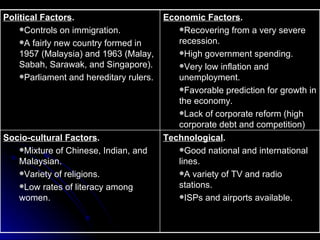
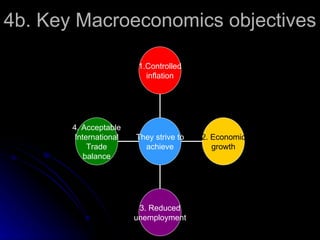
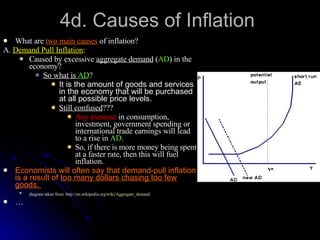
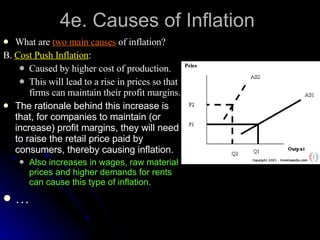
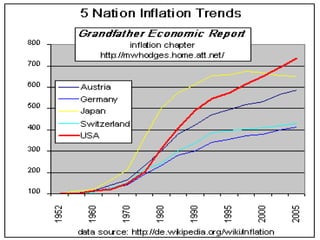
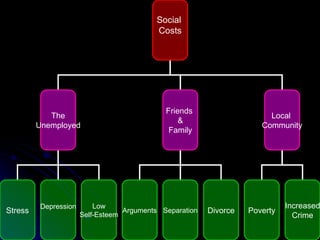
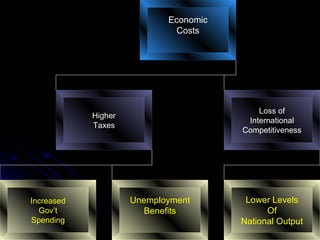
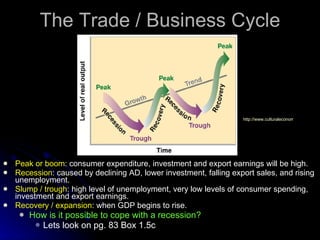
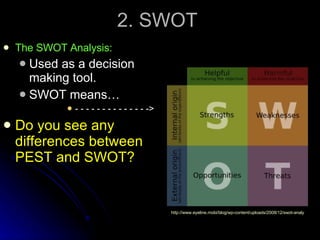
The document discusses PEST analysis, which evaluates internal and external factors affecting a business, including political, economic, social, and technological aspects. It emphasizes the importance of understanding these factors for effective decision-making and strategic planning, particularly when entering new markets. Additionally, it addresses the implications of these factors on employment, economic growth, inflation, and the balance of payments.