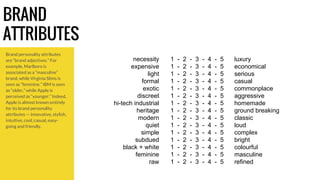
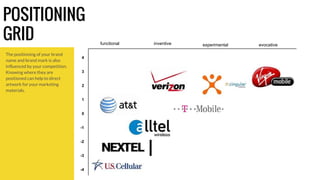
The document outlines essential branding concepts, emphasizing that a brand is defined by individuals' emotional responses rather than company assertions. It discusses the importance of user experience in both retail packaging and online communication while examining brand personality attributes, competitive advantages, and client engagement strategies. Additionally, it highlights the significance of understanding target markets and crafting clear mission and vision statements for effective branding.