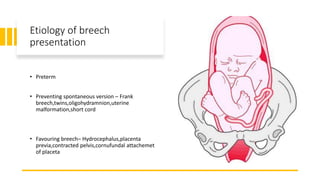
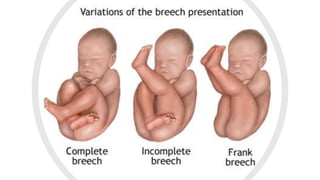
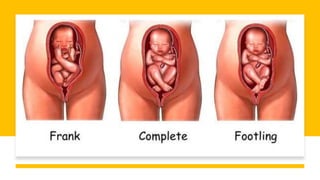
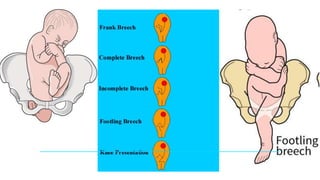
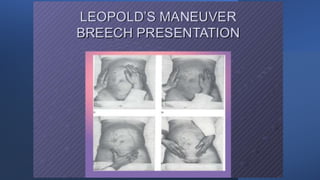
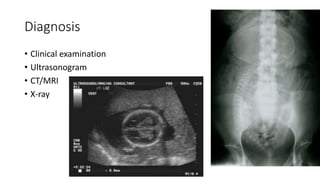
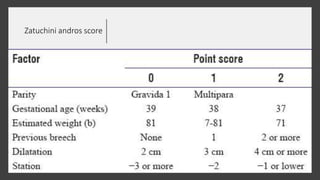
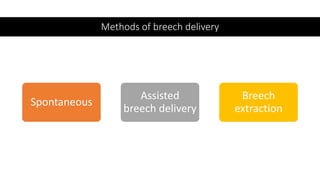
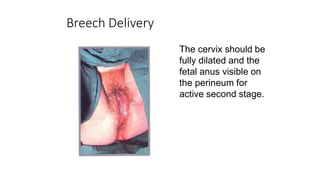
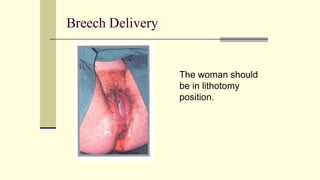
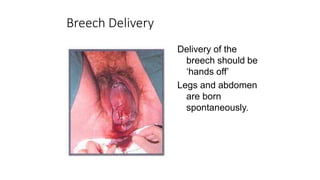
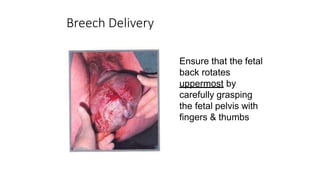
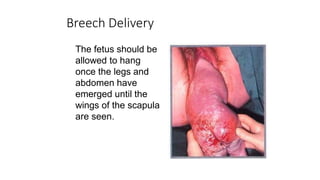
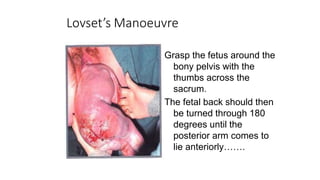
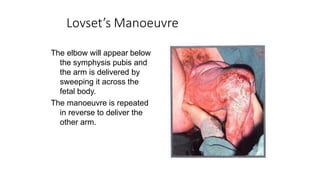
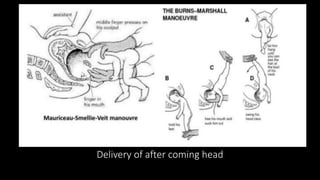
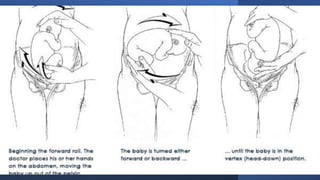
This document discusses breech presentation in pregnancy. It defines breech presentation and notes that the incidence is around 3-4% at term, though higher for preterm births. Risk factors for breech presentation include primigravidity, uterine anomalies, fetal anomalies, preterm labor, and multiple pregnancy. Diagnosis methods include clinical examination, ultrasound, CT/MRI, and X-ray. The document outlines methods of breech delivery including spontaneous vaginal delivery, assisted breech delivery, and breech extraction. It describes maneuvers like Lovset's maneuver and notes complications for both the mother and fetus from breech delivery. External cephalic version is discussed as an option to attempt turning the breech baby, along