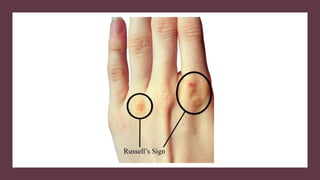
Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating and purging behaviors like vomiting or laxative abuse. Symptoms include evidence of binge eating and purging, as well as medical issues like tooth decay and electrolyte imbalances. The causes are unknown but risk factors include genetics, dieting, psychological issues, and environmental stress. Long-term bulimia can lead to heart problems, digestive issues, depression and even death. Treatment involves a team approach using psychotherapy and sometimes antidepressants to overcome the disorder.