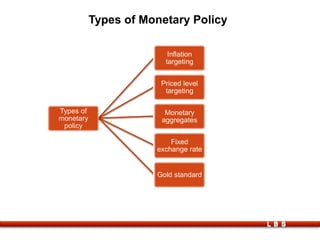
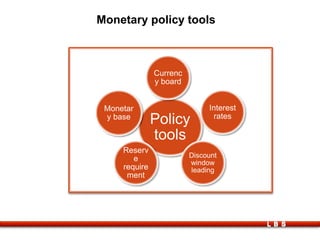
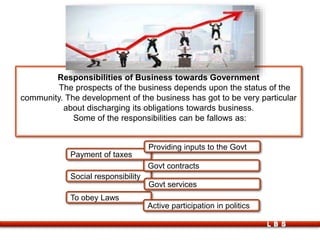
The document discusses the relationship between government and business, outlining the meanings of government and government policy, types of policies, and the responsibilities of both entities. It covers fiscal and monetary policies, the impact of liberalization and industrial policies, and the role of multinational companies in globalization. Key points include the importance of regulatory frameworks, the shift towards economic liberalization in India, and the effects of globalization on economies.