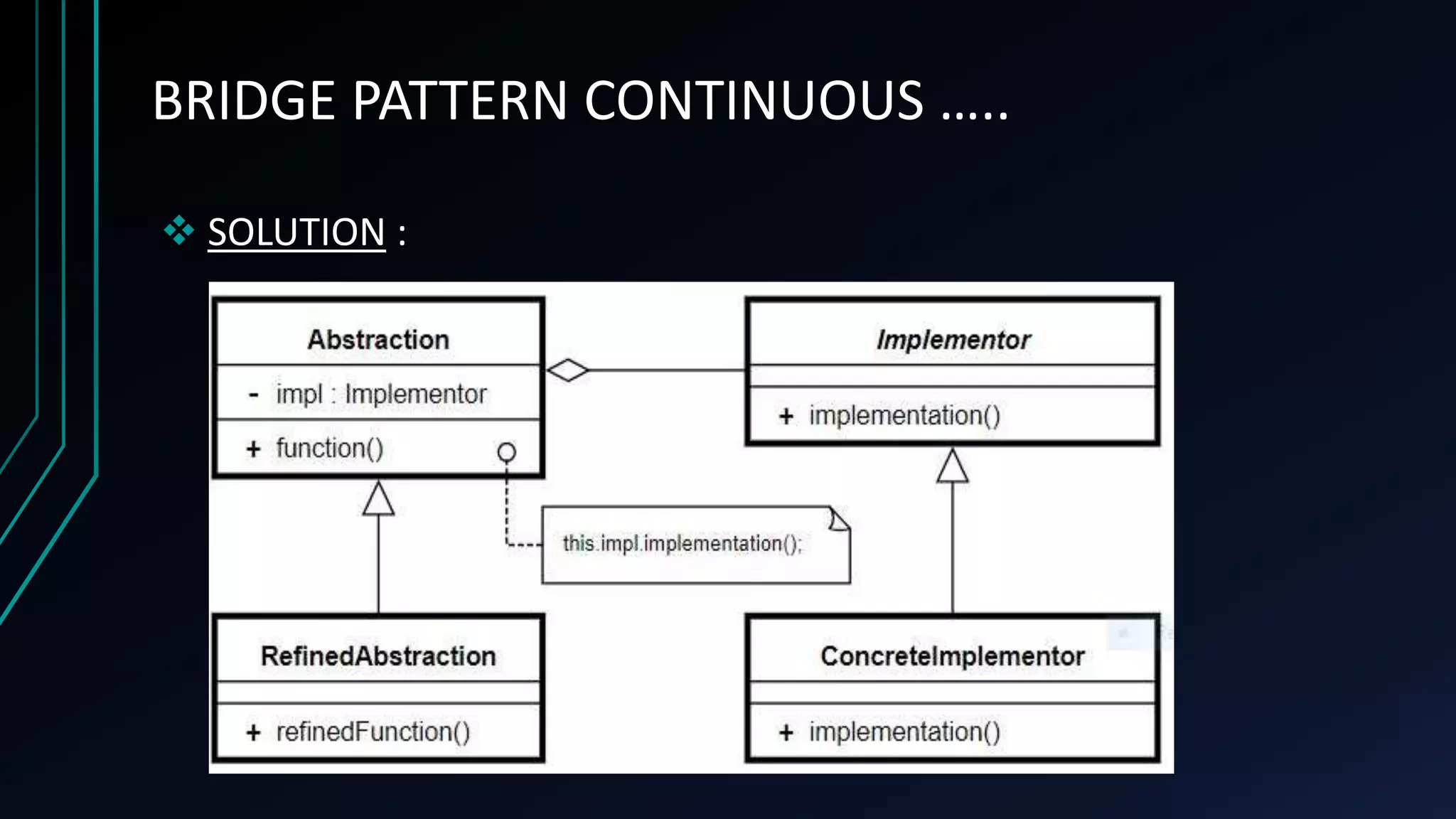
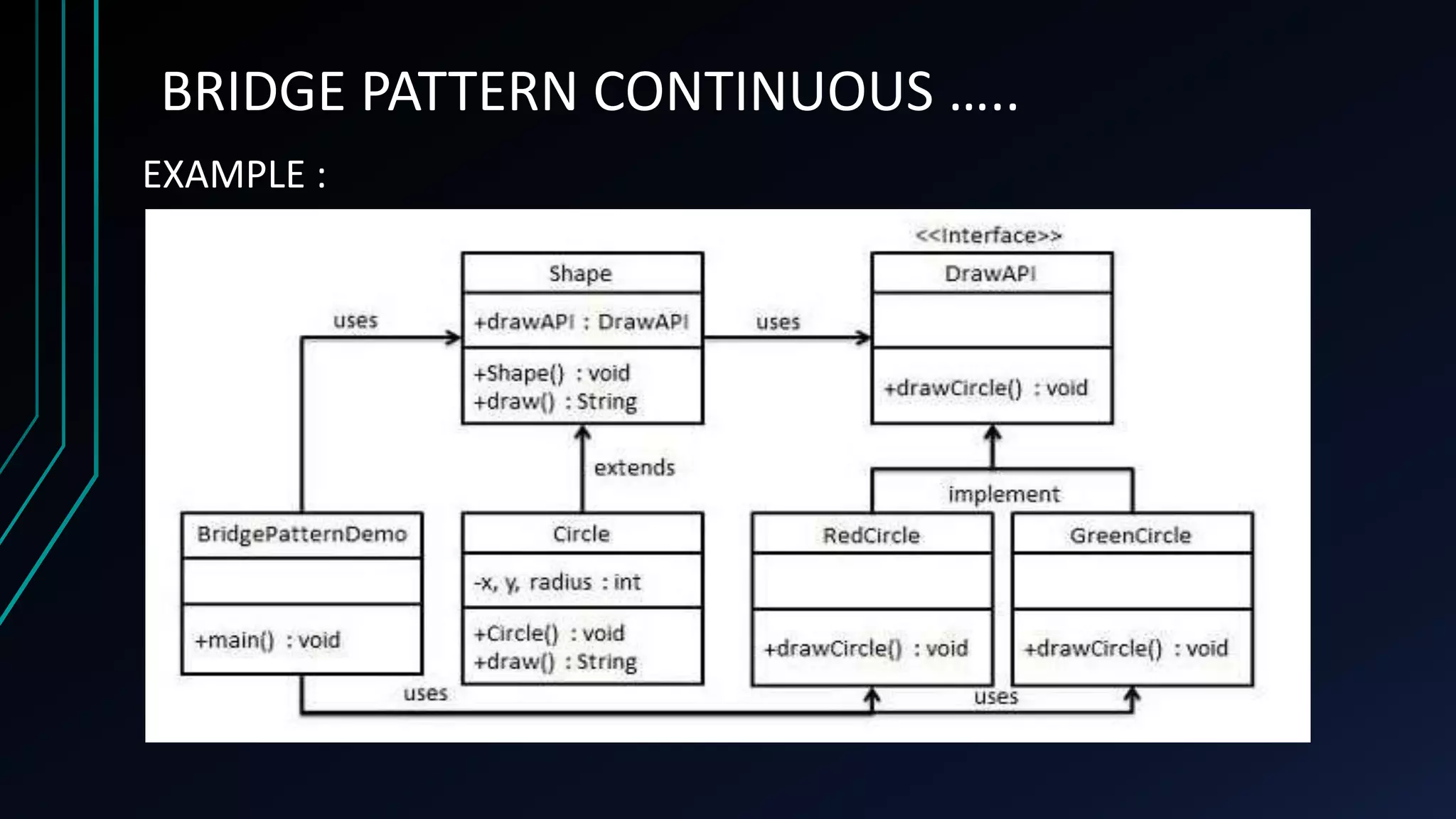
The bridge pattern is a structural design pattern that separates an abstraction from its implementation so that the two can vary independently. It is useful when both a class and what it does need to vary often without affecting other parts of a program. The bridge pattern achieves this separation by creating an interface (DrawApi) for the abstraction and concrete classes (RedCircle, GreenCircle) that implement it. A class (Shape) is defined using the interface and concrete subclasses (Circle) are created that delegate implementation to concrete classes but can vary independently. This allows shapes to be drawn in different colors without changing the core class structure.






![Step 2 : Create concrete bridge implementer classes implementing
the DrawApi interface.
RedCircle.java
public class RedCircle implements DrawAPI {
public void drawCircle(int radius, int x, int y) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle[ color: red, radius: "
+ radius + ", x: " + x + ", " + y + "]");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roll192429-180514024600/75/Bridge-Pattern-11-2048.jpg)
![GreenCircle.java
public class GreenCircle implements DrawAPI {
@Override
public void drawCircle(int radius, int x, int y) {
System.out.println("Drawing Circle[ color: green,
radius: " + radius + ", x: " + x + ", " + y + "]");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roll192429-180514024600/75/Bridge-Pattern-12-2048.jpg)


![Step 5 : Use the Shape and DrawAPI classes to draw different colored
circles.
BridgePatternDemo.java
public class BridgePatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape redCircle = new Circle(100,100, 10, new RedCircle());
Shape greenCircle = new Circle(100,100, 10, new GreenCircle());
redCircle.draw();
greenCircle.draw();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roll192429-180514024600/75/Bridge-Pattern-15-2048.jpg)
![Step 6 : Verify the output.
Drawing Circle[ color: red, radius: 10, x: 100, 100]
Drawing Circle[ color: green, radius: 10, x: 100, 100]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/roll192429-180514024600/75/Bridge-Pattern-16-2048.jpg)
