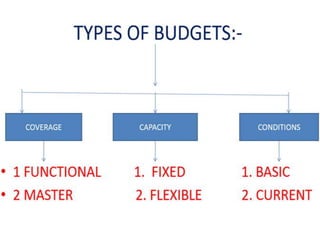
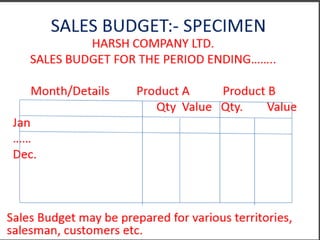
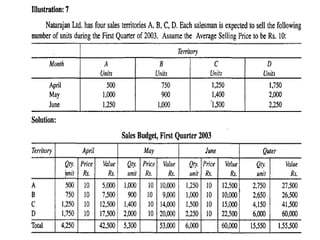
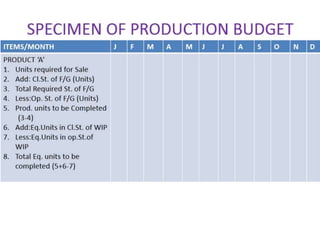
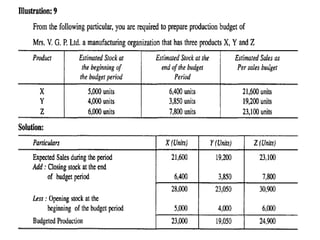
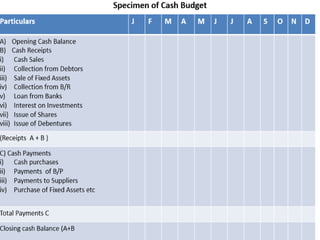
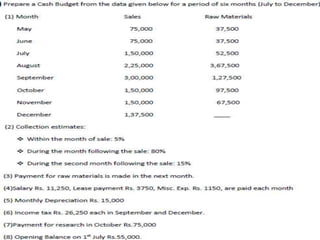
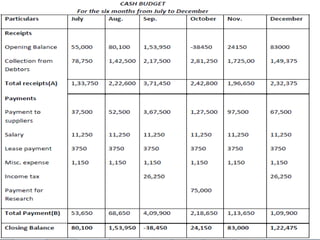
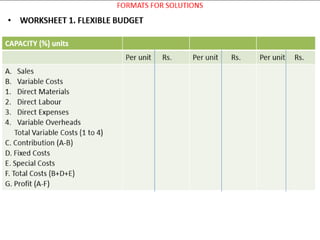
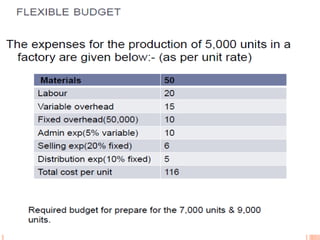
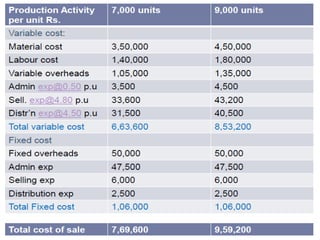
This document provides information about budgets, including their definition, essential components, benefits, and types. It defines a budget as a monetary plan for a defined future period. Budgeting allows organizations to prioritize spending, focus on goals, and identify potential problems in advance. Types of budgets include functional budgets for specific areas like sales and production, the master budget which combines these, and flexible versus fixed budgets. The document also provides examples of how to format budgets for different areas.