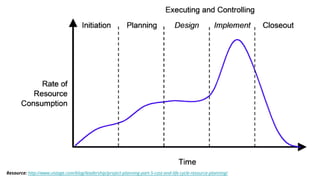
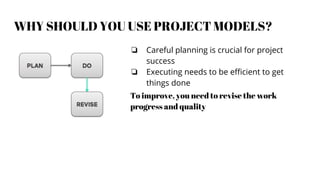
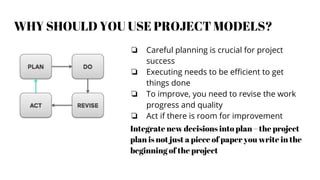
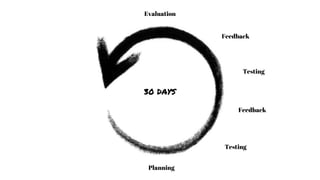
This document provides an overview of project management. It defines a project as a specified amount of work to be completed within a certain time frame and budget. Project management involves applying processes, methods and skills to achieve project objectives within constraints of time, cost, quality and scope. The document discusses project life cycles, examples of historical and current projects, and challenges such as uncommitted clients or poor testing. It also covers topics such as stakeholder management, project planning, scheduling tools, collaboration tools, the roles of project managers and models like Waterfall and Scrum for managing projects.