BONE INFECTIONS.pptx
- 2. OSTEOMYLITIS INTRODUCTION o Osteomyelitis is one of the most difficult and challenging problems encountered in orthopedics. o From the life-threatening acute osteomyelitis to the disabling chronic osteomyelitis, it frustrates the best efforts of orthopedic surgeons. o The incidence of chronic osteomyelitis is on the rise. This is primarily because of the rise in road traffic accidents (RTAs) leaving a bizarre of compound fractures which are the major cause of infection in bone
- 3. OSTEOMYLITIS DEFINITION osteon – bone myelo – marrow itis – inflammation • Osteomylitis is the inflammation of bone caused by micro organism. • It may be localized or can spread through the bone to involve the bone marrow , cortex ,periosteum , and soft tissue sarrounding the bone. Based on duration of symptoms Acute osteomylitis - less than 2 weeks Subacute osteomylitis – 2 weeks to 6 weeks Chronic osteomylitis - more than six weeks Begins in medullary cavity, spread to cortical bone then extend to periosteum
- 4. ROUTE OF SPREAD OF OSTEOMYLITIS Directly - through break in skin, stab wounds, open fractures and surgery Haematogenous from distant site, Tonsilitis Acute suppurative otitis media Dental abscess Boil or abscess Infected umbilical cord, Indwelling iv lines/urethral catheters Lymphatics – • Spread from neighboring infective sites like septic arthritis
- 5. CLASSIFICATION OF OSTEOMYLITIS Acute osteomylitis - less than 2 weeks Subacute osteomylitis – 2 weeks to 6 weeks Chronic osteomylitis - more than six weeks • Osteomylitis begins in medullary cavity, spread to cortical bone then extend to periosteum FACTORS THAT DETERMINE THE EXTENT OF INFECTION Virulence of infecting organisms Immune status of the host Underlying disease
- 6. ACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS AETIOLOGY • Staphylococcus aureus (60-85%) This is the most common organism causing acute osteomyelitis. • Streptococcus hemolyticus (8-10%) • Salmonella • Pseudomonas • Pneumococcus • Coliforms (E. coli).. • Hemophilus influenza This is known to cause osteomyelitis in the age group of 7 months to 4 years • Treponema pallidum (syphilitic osteomyelitis) Fungal osteomyelitis • Actinomycosis • Blastomycosis • Cryptococcus's
- 7. PREDISPOSING FACTORS TO OSTEOMYLITIS • Age – Affect children incidence is 88 percent because they are more prone for injury and to fall. • Affects adults due to Trauma(compound fractures or ORIF immunosupression,underlying disease i.e. DM, Alcoholism malnutrition • Sex Male preponderance (? more playful). • Economic Status Low socioeconomic groups are more susceptible
- 8. ACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS ,,,,,,,,,, PATHOLOGY • The microorganisms settle at metaphysis of the bone and therefore initiate ; Inflammation, Suppuration, Necrosis(seguestrum) Reactive new bone formation(involucrum) Resolution and healing WHY METAPHYSIS IS INVOLVED Highly vascularized and on injury there's a lot of bleeding U shaped end arteries from nutrient artery which twist back in hair pin loops before entering the veins Vascular stasis due to looping of blood vessels thus favoring bacterial colonization. There is presence of rapidly changing cells hence weakness
- 10. ACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS CONT……. PATHOLOGY • Organisms reach the bone from a septic focus elsewhere in the body through blood stream (haematogenous) • Settle in metaphysis of the bone(highly vascularized with a lot of looping of blood vessels from nutrient artery. • Organisms induce an acute inflammatory reaction with fluid exudation resulting into pus formation(suppuration) . • The exudates(pus) may spread outwards to involve the bone cortex leading to periosteal stripping (periosteal reaction) and elevation by pus. Bone dies due to lack a blood supply. • Pus may extend to the adjacent joint to form pyogenic arthritis • Formed pus finds its way to the surface of the bone to form sub periosteal abscess or it may spread towards bone medullary cavity to affect the whole bone.
- 11. PATHOLOGY OF OSTEOMYLITIS CONT…….. • The abscess can find its way into the soft tissues and reach the skin surface to form a sinus. • The intraosseous pressure rises rapidly, causing intense pain, obstruction to blood flow and intravascular thrombosis resulting to bone ischemia • The ischemic bone dies and separates from the surrounding living bone as seguestra. • A new bone is laid down around the seguestra called an involucrum RESOLUTION AND HEALING • If infection is controlled and intraosseous pressure released at an early stage the infection is arrested . • With efficient treatment, the infection can be prevented in early phase from complicating to chronic osteomylitis • Bone around the zone of infection is osteoporotic. • With healing, there is fibrosis and new bone formation this, together with the periosteal reaction, results in sclerosis and thickening of the bone.
- 13. CLINICAL FEATURES Symptoms • Acute in onset • Pain • Swelling • Fever (95%) • • Local swelling (80%) • malaise • Sweating •Chills • Rigors • Dehydrated/shock On examination • Local swelling • limitation of movement • Tenderness over affected bone • Raised temperature • Fluctuating mass • Local erythema • Increased pulse rate • Anemic • Failure to thrive
- 14. DIAGNOSIS OF ACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS` • By history taking ,clinical presentation, and physical examination LAB FINDINGS FBC - leucocytosis pus culture – positive Gram staining – positive RADIOLOGY XRAYS less than 2 weeks - normal but only soft tissue swelling After 2 weeks –periosteal thickening/elevation - New bone formation - involucrum - Bone destruction/necrosis -sequestrum - Regional osteoporosis - Bone rare faction at metaphysis - Bone sclerosis • With early and effective treatment the above radiological features are absent. BONE SCAN – Confirms diagnosis
- 16. MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS • Acute osteomyelitis is an orthopedic emergency which needs in patient admission. Conservative mnx • Rest in bed • Nutritional support • protect affected part with splints to reduce pain and muscle spasm. • Elevation of the part, warm and moist packs to reduce the swelling. • Analgesics to relieve pain Treatment— • Admit patient • Blood transfusions, • Intravenous fluids to correct shock and hypovolemia caused by fever and sepsis. • Treatment with antibiotics helps to reduce toxicity. • Surgery— Timed to prevent complications INDICATION OF SURGERY • Abscess formation • Failure to respond to antibiotics • Very sick
- 17. MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS Antibiotic therapy • To prevent chronic osteomyelitis , broad spectrum bactericidal agent given intravenous for the first 2 weeks and oral for the next 4 weeks • intravenous flucloxacillin and fusidic acid till child show improvement then per oral for 3-6 weeks • Children under 4 years(gram negatives) give cefuroxime or cefotaxime(BSA) • SCD(salmonella) give chloramphencal, or septrin • Immunocompromised ( pseudomonas, proteus ) give flucloxacillin and gentamycin • Local antibiotics: Antibiotics impregnated with cement beads provide high dose of antibiotics locally.
- 18. MNX OF ACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS CONT……….. Surgical Methods • Aspiration: it helps in decompression and pus obtained is cultured to identify the organism and check for antibiotic sensitivity. • Incision and drainage helps to drain the abscess. • Multiple drill holes helps to drain the pus by making multiple holes in the cortex. • Small bone window If the multiple drill holes do not drain the pus, a small window of bone is removed from the cortex and the pus is evacuated
- 19. ACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS CONT………. DDX • Septic arthritis • Cellulitis • Osteoid osteoma • Ewings sarcoma • Soft tissue infection COMPLICATIONS • Septicemia to brain and lungs • Septic arthritis due to extension of the neighboring foci of infection into the joint. • Chronic osteomyelitis develops due to improper and inadequate treatment. • Pathological fractures • growth disturbances • Pulmonary embolism • Deep venous thrombosis PROGNOSIS • Ninety percent resolve due to early diagnosis and effective antibiotic therapy. • Eight percent show morbidity. • Two percent have mortality
- 20. SUBACUTE OSTEOMYLITIS • Subacute osteomylitis – 2 weeks to 6 weeks • Insidious and not severe because organism is less virulence or host more resistance, • It is caused by Staphylococcus aureus Staph Epidermis. • The patient complains of pain, limping ,slight swelling, temperature may be increased or normal. • Blood culture is positive , and WBC and ESR are raised, IMAGING • Oval cavity with sclerosis containing seropurulent fluid TREATMENT • Immobilize • antibiotics
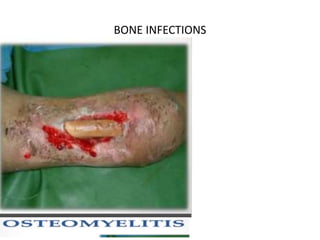
- 21. CHRONIC OSTEOMYLITIS (CHRONIC PYOGENIC OSTEOMYLITIS) Osteomyelitis lasting for more than three weeks is termed as chronic. Chronic osteomyelitis can arise from any one of the following ways: Sequelae of acute osteomyelitis (5-10%) Following compound fractures Following surgery on bones and joints Fungal osteomyelitis Chronic osteomylitis is denoted by; o Abscess cavities o Sequestrium/involucrum o Multiple scars and sinuses tract o Cavity, o Irregular thickening of bone, o Sprouting granulation tissue, o Discharge of bony spicules - involucrum and pus
- 23. PATHOLOGY OF CHRONIC OSTEMYLITIS • Follows acute osteomylitis • Cavities containing pus and pieces of dead bone (sequestra) are surrounded by involucrum • Involucrum is dense and sclerotic with multiple openings called cloacae through which exudate , bone debris and sequestra find exit and pass through the sinus. • The sequestra act as substrates for bacterial adhesion. • Sinuses may seal off for weeks or even months, giving the appearance of healing, only to reopen or appear somewhere else. • Constant bone destruction, leads to a pathological fracture.
- 25. CLINICAL FEATURES • Fever, pain, swelling • Night sweats • Malaise • Restlessness ON EXAMINATION • Irregular thickening of bone develops due to unequal pace of destruction of bone and new bone formation. • Bone deformity seen • Multiple sinuses ,some draining and others healing. • Scars and muscle contractures develope due to the spread of infection from the bones to the muscles and the consequent fibrosis. • There is flare up or reappearance of a sinus that had already healed.
- 26. DIAGNOSIS OF CHRONIC OSTEOMYLITIS • From history and physical examination LAB FINDINGS • FBC – Elevated ESR/WBC • Blood culture reveals bacteremia • Aspiration of pus for C/S and gram straining • Biopsy(gold standard) for histology to R/o malignancy change X-RAYS • show bone resorption or as frank excavation with thickening and sclerosis of the surrounding bone. • Area of osteoporosis, or periosteal thickening • Sequestra show up as dense fragments Radioisotope scintigraphy is sensitive and are useful for showing up hidden foci of infection. CT and MRI together will show the extent of bone destruction and reactive oedema, hidden abscesses and sequestra.
- 28. MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC OSTEOMYLITIS SURGERY – • Bone debridement – repeat several times • Sequestrectomy is done next then the cavity is curetted until fresh bleeding occurs. • Saucerization - is removal of adjacent bone cortex on debridement then open packing done to allow healing. • Local closure if the space left is very small. • Myoplasty for slightly larger space, surrounding muscles can be packed into the cavity. • Cancellous bone grafts for a space less than 2.5 cm. • Free vascularized bone graft for larger areas • Amputation is done If the patient’s life is endangered by infection ,malignant change has formed ,arterial insufficiency or neuropathy It should be the last choice and not the first.
- 30. COMPLICATIONS Pathological fractures Malignancy change Deformity Growth disturbances due to muscle and soft tissue contracture's Joint stiffness Septic arthritis
- 31. BRODIES ABCESS • Brodie’s abscess is a localized form of chronic osteomyelitis, involves metaphyseal and epiphyseal area, and is common in young adults • Age 11- 20 yrs and affect metaphysis. Clinical Presentation • The patient complains of intermittent pain of long duration and local tenderness. Etiology • Causative organism is low virulence Staph. aureus in 50 percent of the cases. Radiograph • It shows circular or oval appearance. Usually, a cavity with a rim of sclerotic bone is seen at the metaphysio epiphyseal junction. Treatment • Rest • Antibiotics, • Curettage and bone grafting, and the wound is Loosely closed over a drain • surgery
- 33. THANKS YOU