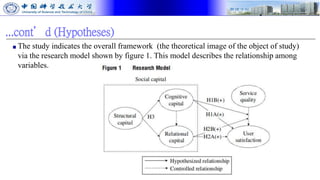
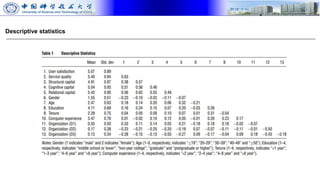
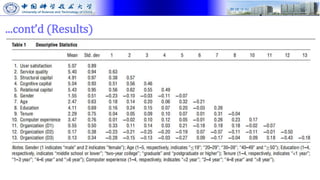
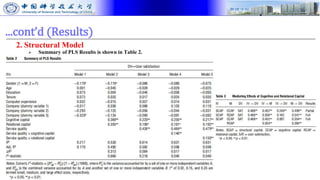
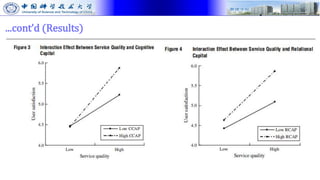
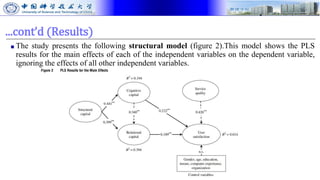
The document presents research on how social capital between users and IT service delivery units impacts user satisfaction with IT services. The research tests hypotheses about the relationships between structural, cognitive, and relational social capital and user satisfaction. Data was collected through questionnaires from four financial services firms and analyzed using partial least squares structural equation modeling. The results supported the hypotheses, finding that cognitive and relational social capital positively influence user satisfaction directly and strengthen the relationship between service quality and user satisfaction. The study contributes to literature on user satisfaction and social capital theory.