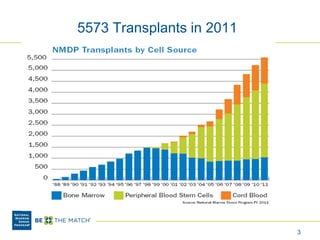
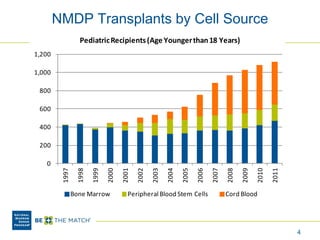
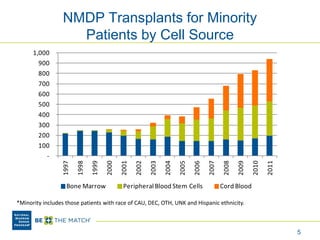
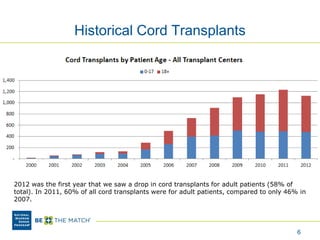
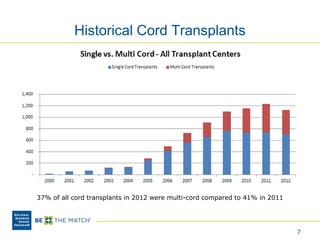
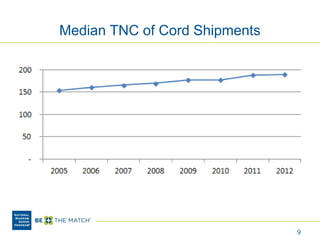
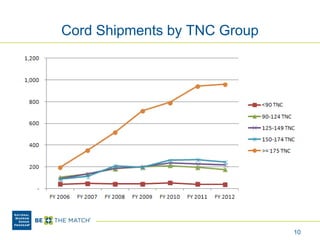
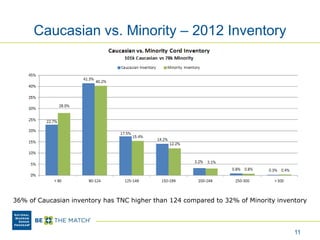
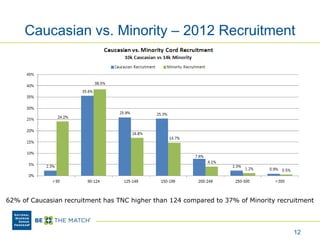
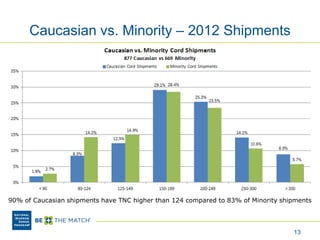
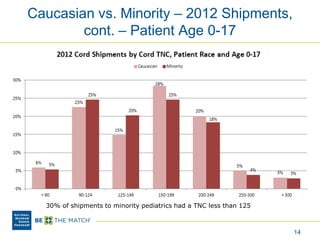
This document discusses the costs associated with cord blood transplantation and how they impact its use. It notes that insurance coverage and the time commitment are barriers. The main costs are the cord blood product itself, collection and banking fees, and higher expenses during the medical procedure due to slower engraftment times and potential complications. Suggestions to address these issues include improving education, identifying selection criteria to reduce multi-cord transplants, expanding cord blood units, and making cord blood banking more efficient.