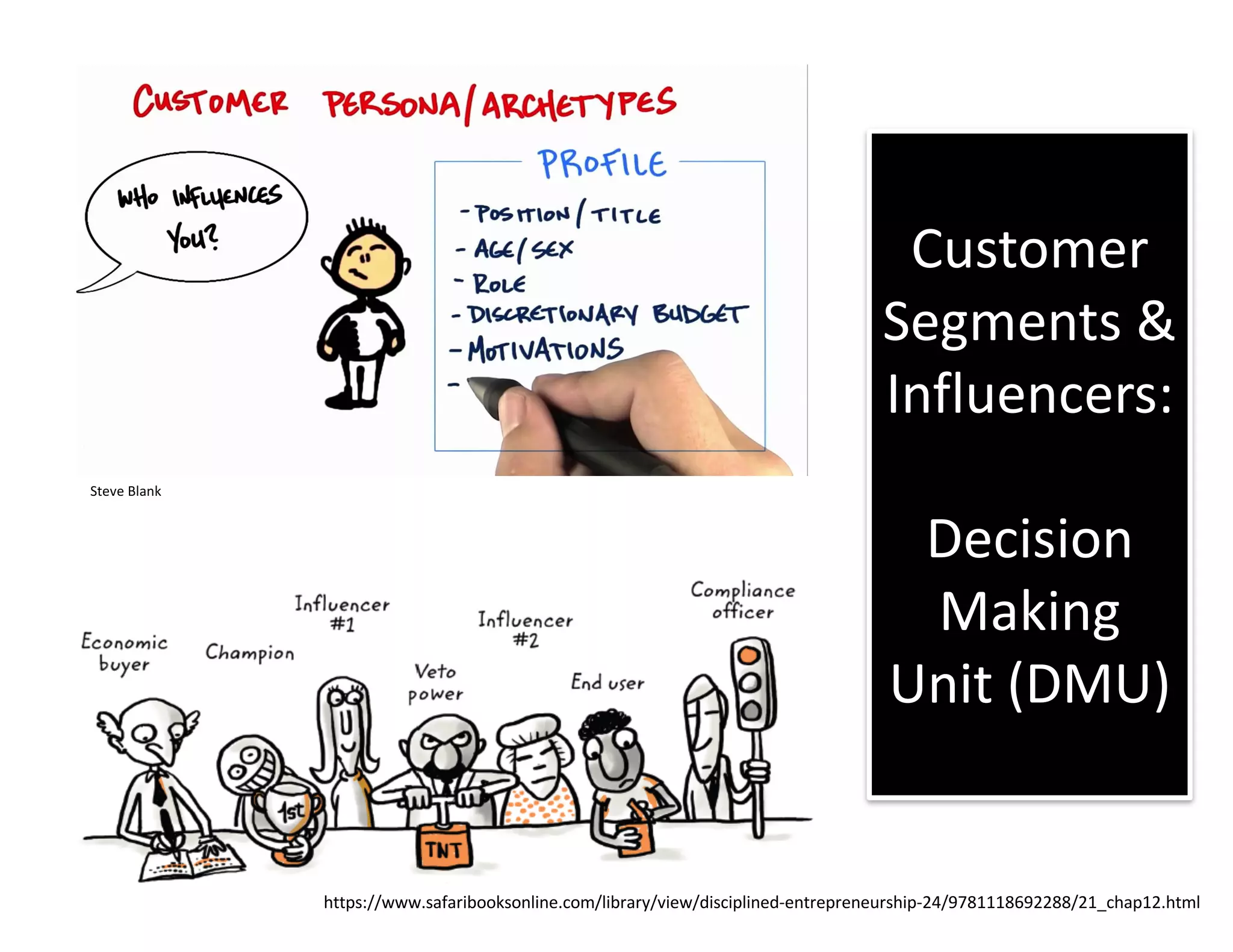
- Understand your target customer segments and how to acquire customers at a reasonable cost over their lifetime value.
- Develop a revenue model that considers customer acquisition costs, lifetime value, marketing, sales cycles and growth.
- Use tools like the Business Model Canvas to define the key elements of your business model in a clear way.
- Continually observe the environment and market to ensure your business vision remains aligned with reality.