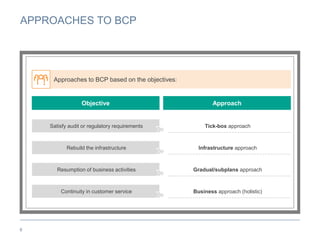
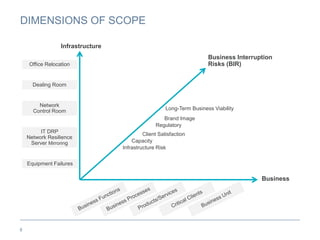
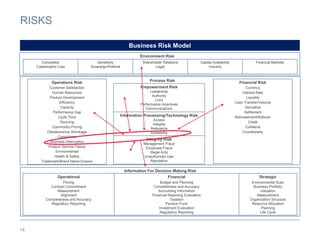
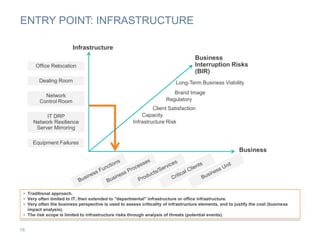
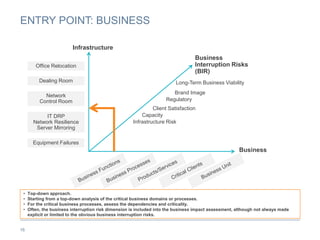
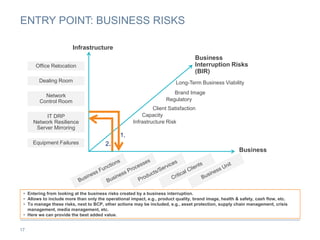
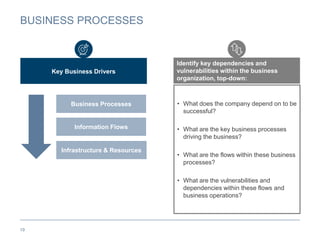
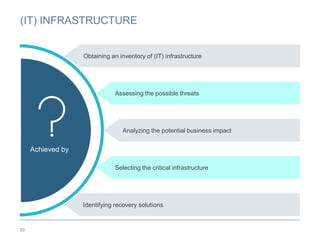
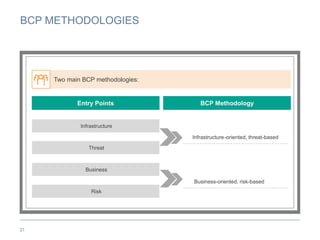
The document provides an overview of business continuity planning (BCP) by outlining key concepts such as objectives, approaches, dimensions of scope, and entry points. It discusses satisfying audit requirements, rebuilding infrastructure, resuming business activities, and ensuring customer service as potential objectives. The document also describes infrastructure, business, and business risk-based approaches and entry points. Finally, it provides examples of identifying business processes, information flows, infrastructure dependencies, and assessing risks.