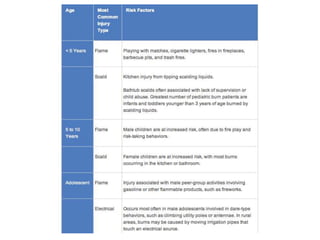
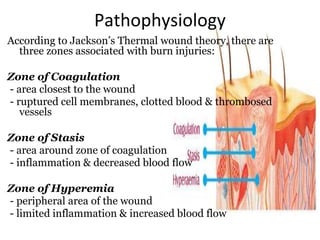
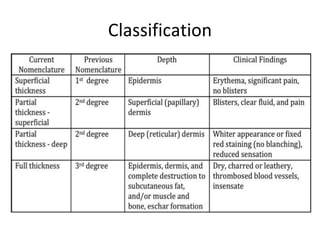
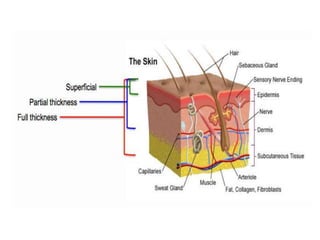
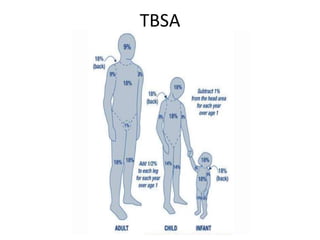
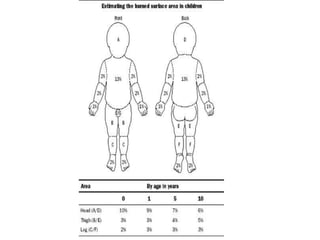
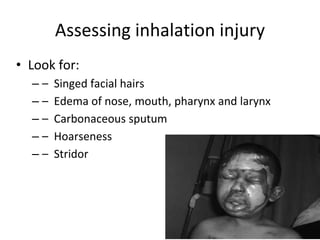
Burns are a leading cause of accidental pediatric injuries and deaths worldwide. Scalding from hot liquids is the most common cause of burns in children, often related to cooking practices. Initial management involves fluid resuscitation, antibiotics, dressings, and nutrition to support wound healing. Complications can include disfigurement, contractures, and emotional trauma. Ultimately, decreasing the burden of pediatric burns requires prevention through education, legislation, and environmental modifications.