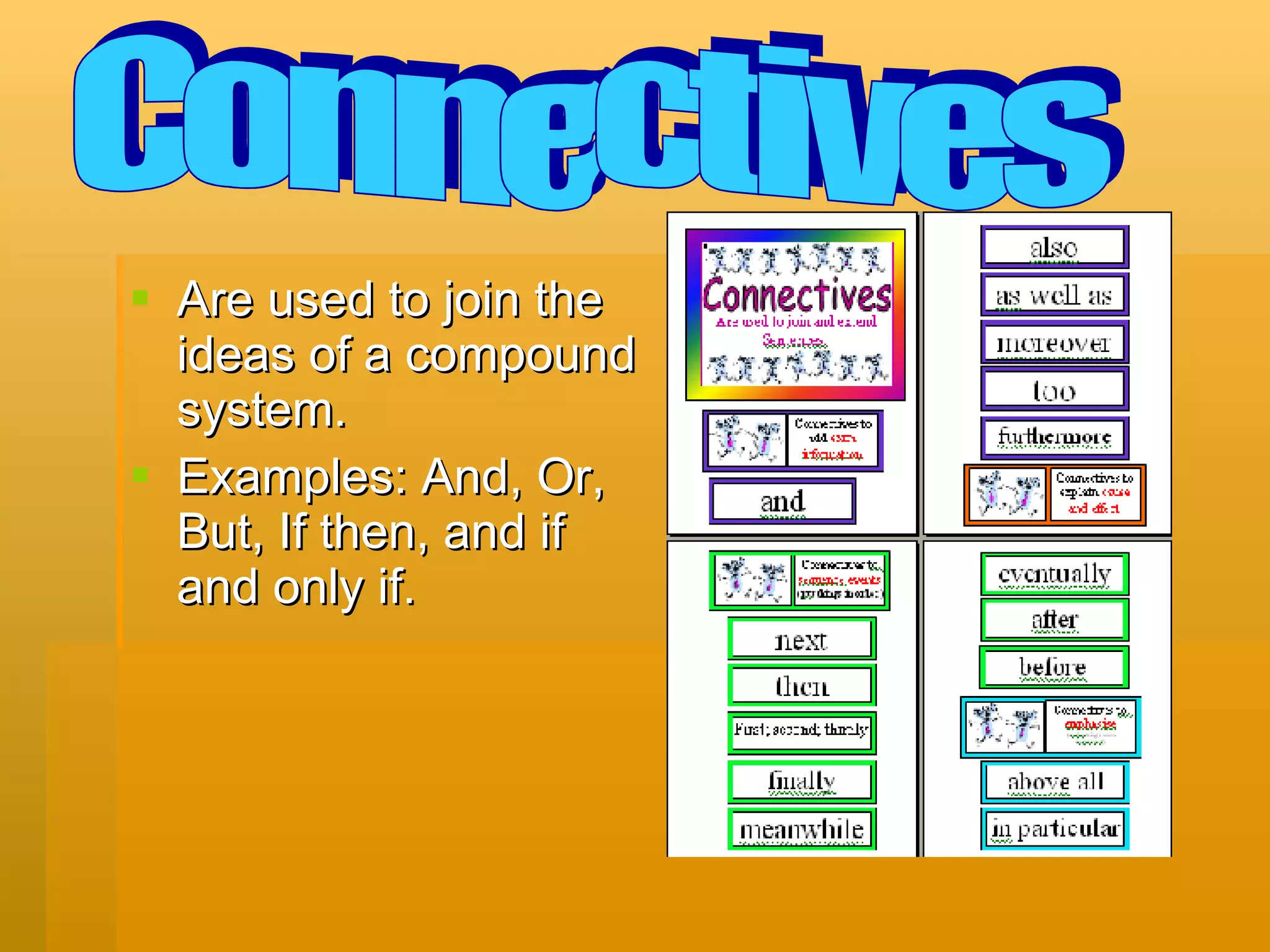
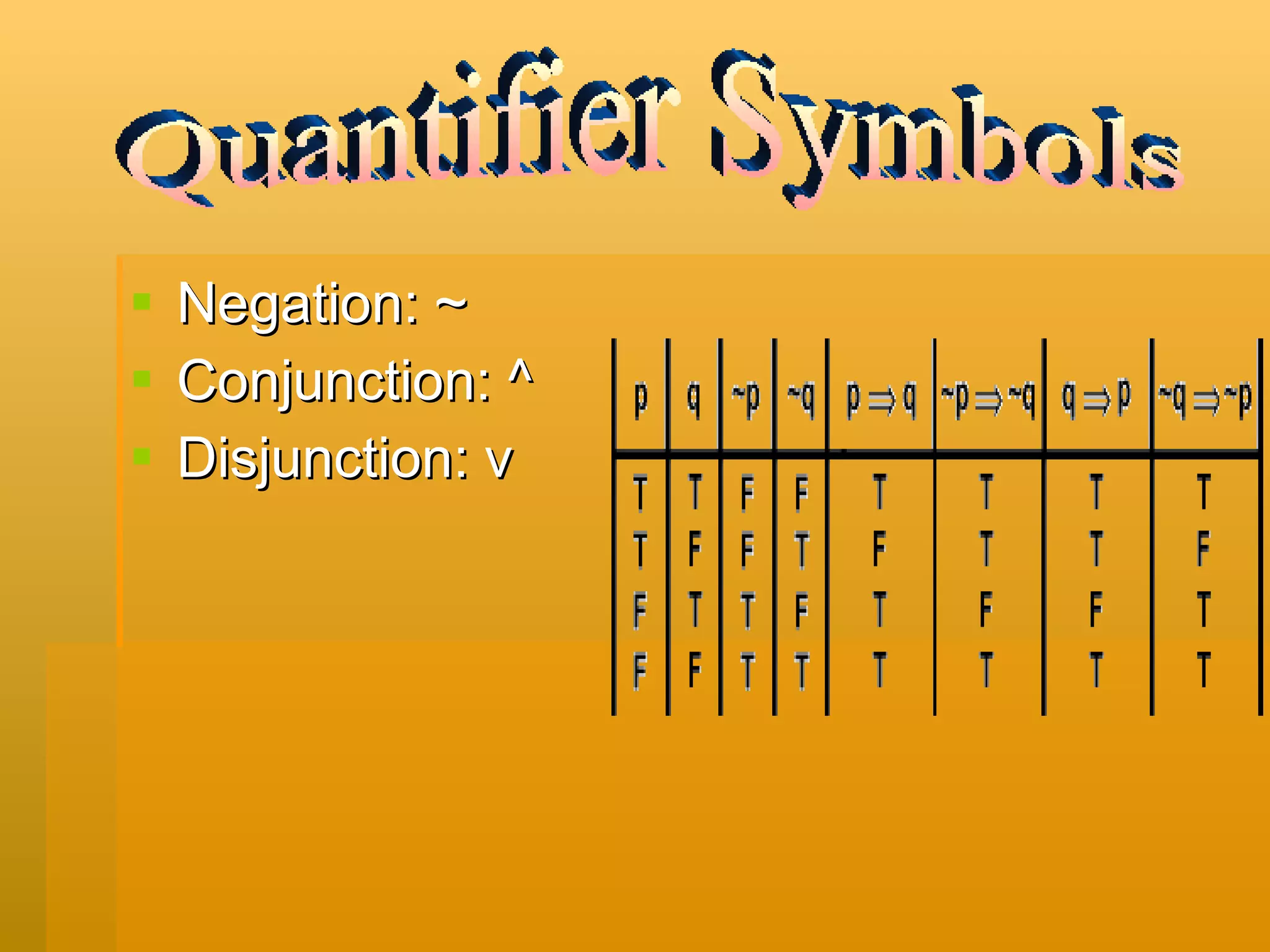
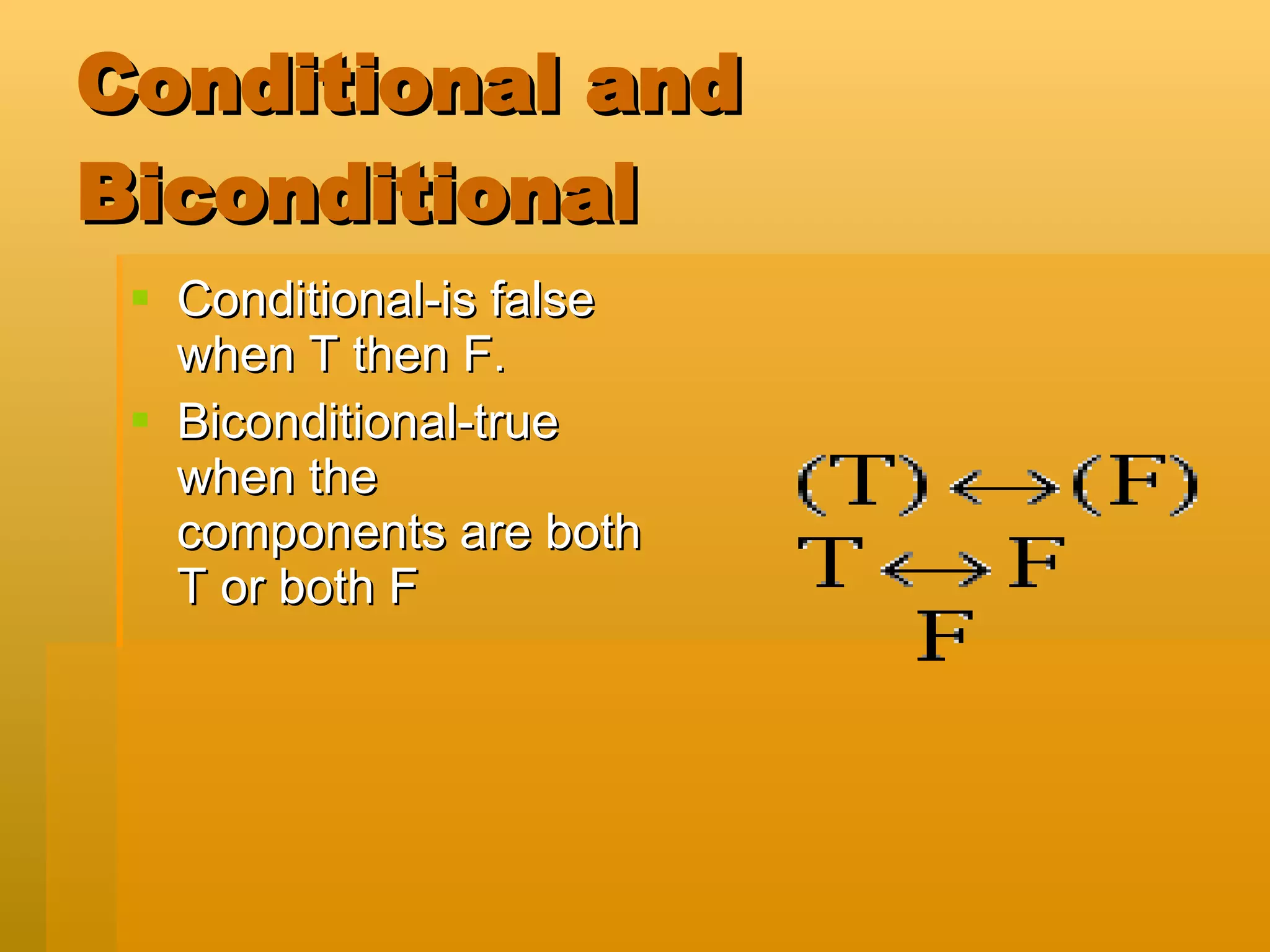
Inductive reasoning uses patterns while deductive reasoning uses facts. Logical statements can be true or false. Simple statements contain one idea while compound statements contain several ideas. Connectives like "and", "or", and "if...then" are used to join the ideas in compound statements. There are five basic connectives: negation, conjunction, disjunction, conditional, and biconditional. Quantifiers include universal and existential words. Truth tables are used to determine if statements are tautologies or always true based on the combinations of true and false for each component. Arguments contain premises that lead to a conclusion, and are valid if the premises are true.