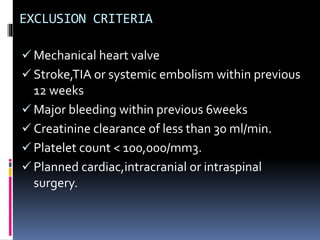
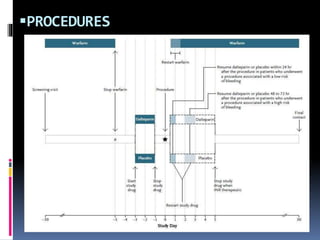
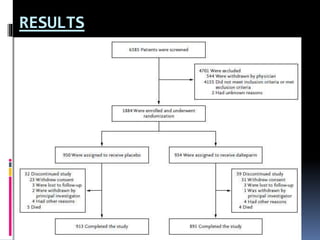
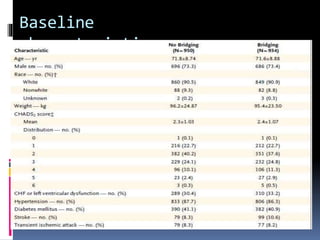
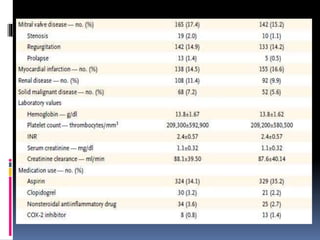
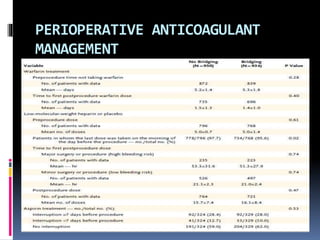
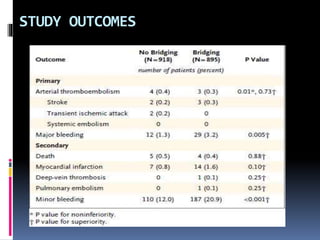
This document summarizes the BRIDGE study published in NEJM in 2015, which compared bridging anticoagulation versus no bridging in atrial fibrillation patients undergoing elective surgery requiring interruption of warfarin therapy. The study found discontinuing warfarin without bridging anticoagulation was noninferior to bridging in preventing arterial thromboembolism and resulted in less major and minor bleeding compared to bridging. Bridging anticoagulation tripled the risk of major bleeding but did not reduce thromboembolic risks. The findings suggest perioperative thromboembolism risk in AF may be overstated and not mitigated by bridging, which increases bleeding risks.