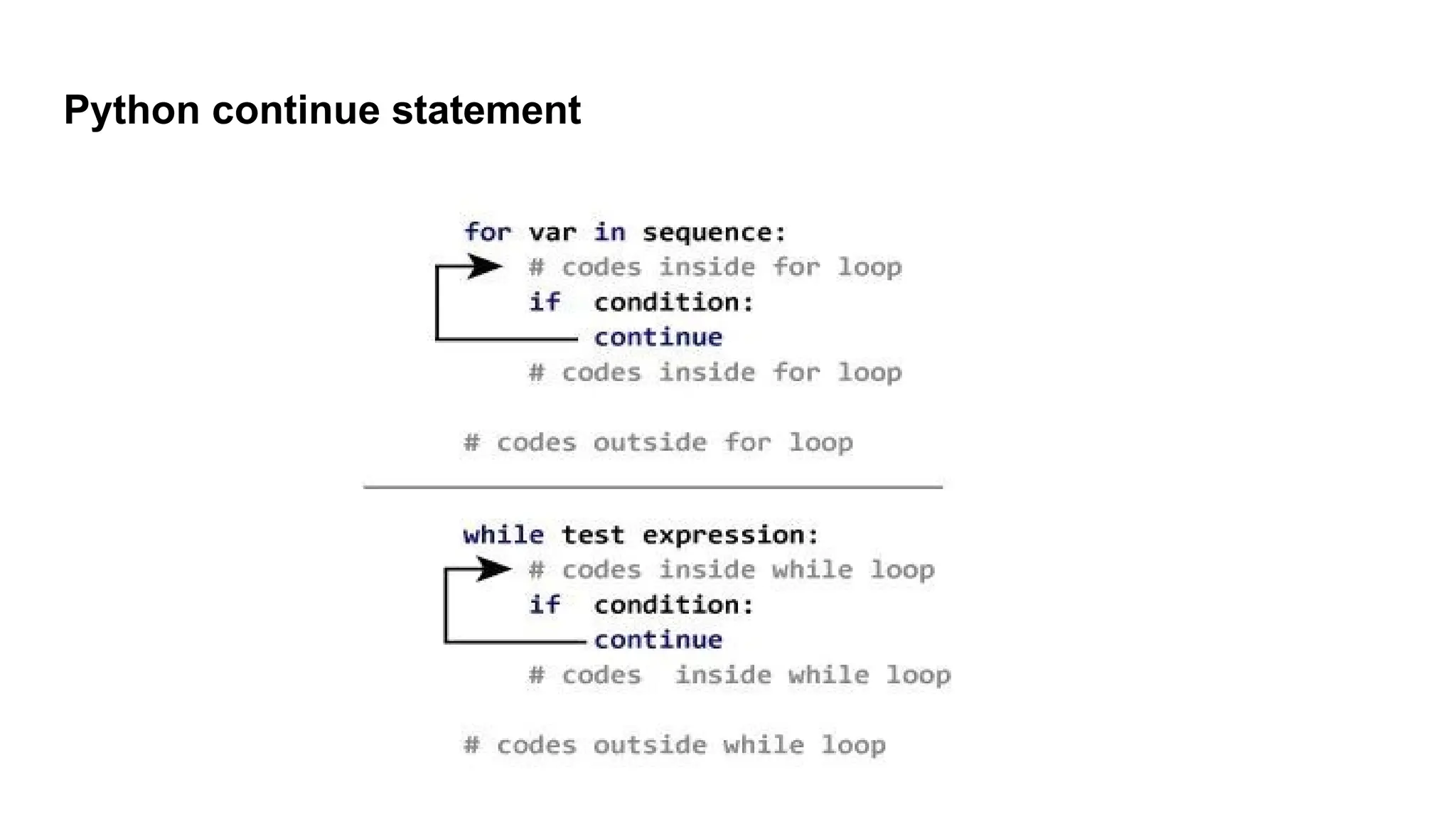
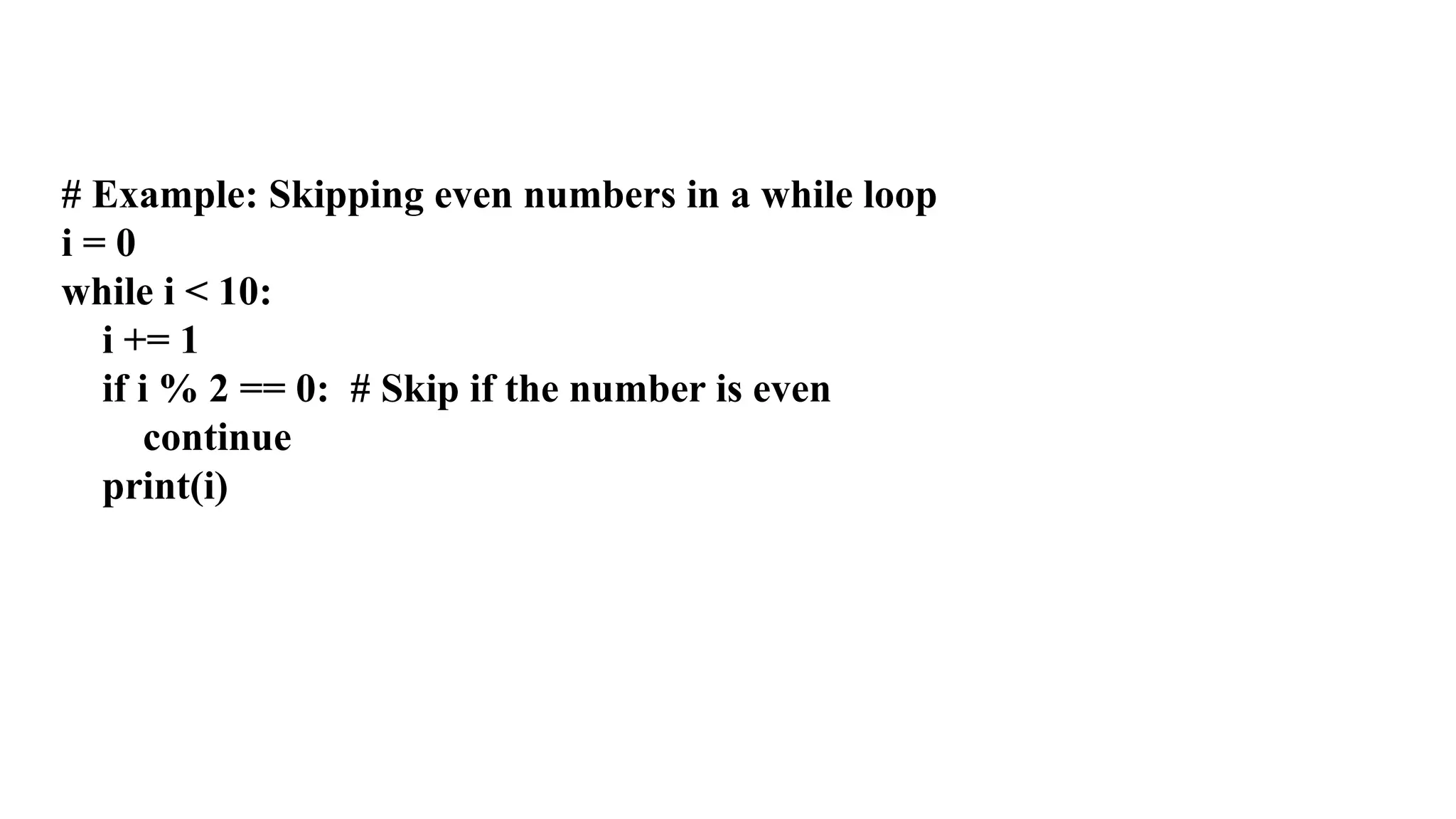The document explains the usage of three control flow statements in Python: break, continue, and pass. The break statement exits loops, the continue statement skips to the next iteration, and the pass statement serves as a placeholder for future code without causing errors. Examples illustrate how each statement can be implemented within loops and conditional structures.